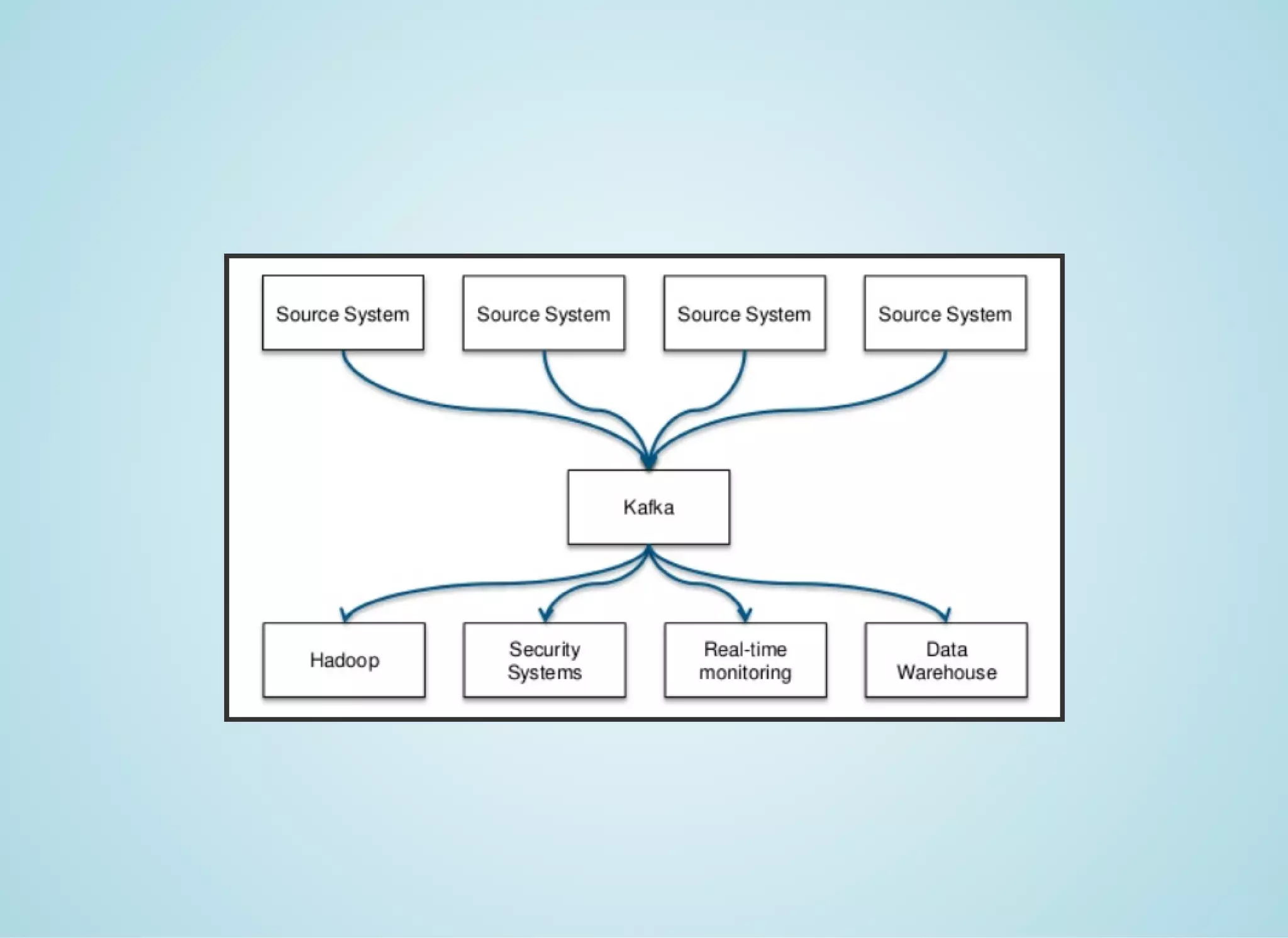
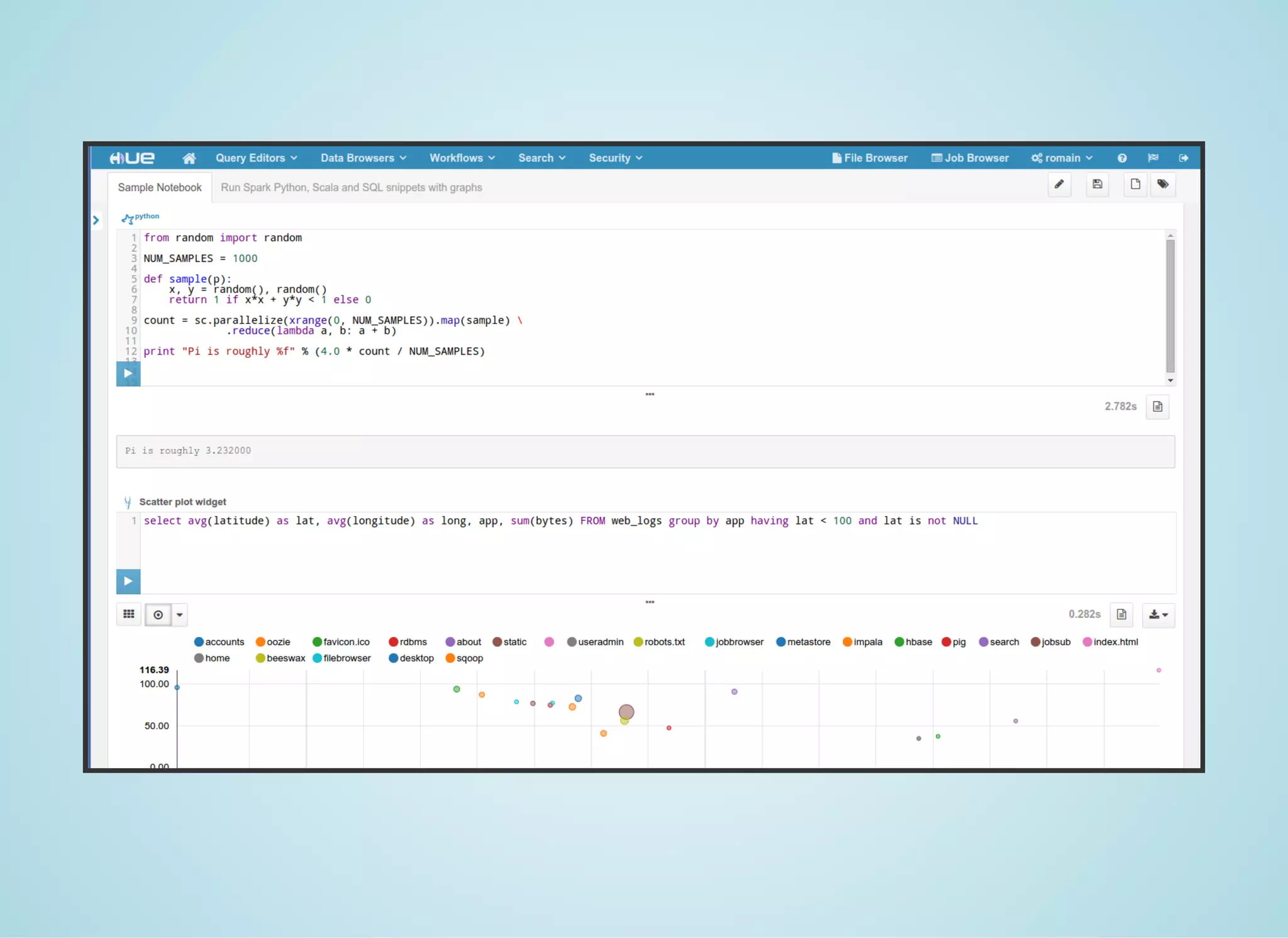
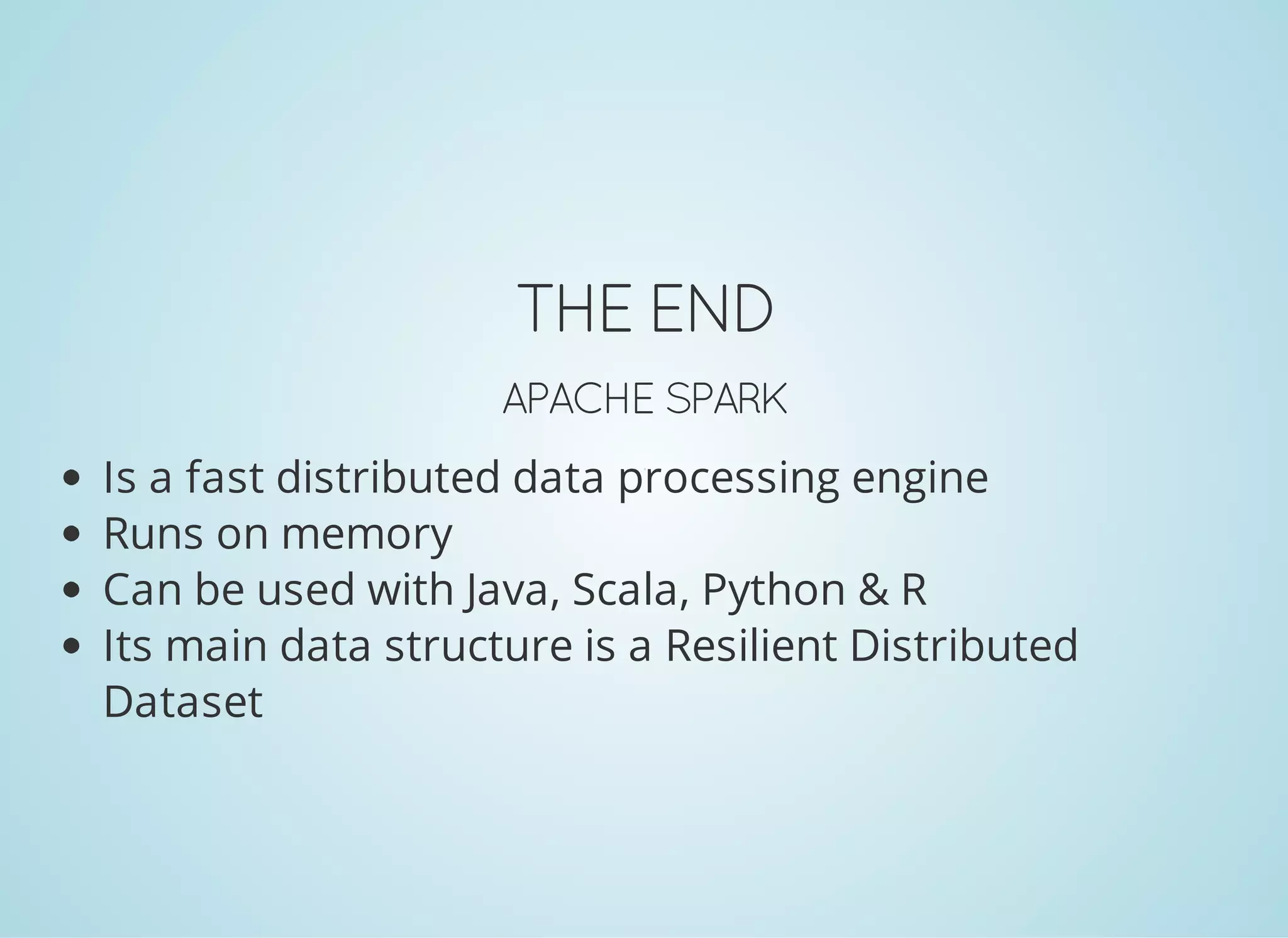
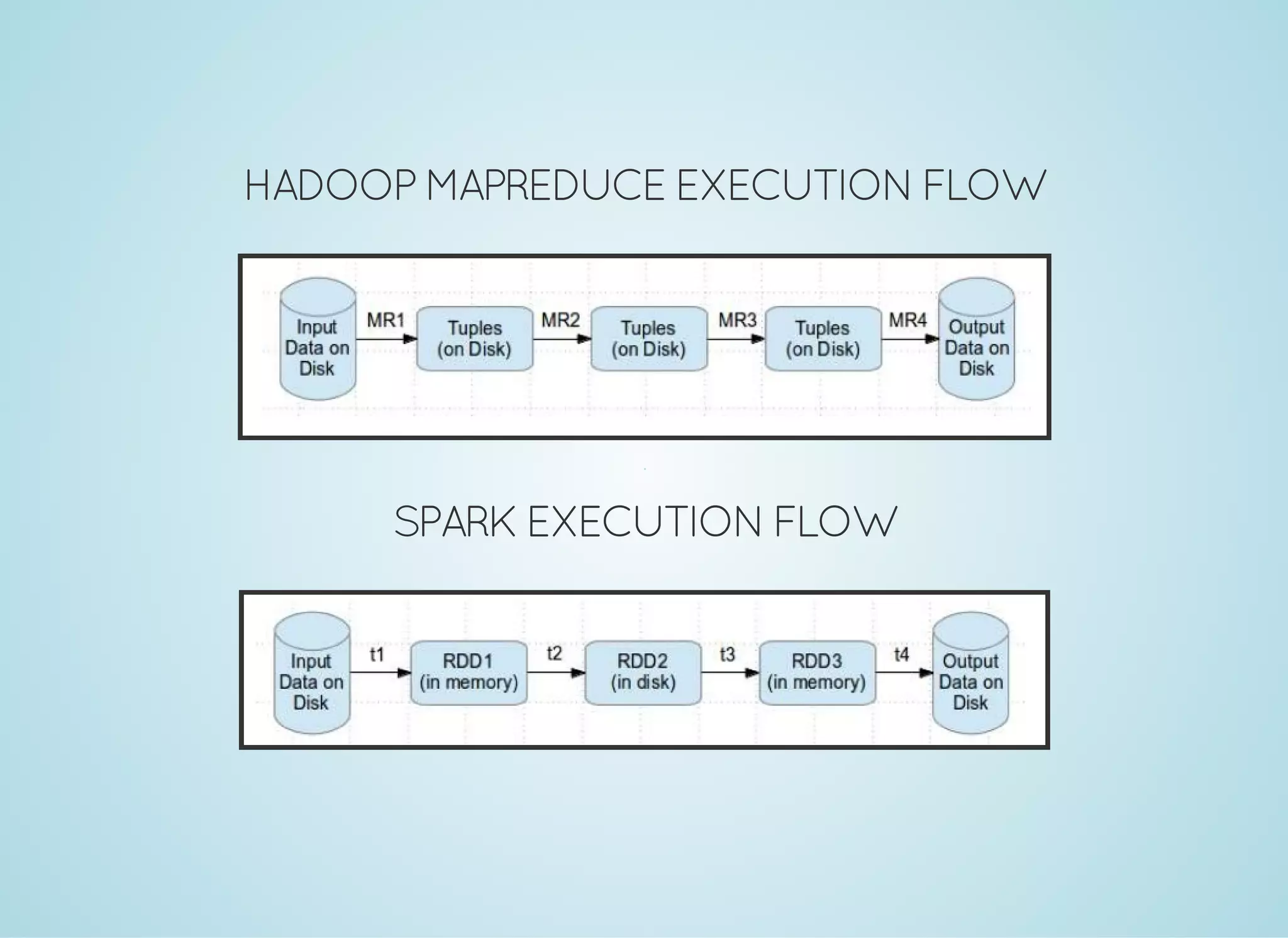
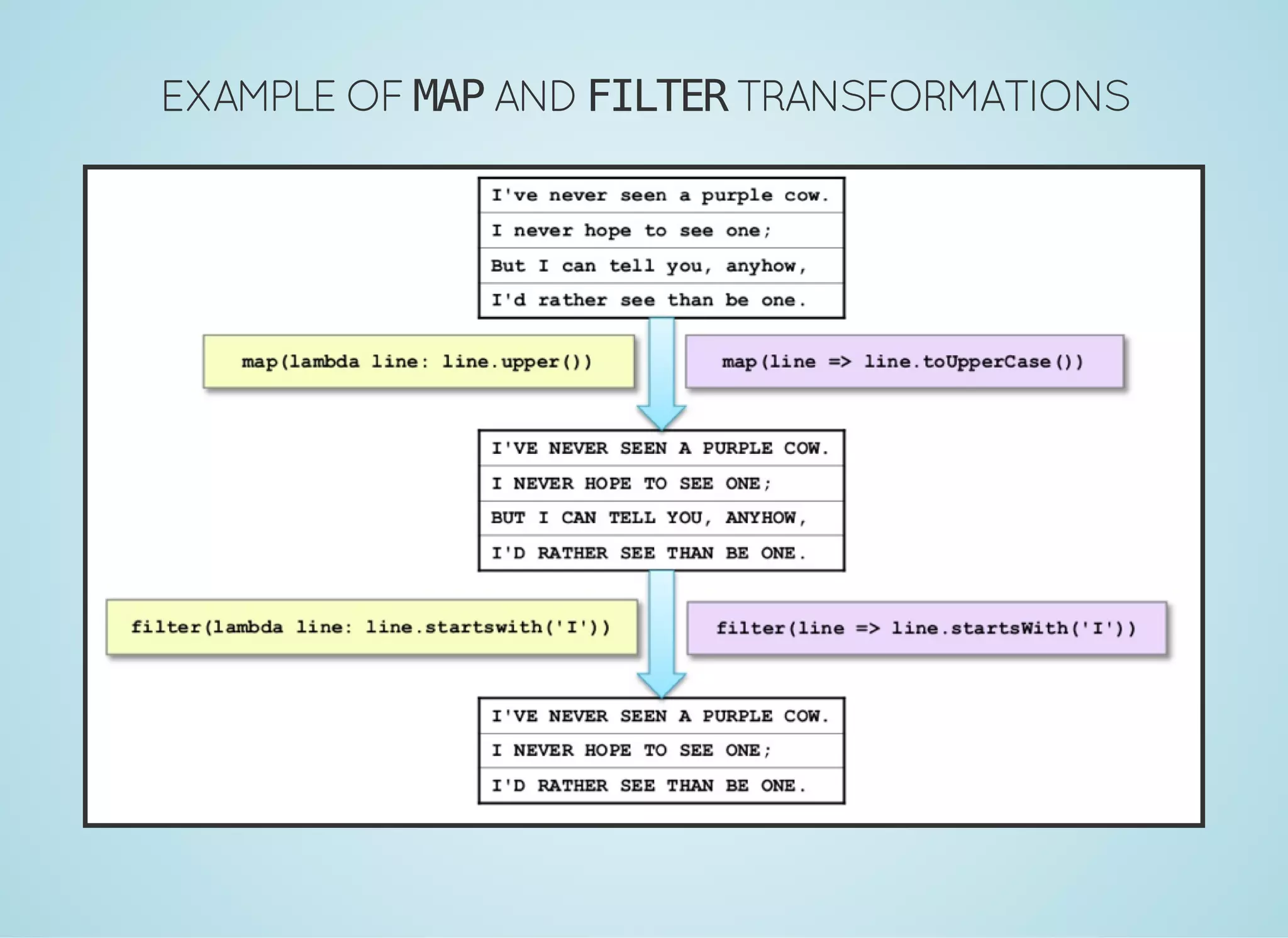
Apache Spark is a fast distributed data processing engine that runs in memory. It can be used with Java, Scala, Python and R. Spark uses resilient distributed datasets (RDDs) as its main data structure. RDDs are immutable and partitioned collections of elements that allow transformations like map and filter. Spark is 10-100x faster than Hadoop for iterative algorithms and can be used for tasks like ETL, machine learning, and streaming.


















![ASASPARKAPPLICATION
By adding spark-core and other Spark modules as project
dependencies and using Spark API inside the application
code
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val conf = new SparkConf()
.setAppName("Sample Application")
.setMaster("local")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val logData = sc.textFile("/tmp/spark/README.md")
val lines = textFile.filter(line => line contains "Spark")
lines.collect()
sc.stop()
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prez-spark-160402193358/75/Introduction-to-Apache-Spark-34-2048.jpg)
![BYSUBMITTING SPARKAPPLICATION
TO SPARK-SUBMIT
./bin/sparksubmit
class <mainclass>
master <masterurl>
deploymode <deploymode>
conf <key>=<value>
... # other options
<applicationjar>
[applicationarguments]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prez-spark-160402193358/75/Introduction-to-Apache-Spark-35-2048.jpg)