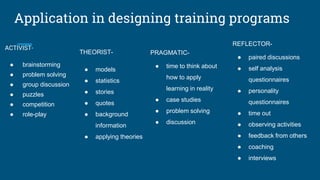
The document discusses the importance of considering different learning styles when designing training programs for employees in a corporate environment. It emphasizes that recognizing these styles can reduce training time and costs, enhance employee engagement, and provide a clearer understanding of team strengths and weaknesses. Various learning styles are outlined, including activists, theorists, pragmatists, and reflectors, each with specific characteristics and preferred training methods.