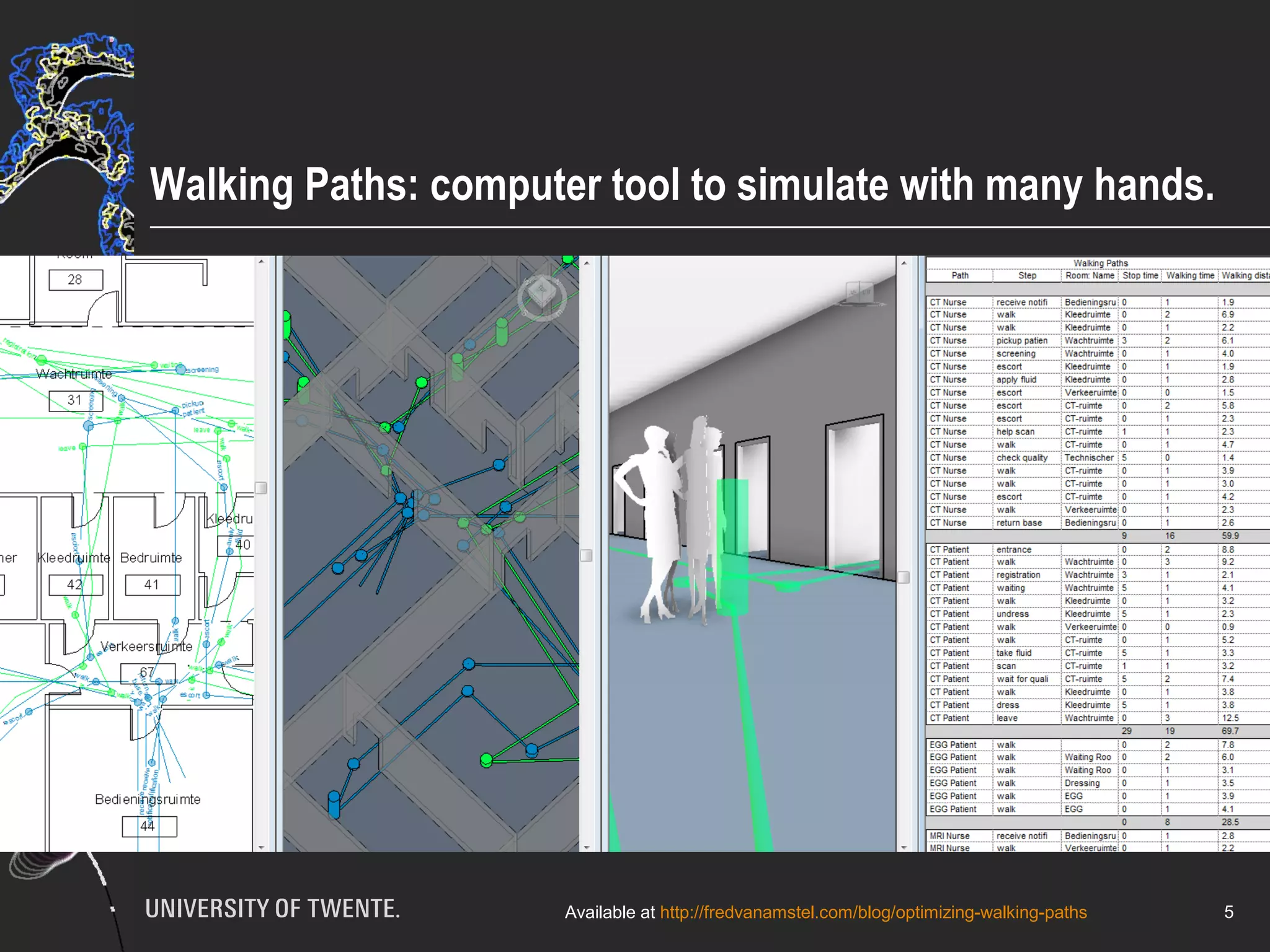
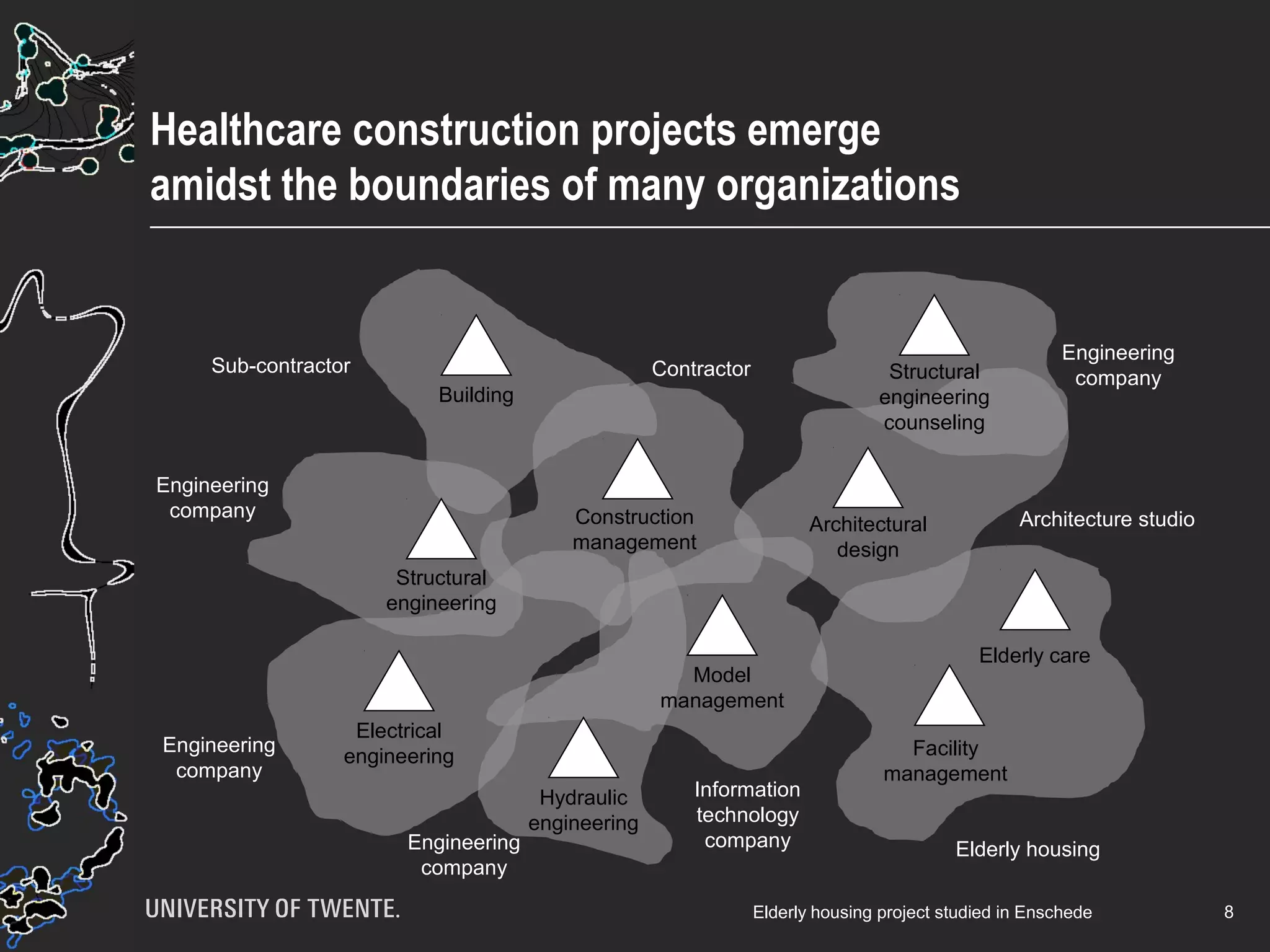
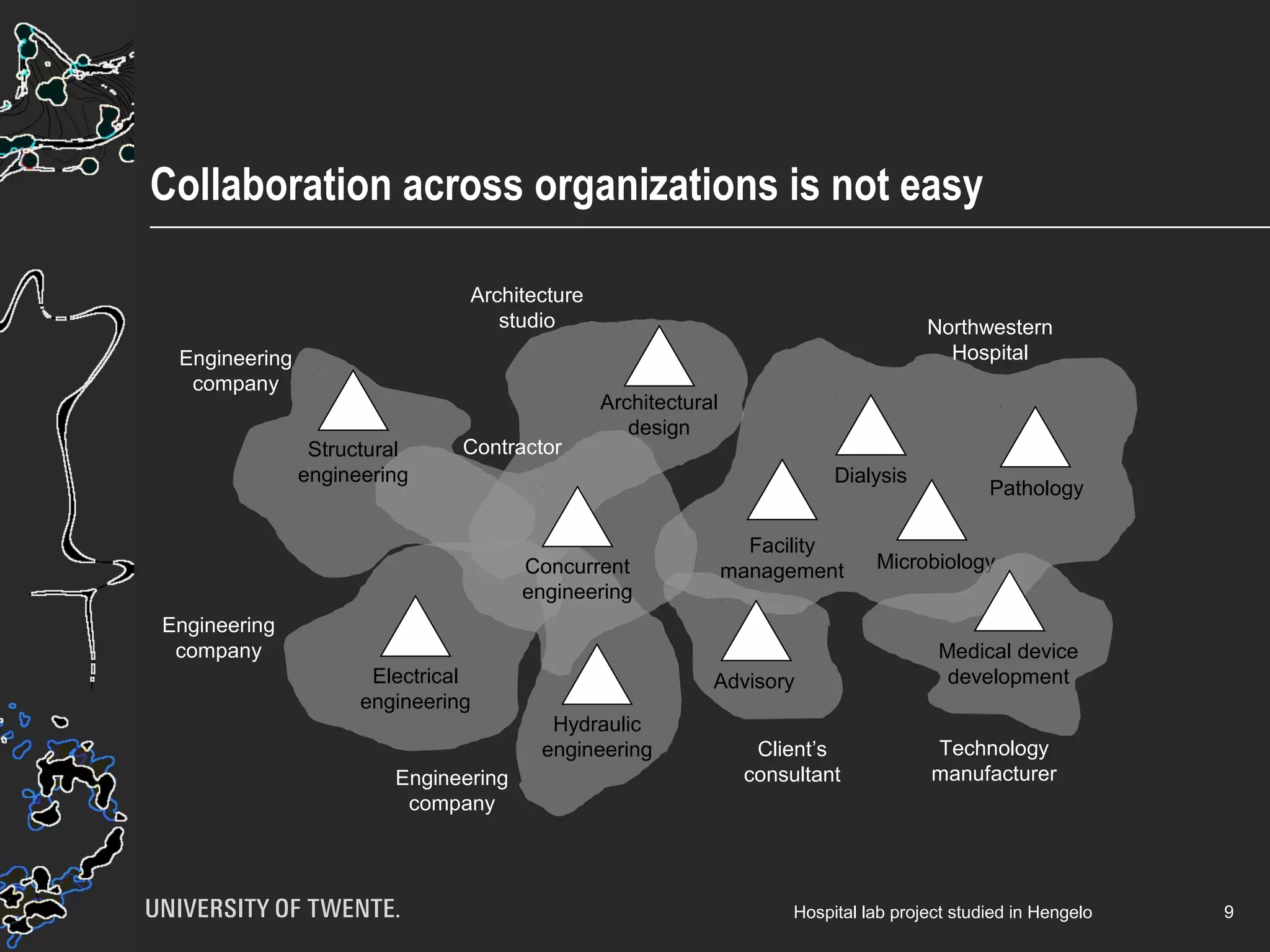
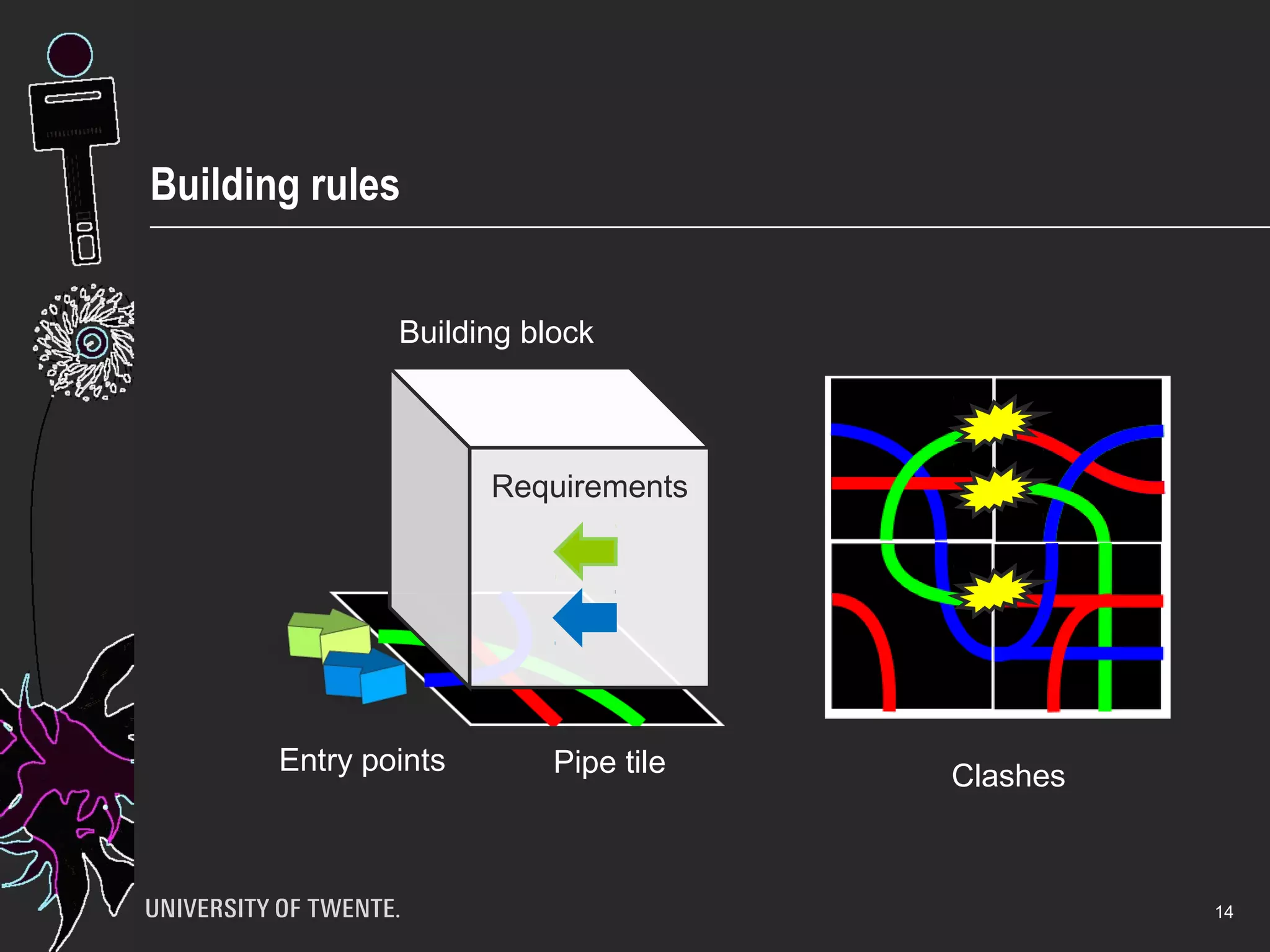
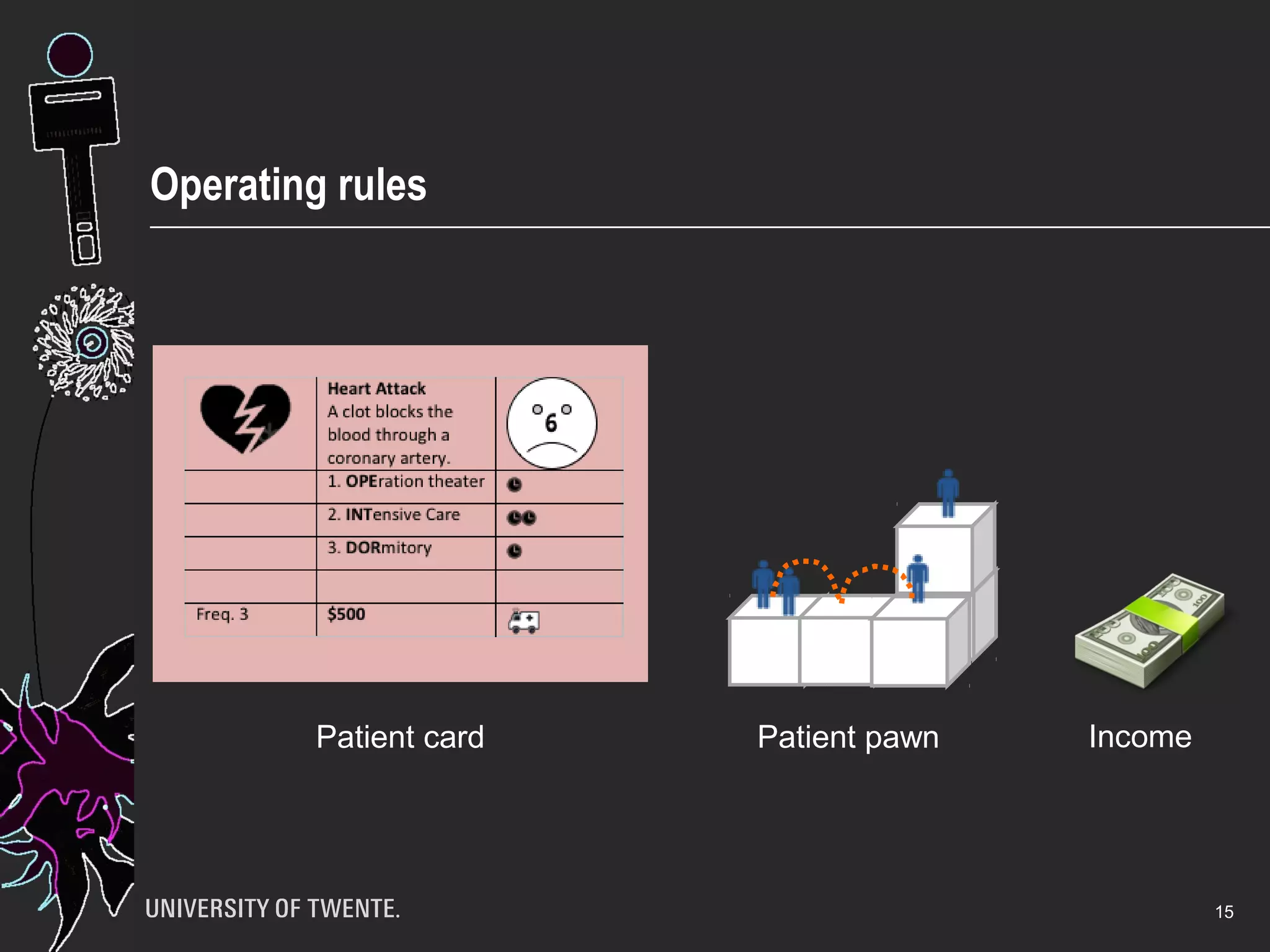
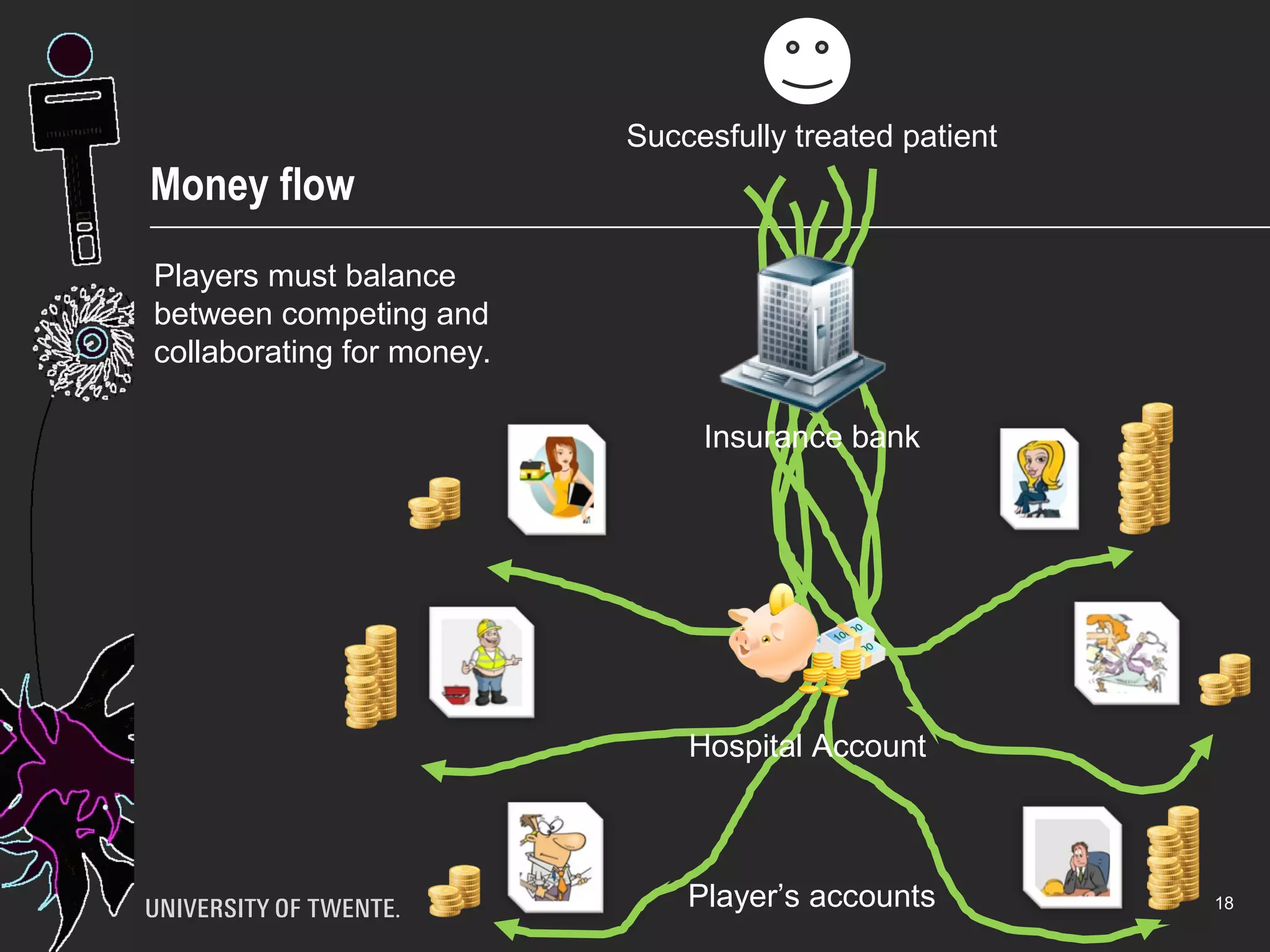
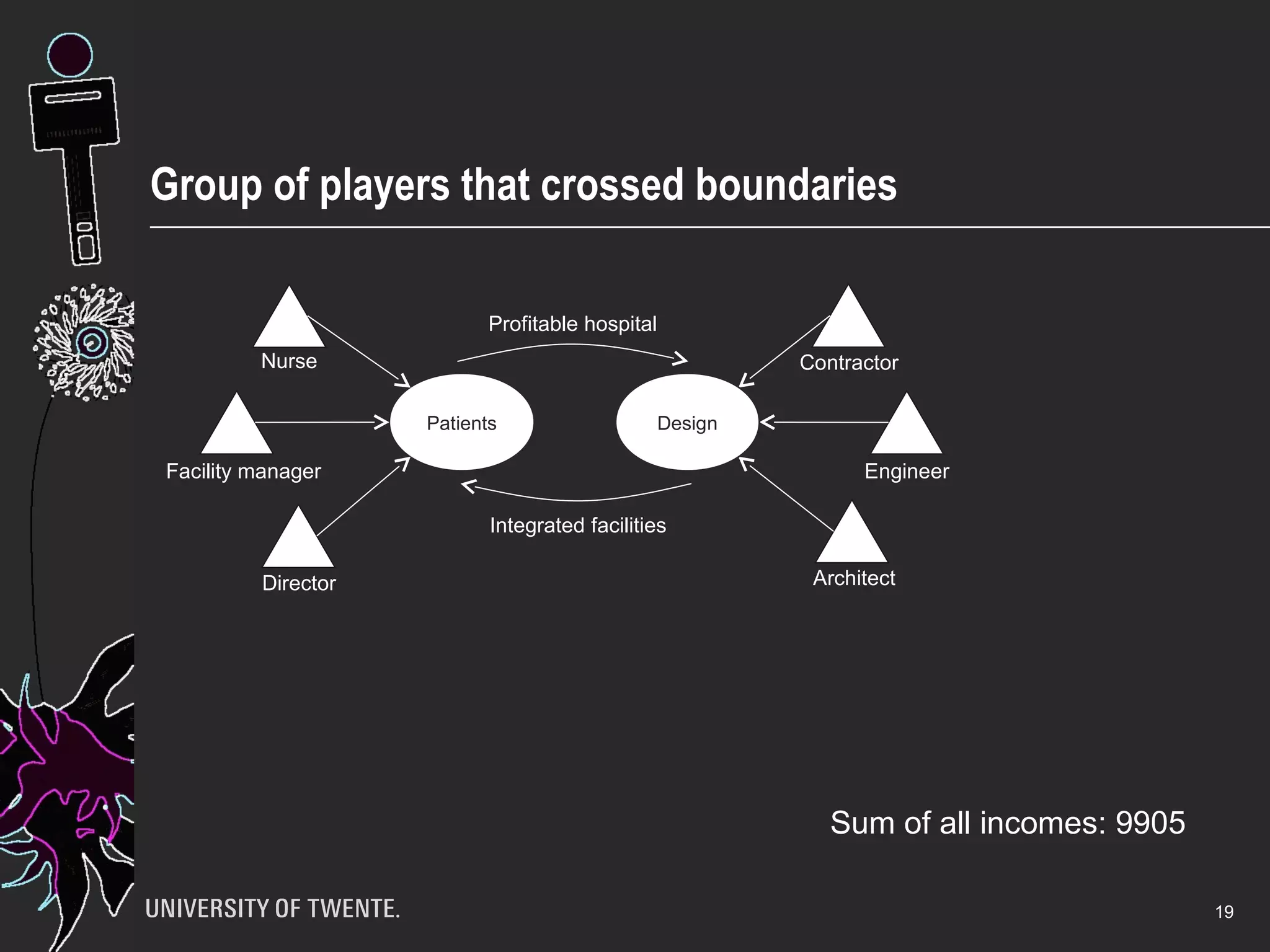
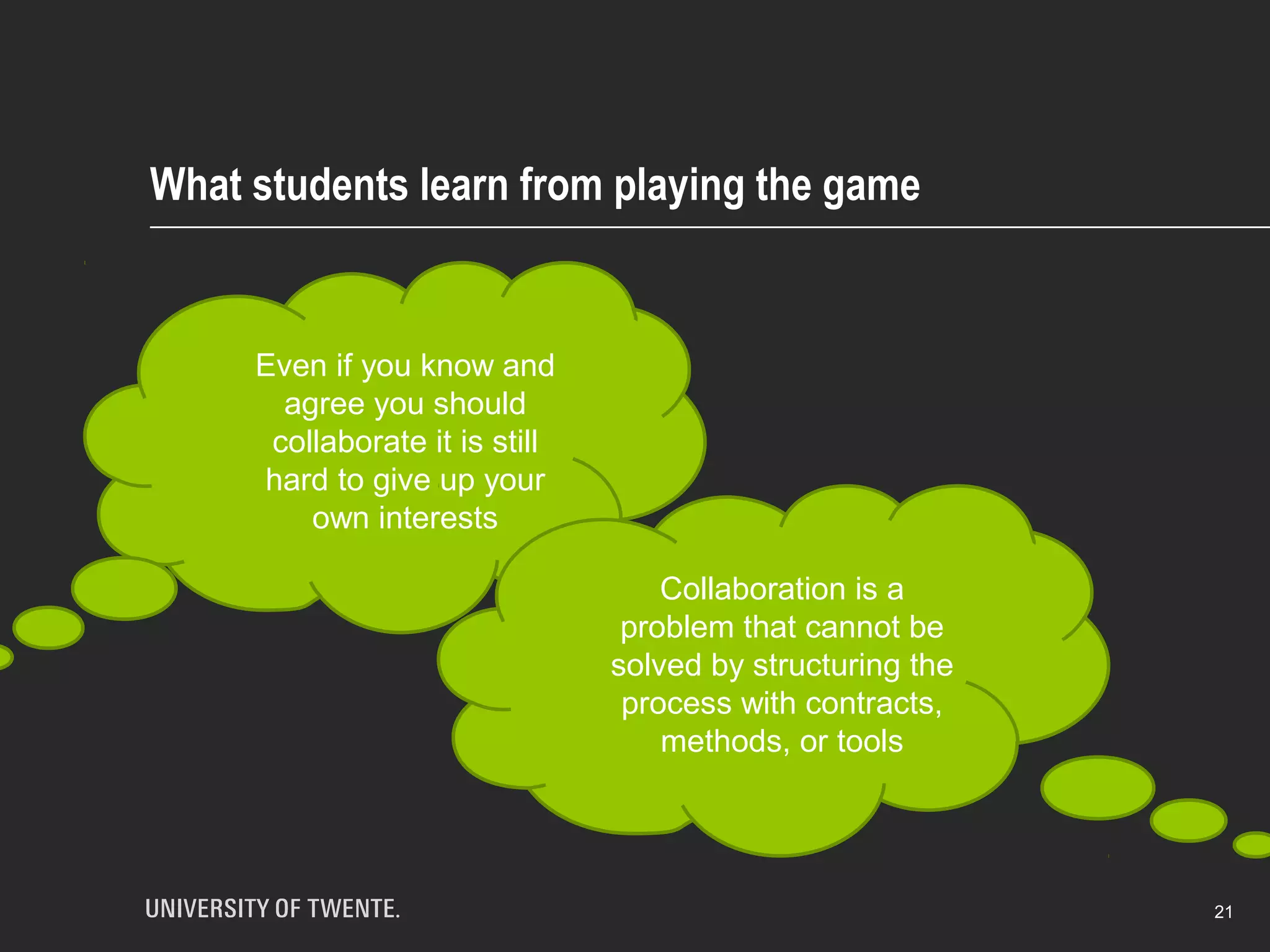
The document discusses the integration of healthcare professionals and architects through game-based workshops aimed at enhancing collaborative design for medical facilities. It highlights the importance of prioritizing use value over exchange value to promote expansive learning and effective teamwork. The findings suggest that collaboration is driven by shared interests and the recognition of use value, indicating that boundaries in design cannot be eliminated merely through structural strategies.