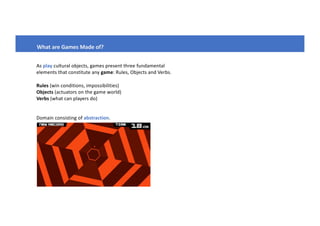
This document discusses how games can be used for learning. It outlines that games have three fundamental elements - rules, objects, and verbs for gameplay; worlds, characters, and conflicts for narrative; and manipulation, navigation, and participation for simulation. These elements allow players to explore, improvise, create, problem solve, overcome challenges, and compete. The document also discusses how different types of games like those focused on logic/patterns, causality/meaning making, or freedom/control can impact learning in areas like mathematics, languages, science, and arts. While games can operate as simulators for any domain, the document cautions that just transforming school content into games will not necessarily increase student motivation on its own.