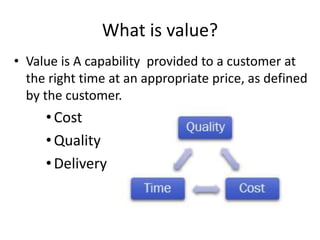
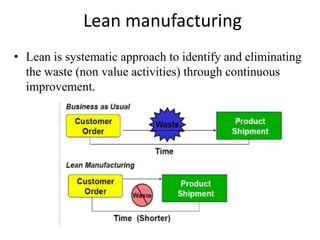
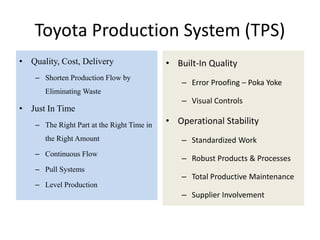
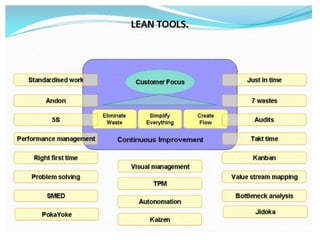
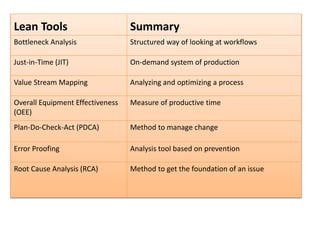
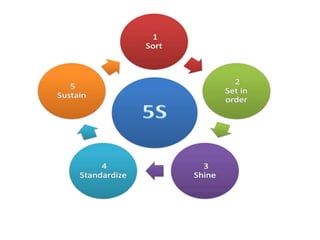
This document provides an overview of lean systems and lean manufacturing. It defines key lean concepts like identifying and eliminating waste, continuous improvement, and value from the customer perspective. Lean aims to systematically identify and remove non-value activities. The document also discusses lean tools and techniques, the Toyota Production System approach, benefits of lean, and the history of lean management.