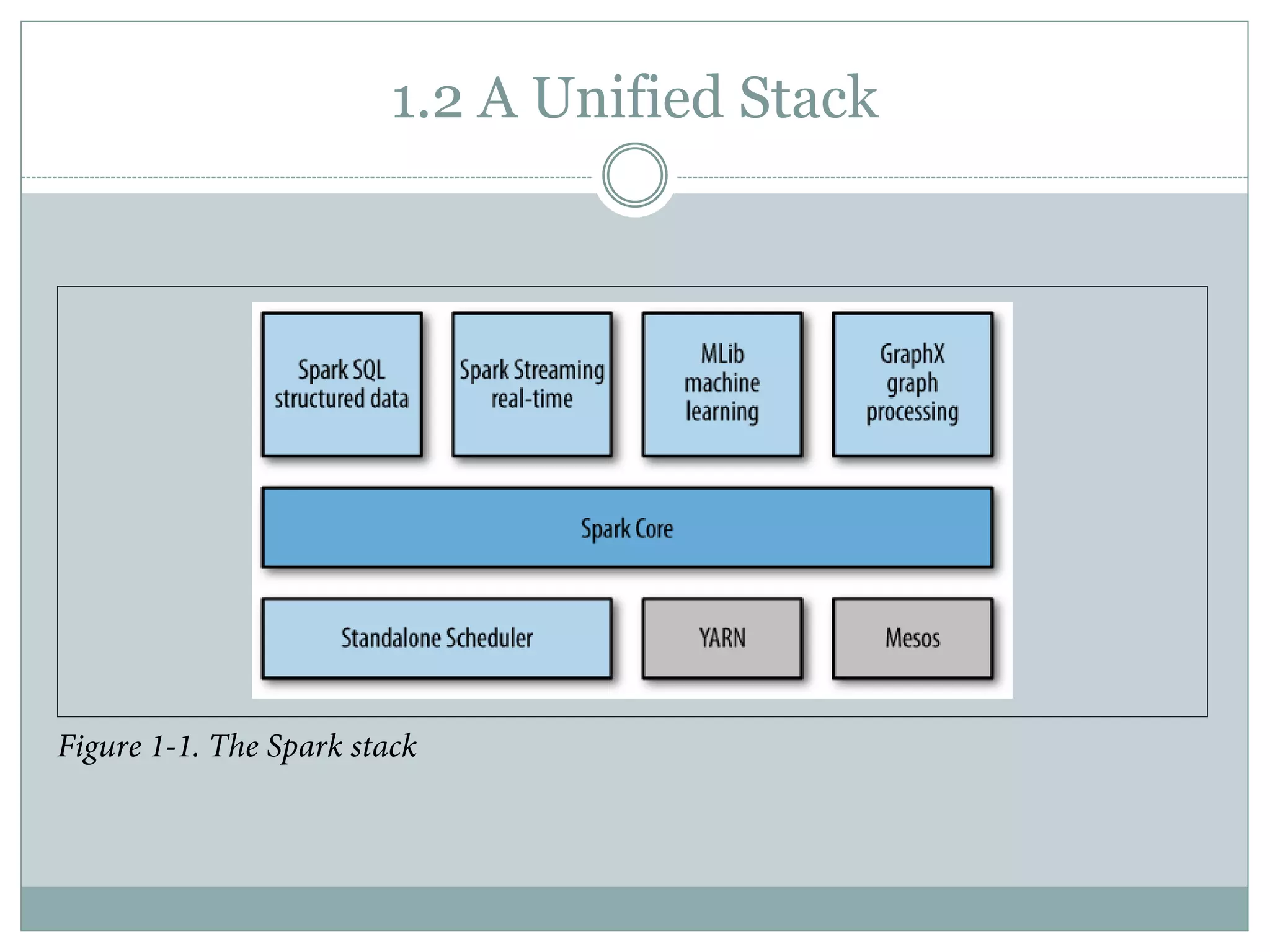
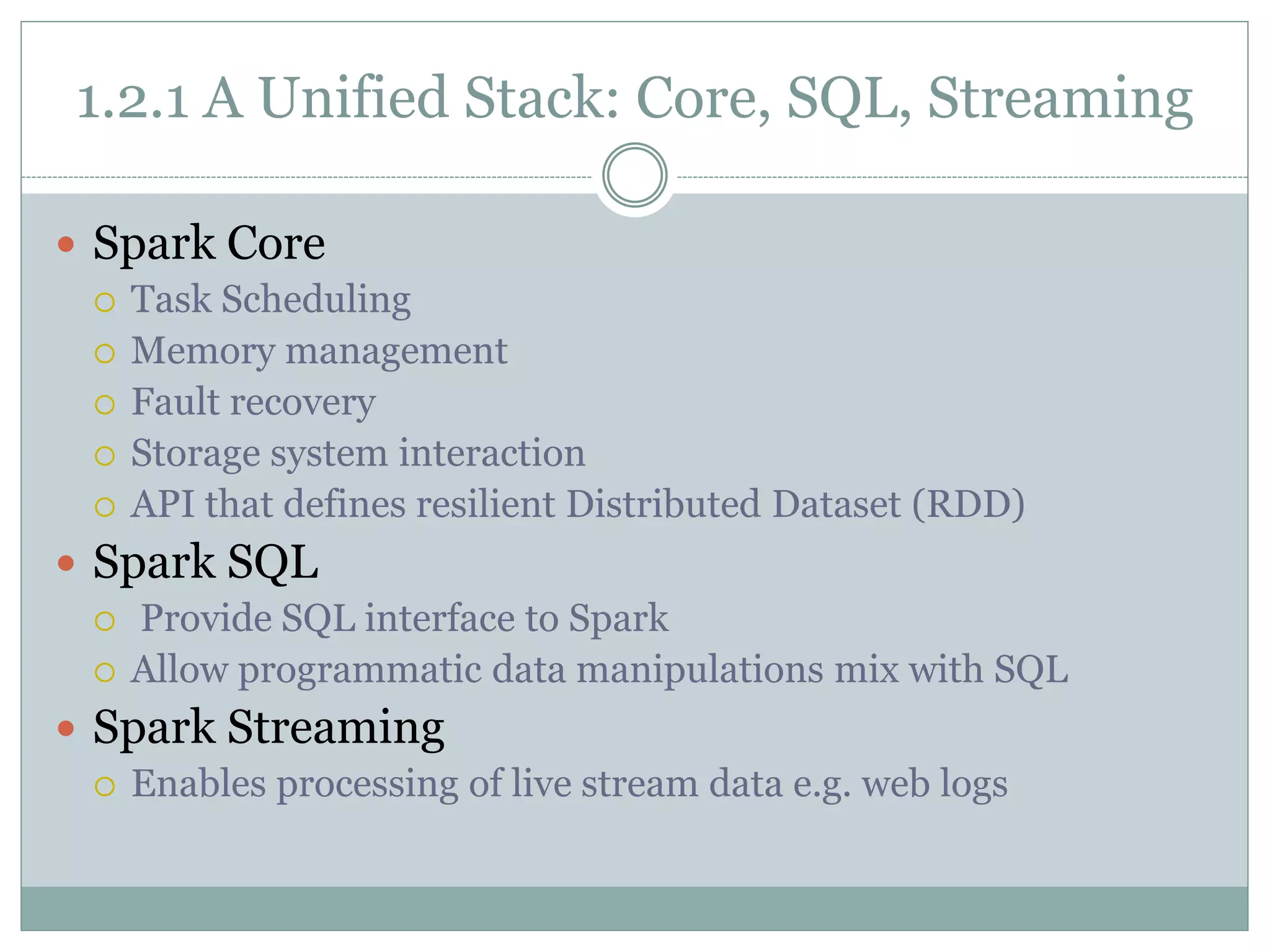
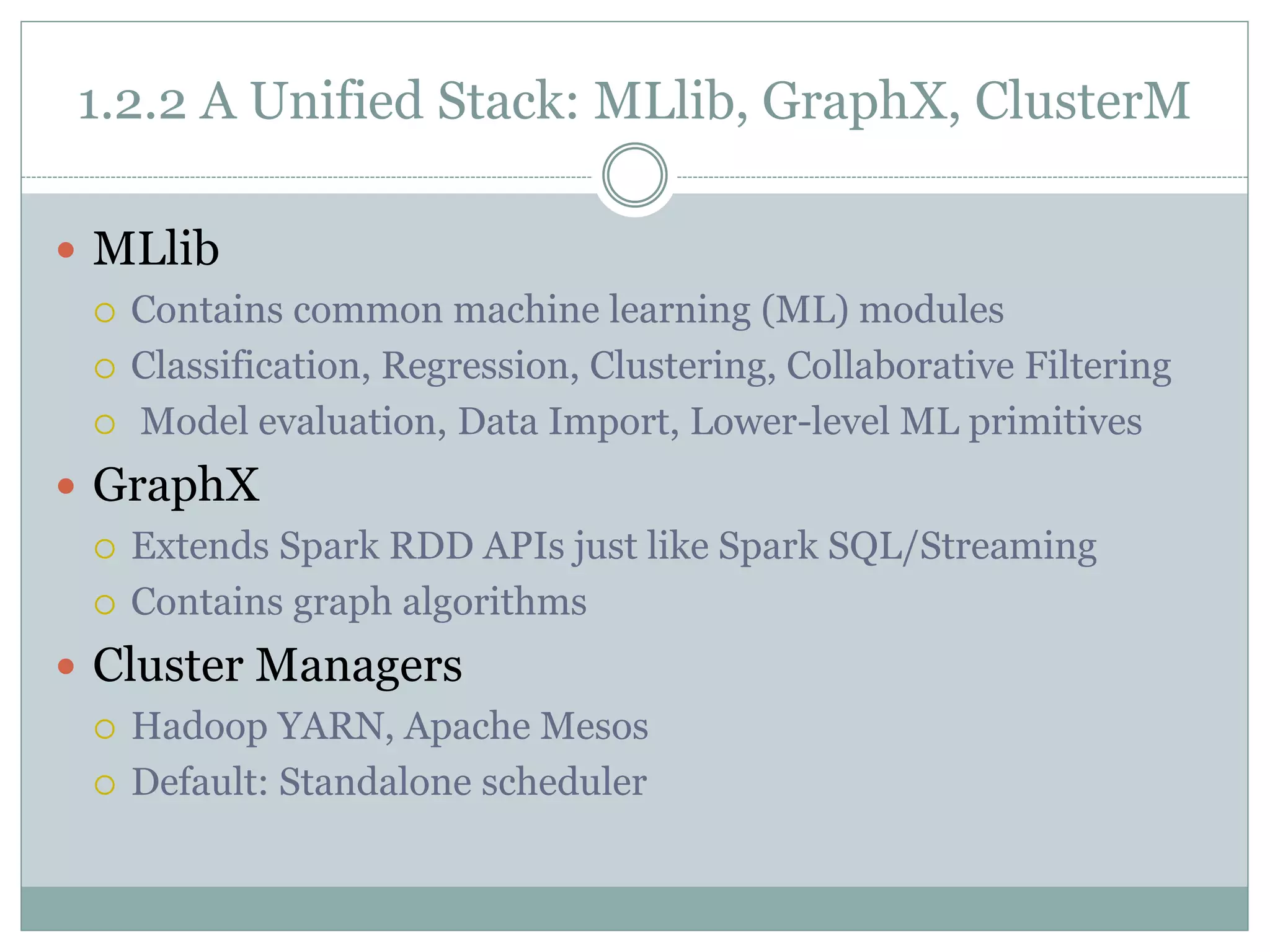
The document provides an introduction to Apache Spark, a cluster computing platform that enhances the MapReduce model for various data processing tasks. It discusses Spark's unified stack, which includes core functionalities, SQL, streaming, machine learning (MLlib), and graph processing (GraphX), highlighting its applications in data science and engineering. Additionally, it covers Spark's history, versions, and compatibility with multiple storage layers.