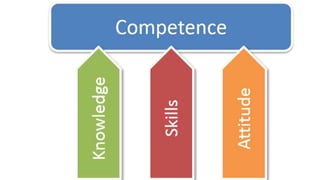
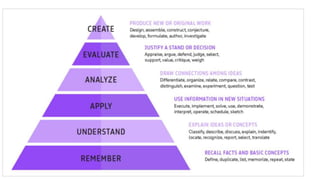
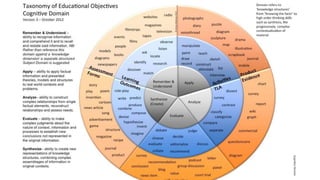
The document discusses how to properly structure learning objectives for training activities. It emphasizes that objectives should be based on the overall learning goal and translated into specific, measurable steps. Learning objectives should use action verbs from Bloom's Taxonomy to clearly define what knowledge and skills participants will develop. Well-structured objectives ensure the content, methods, and assessments used are tailored and effective for helping participants achieve the desired competencies.