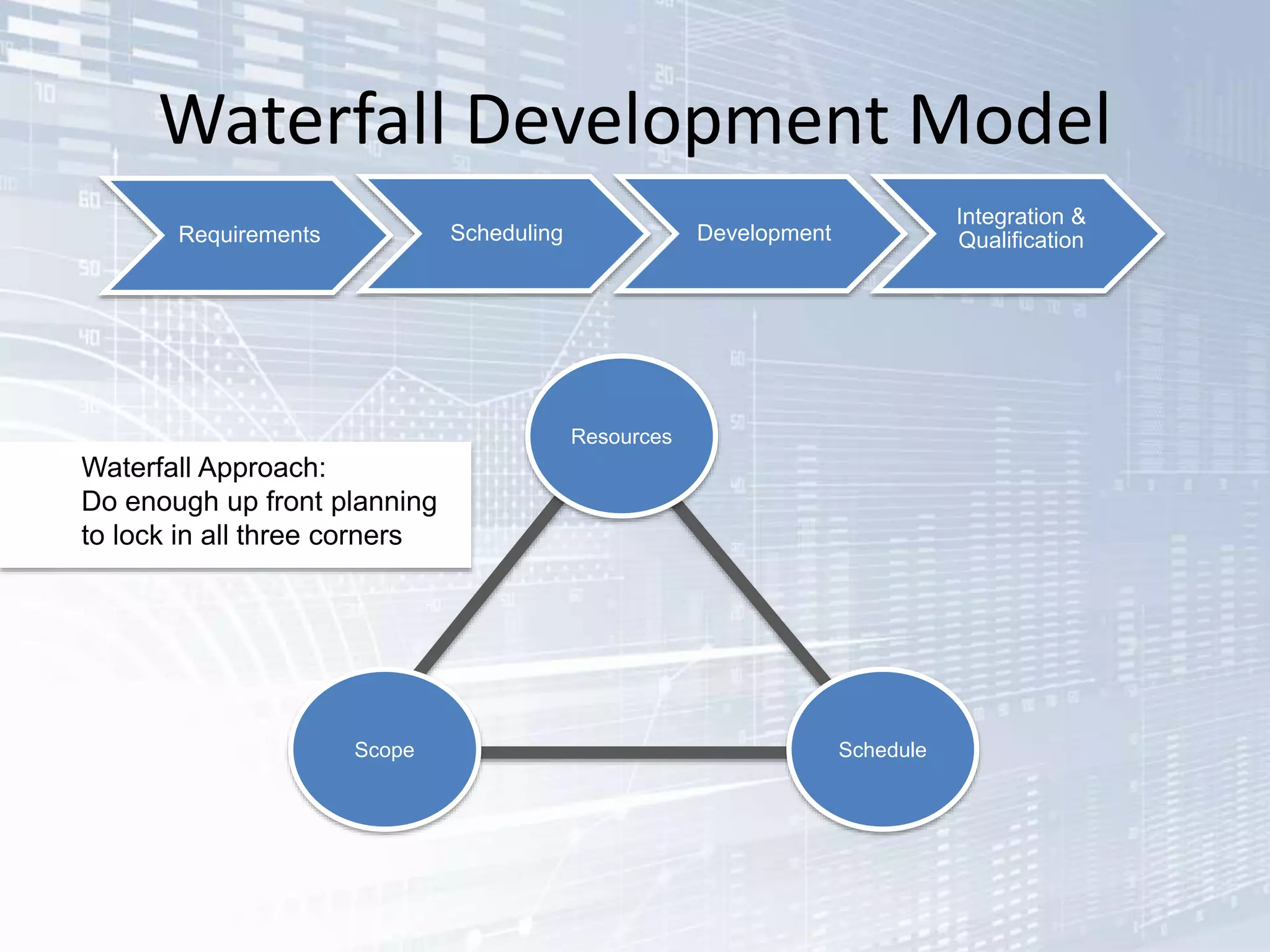
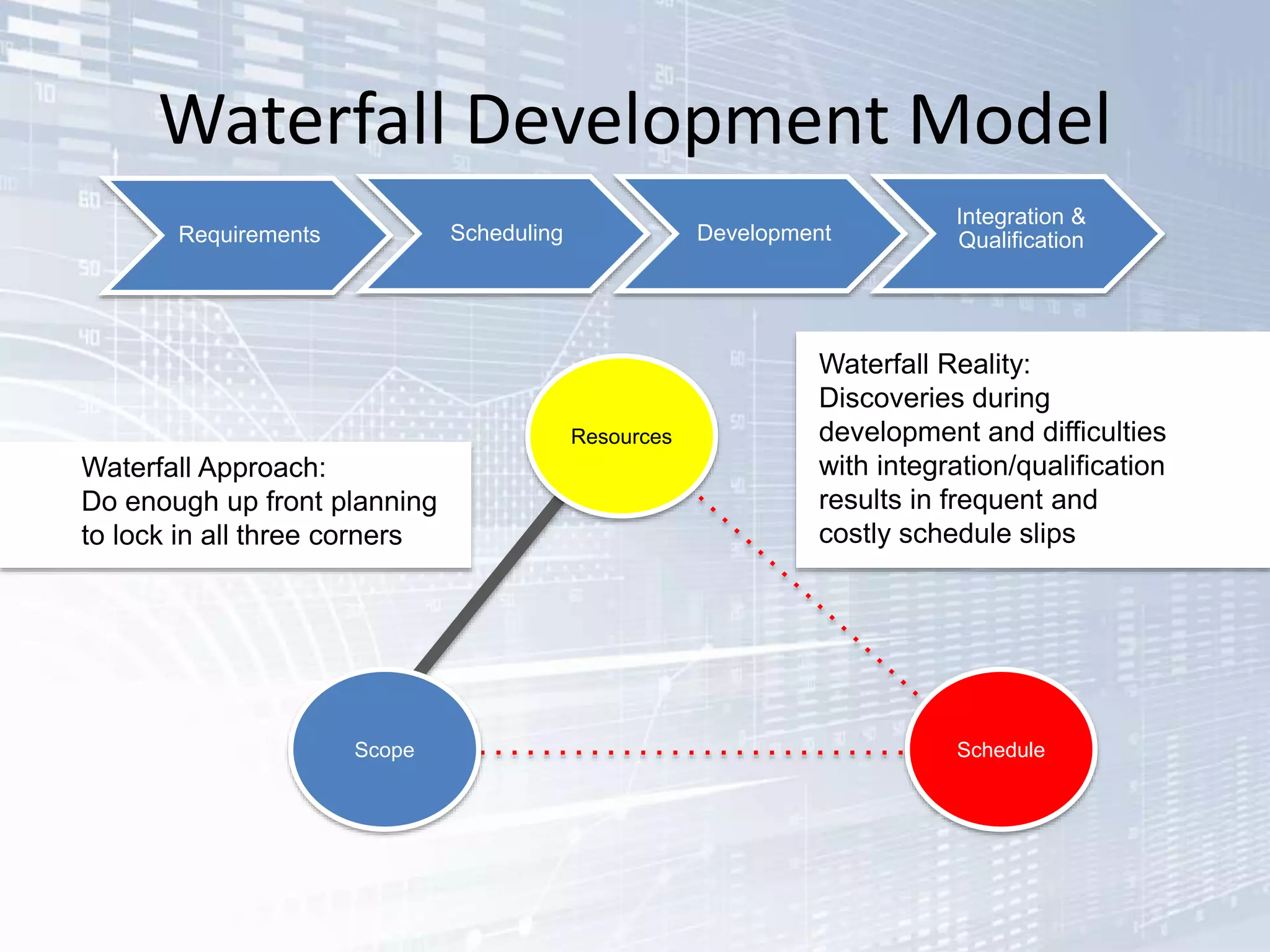
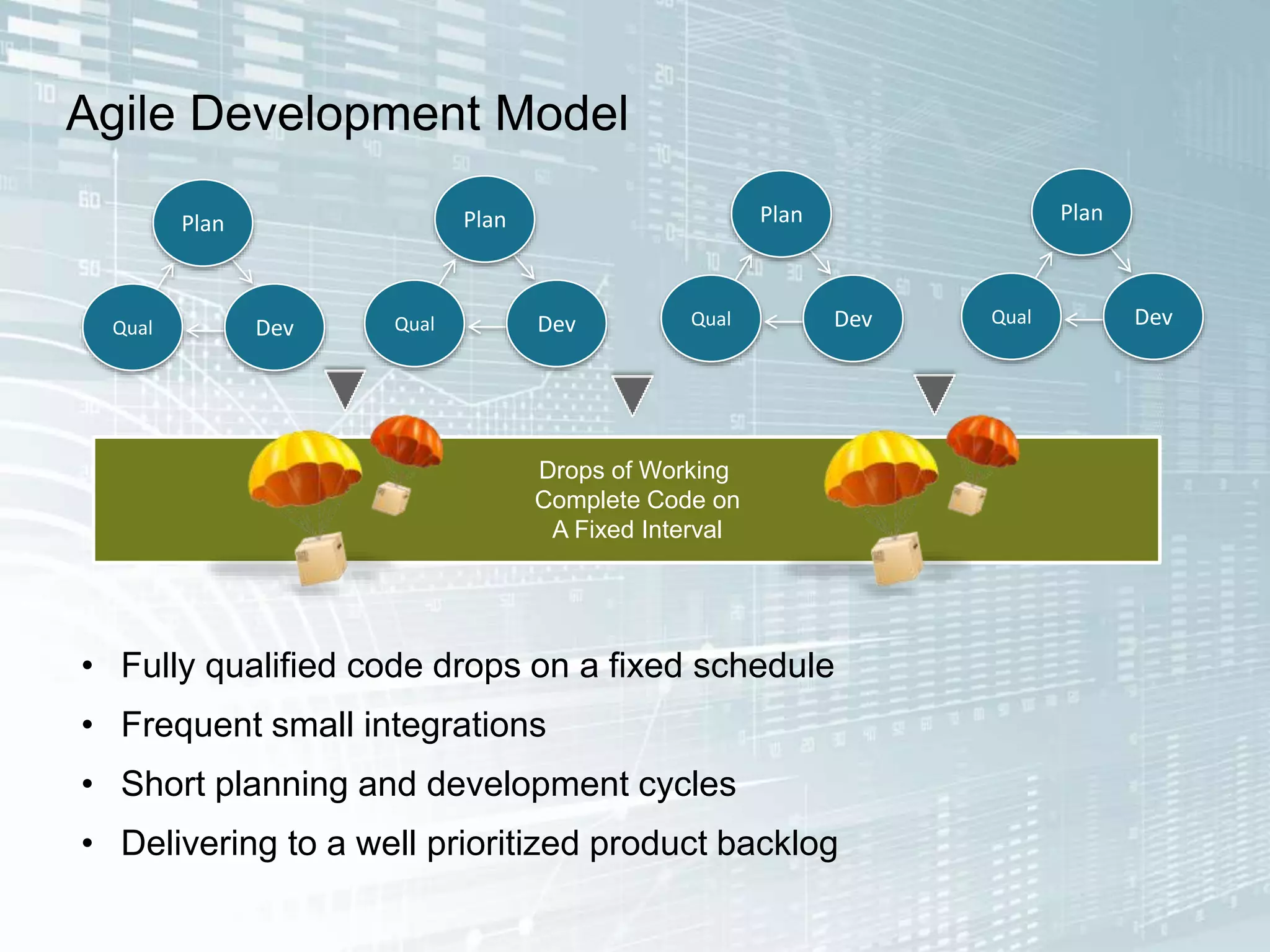
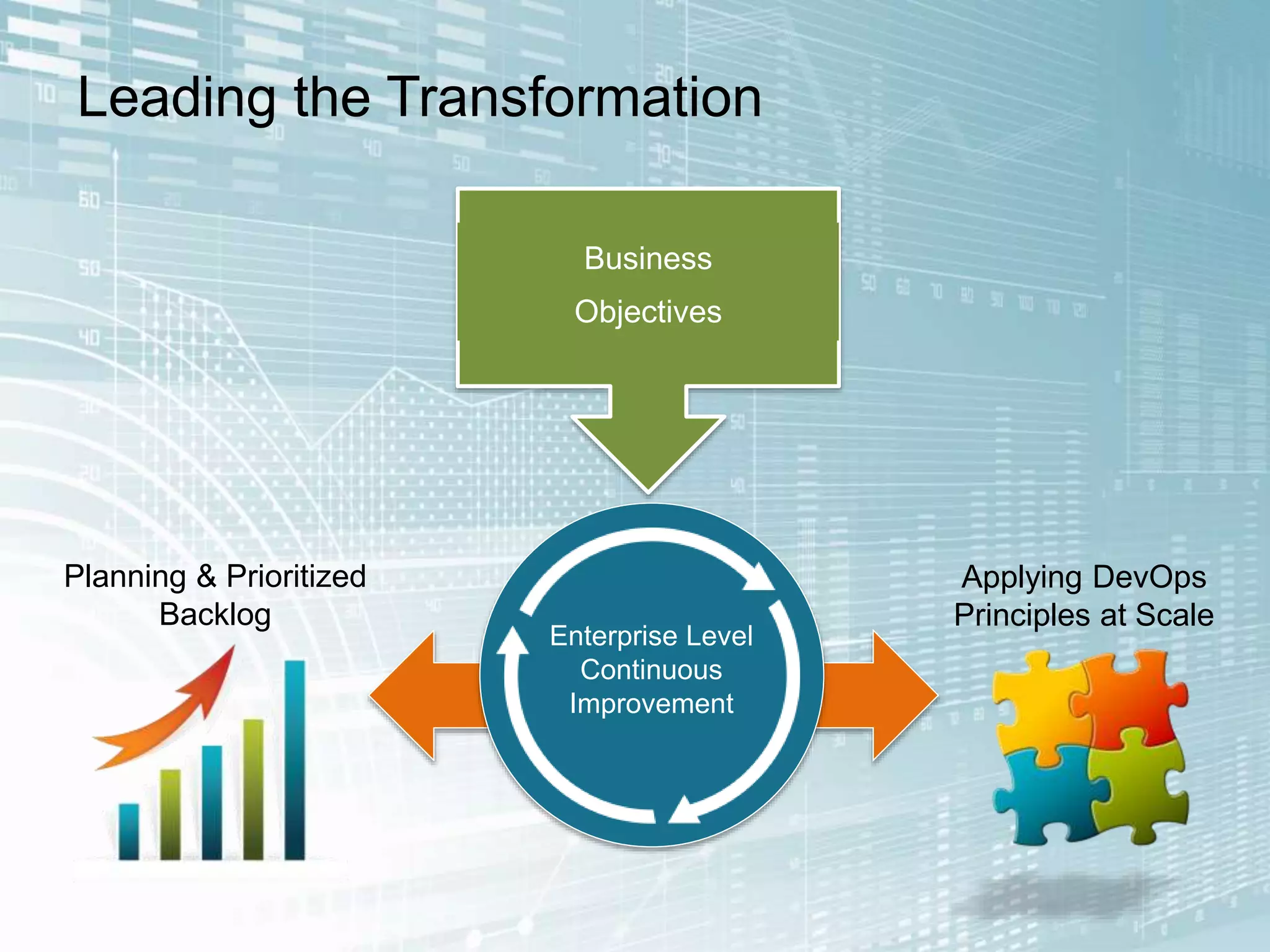
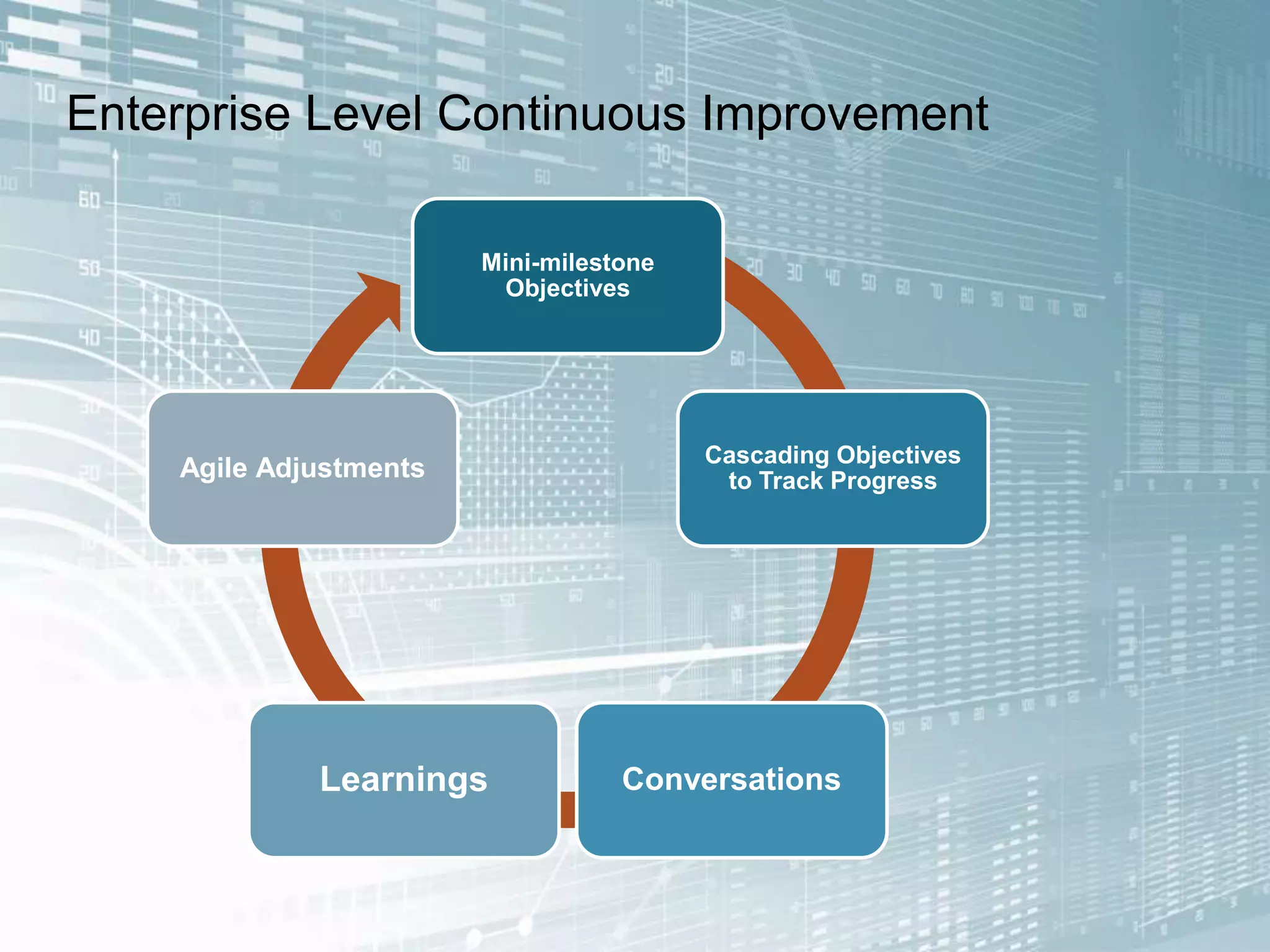
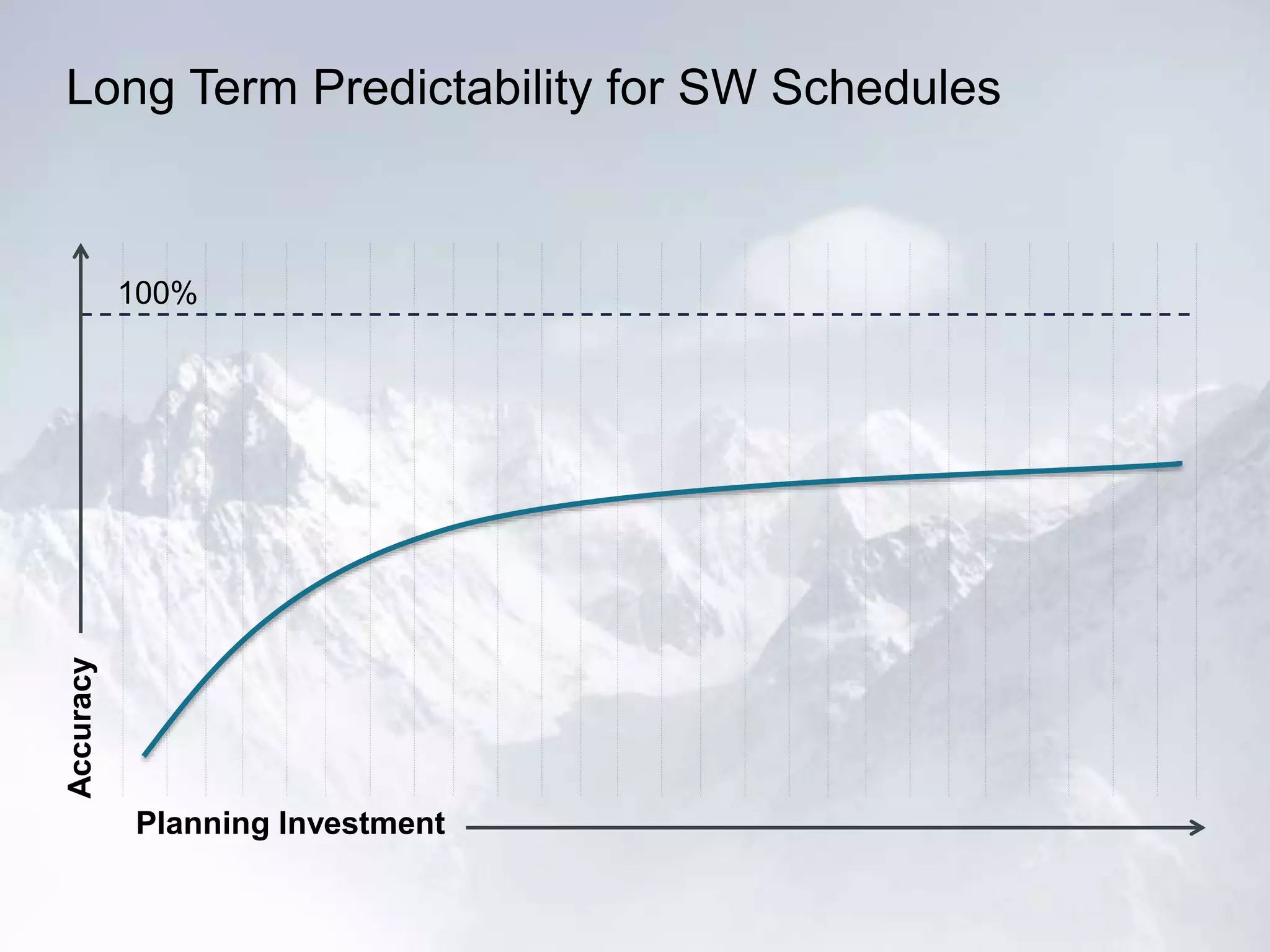
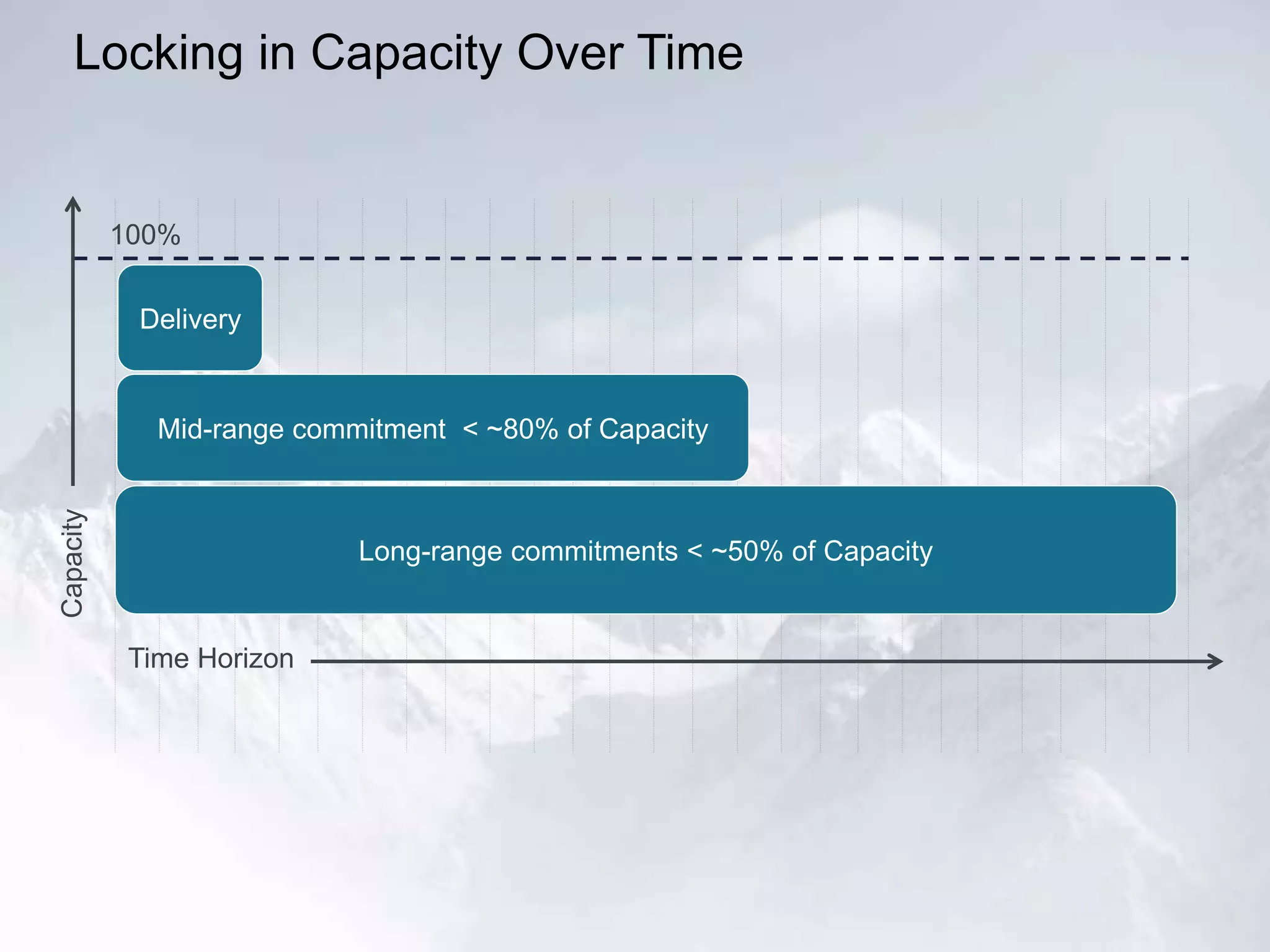
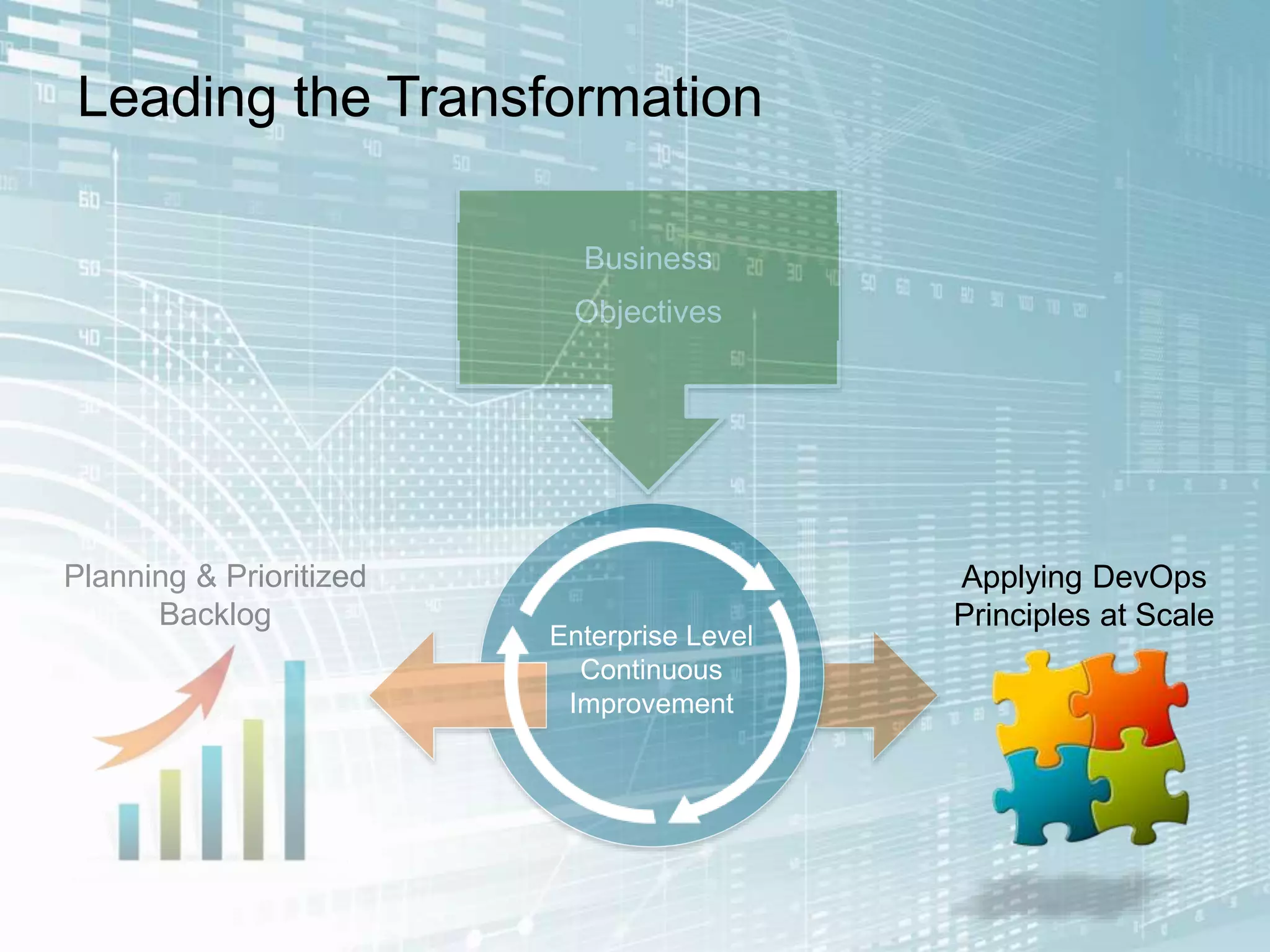
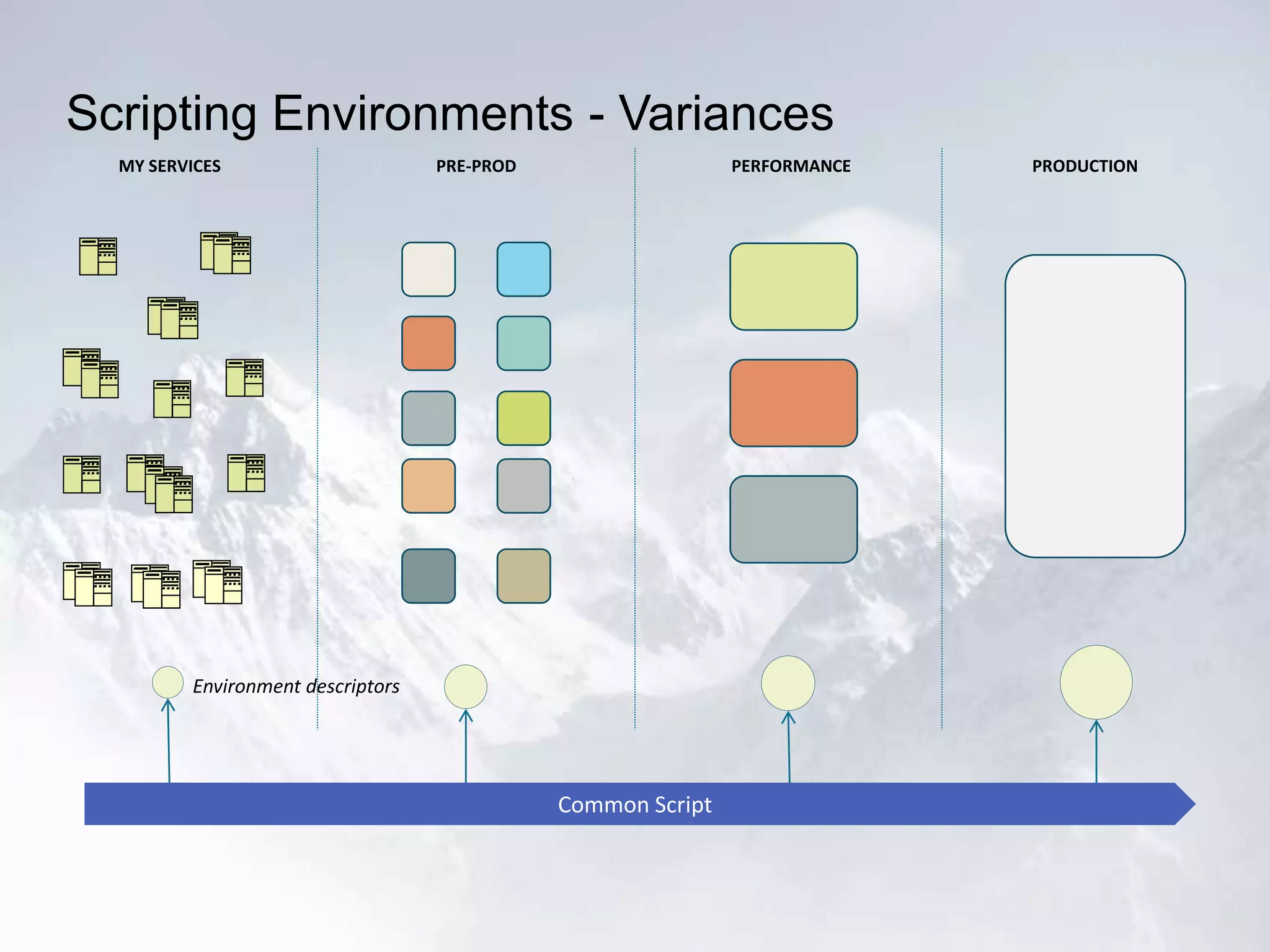
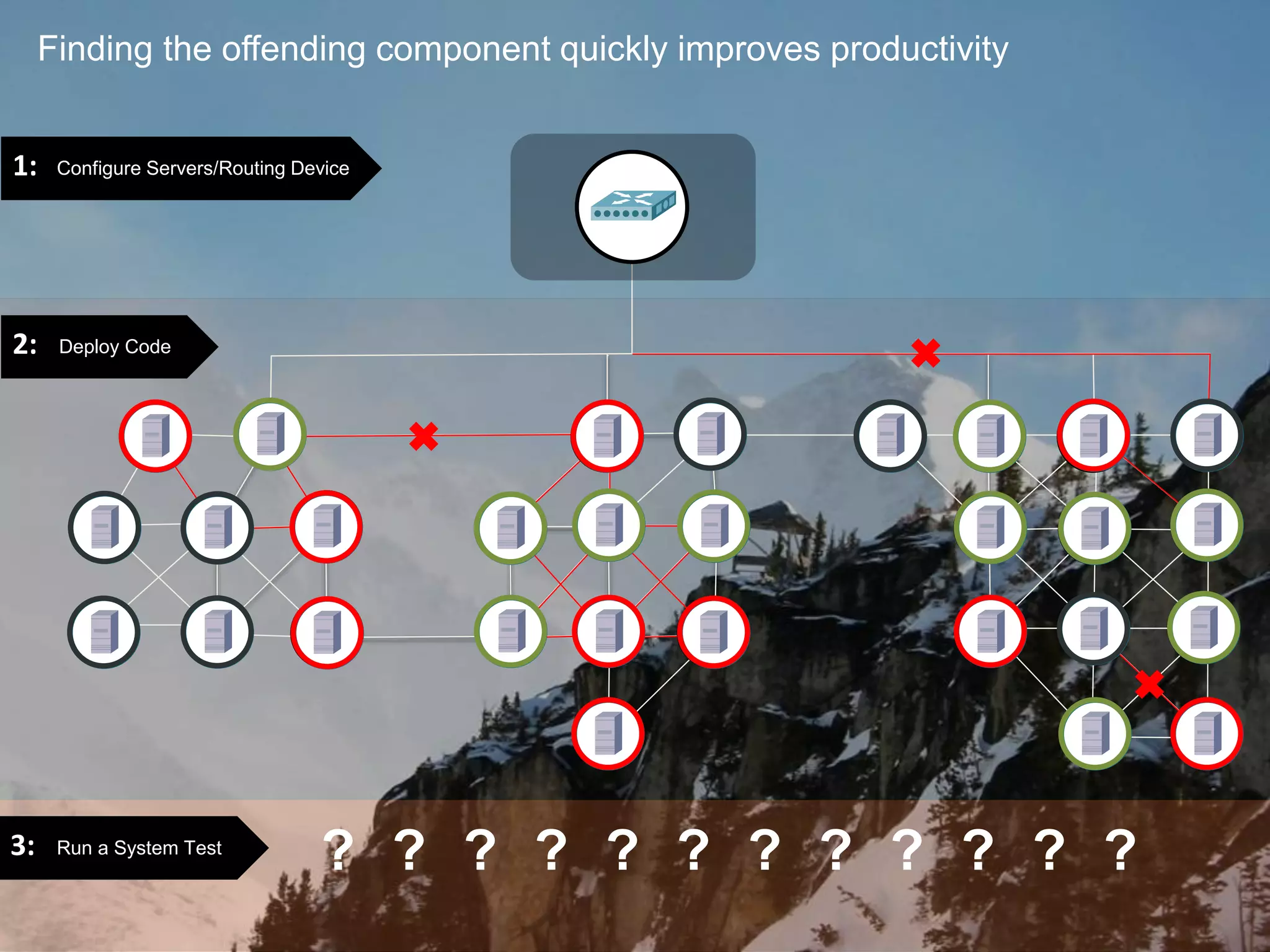
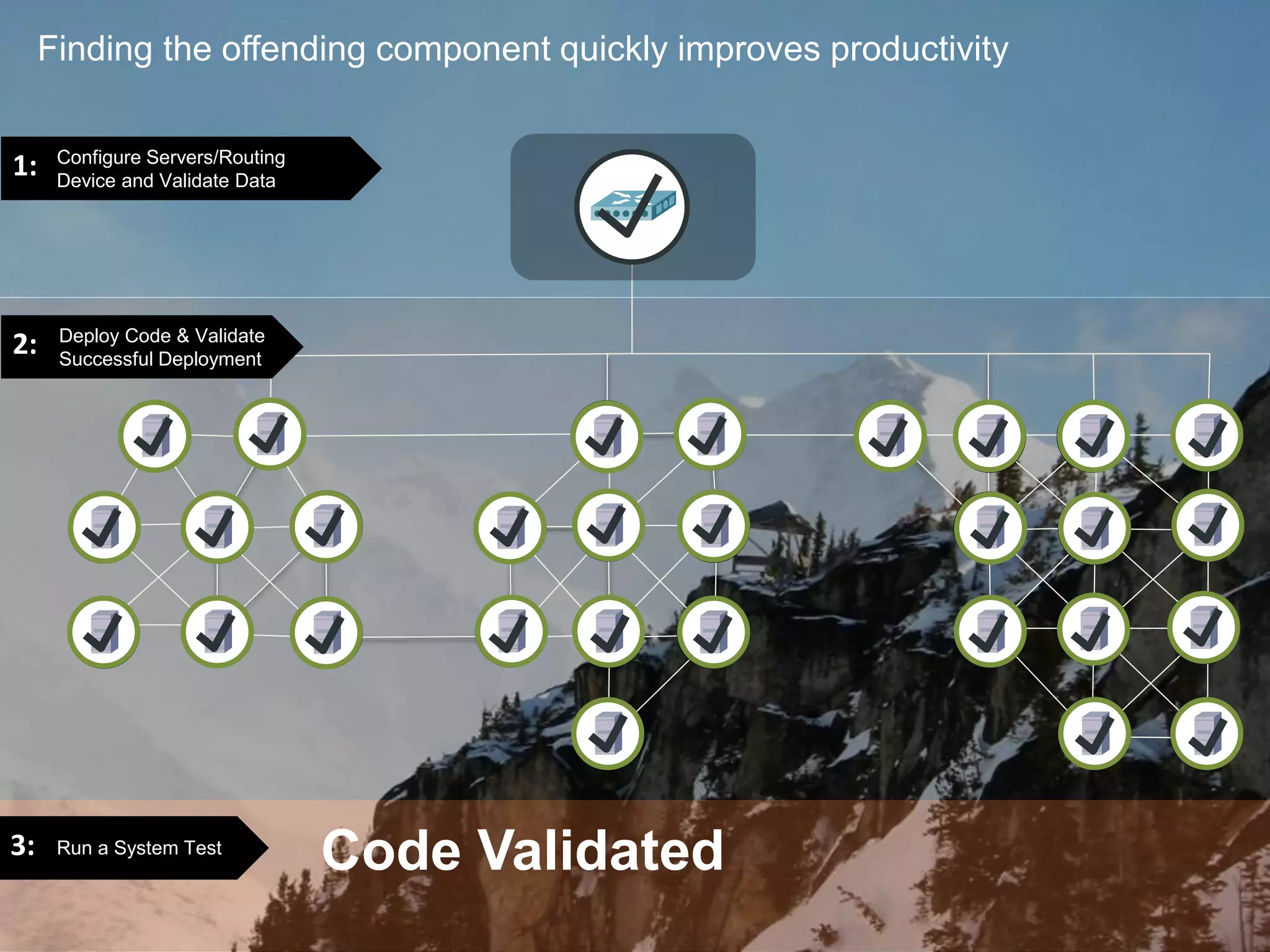
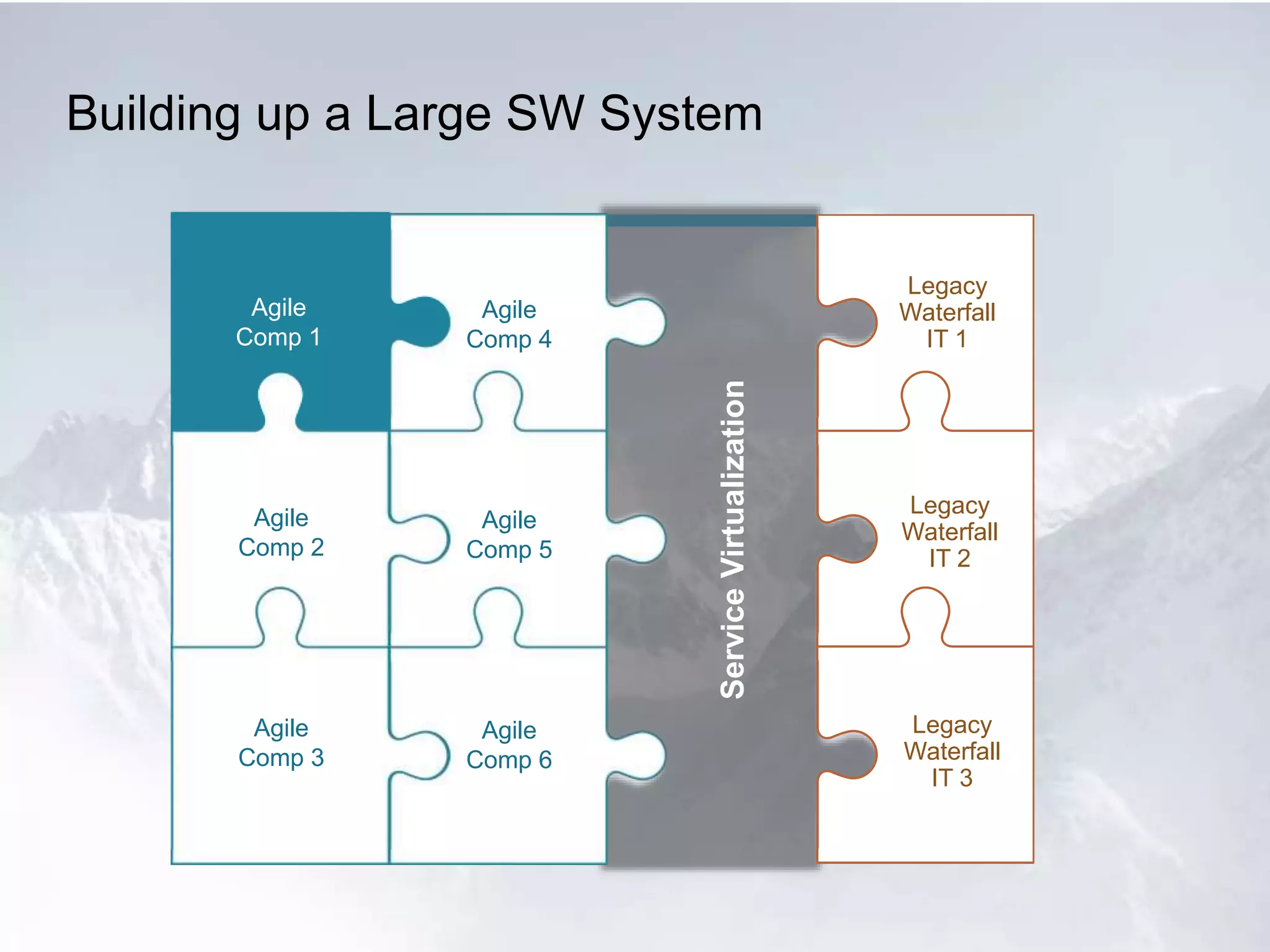
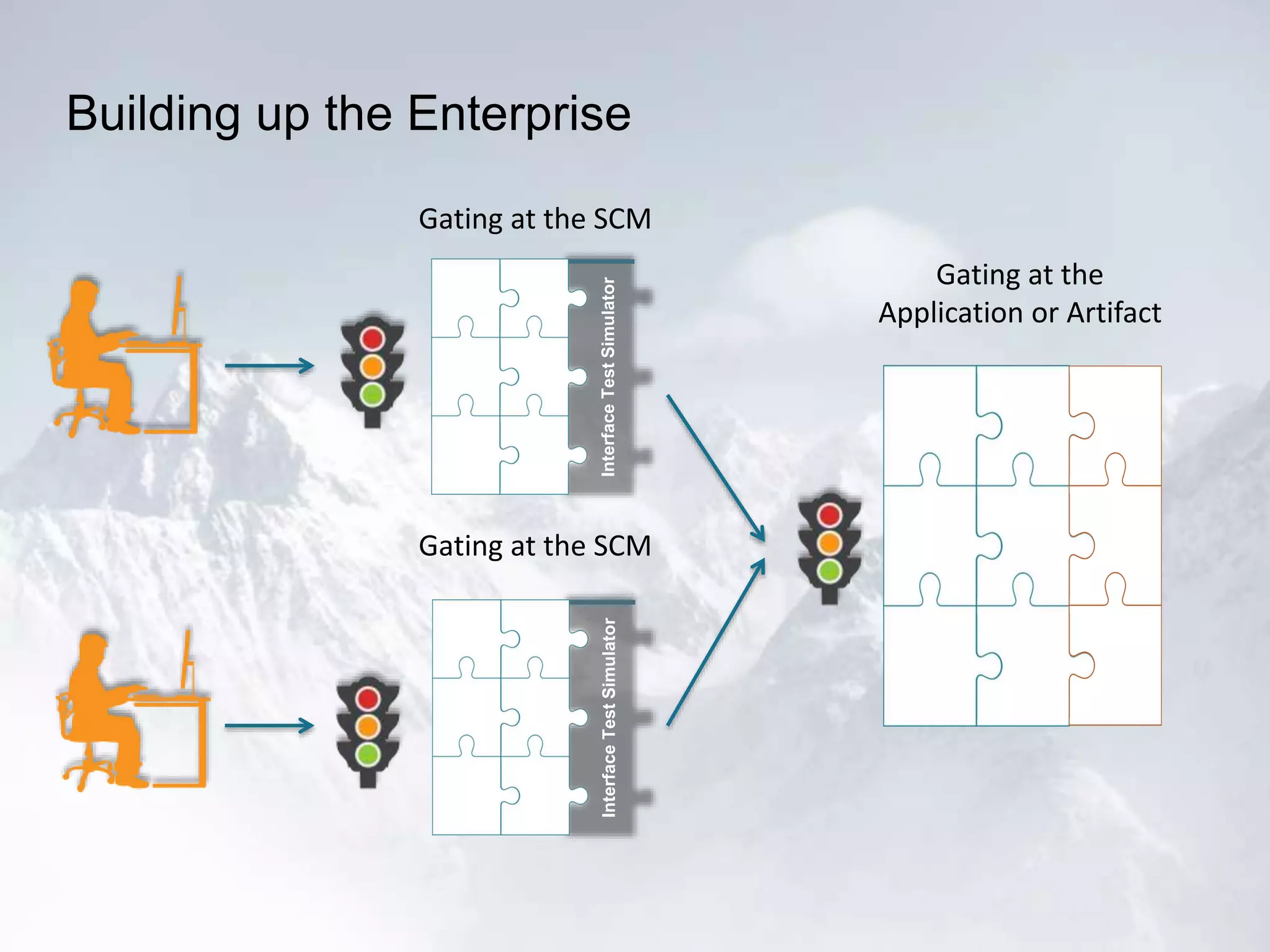
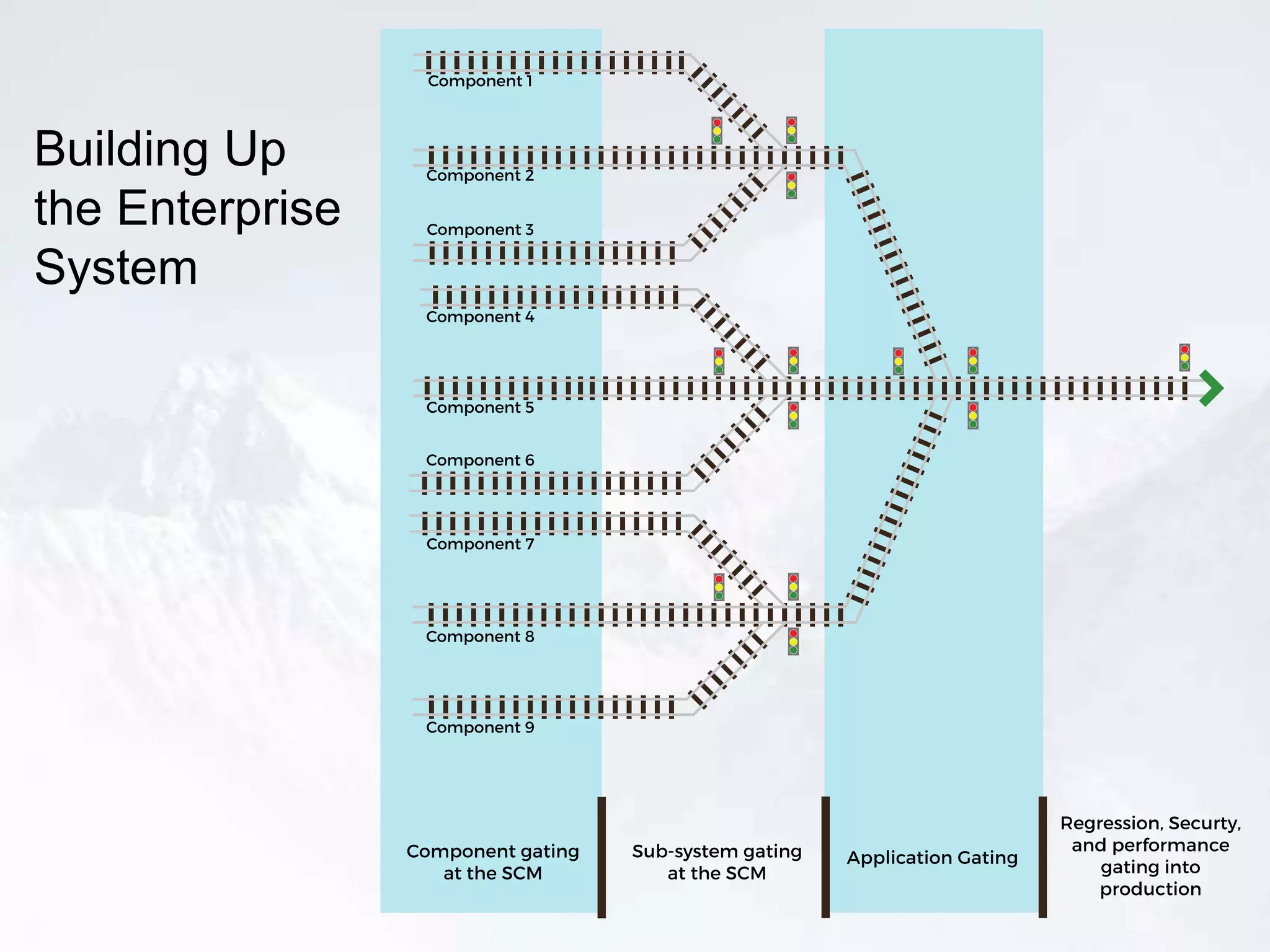
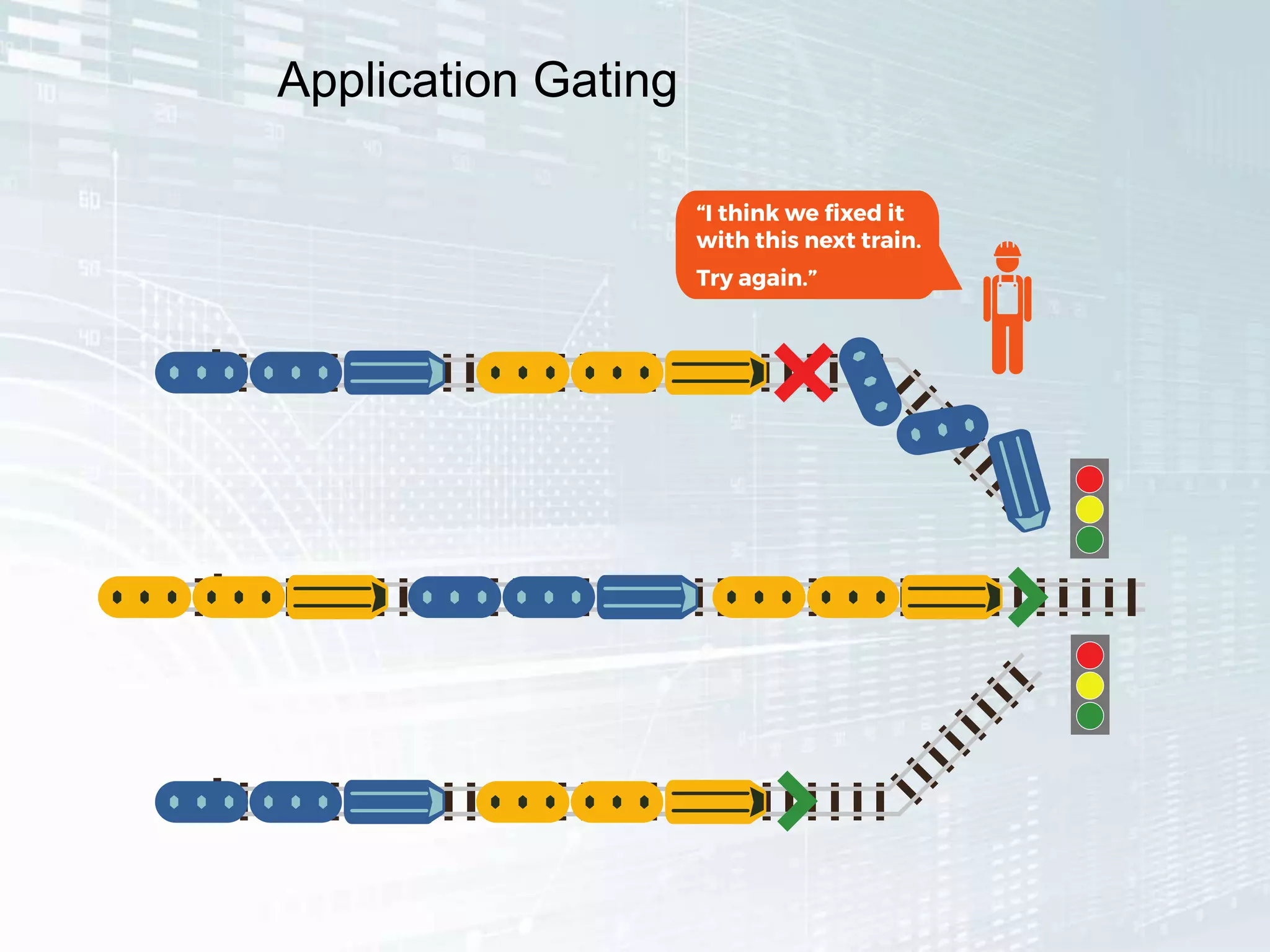
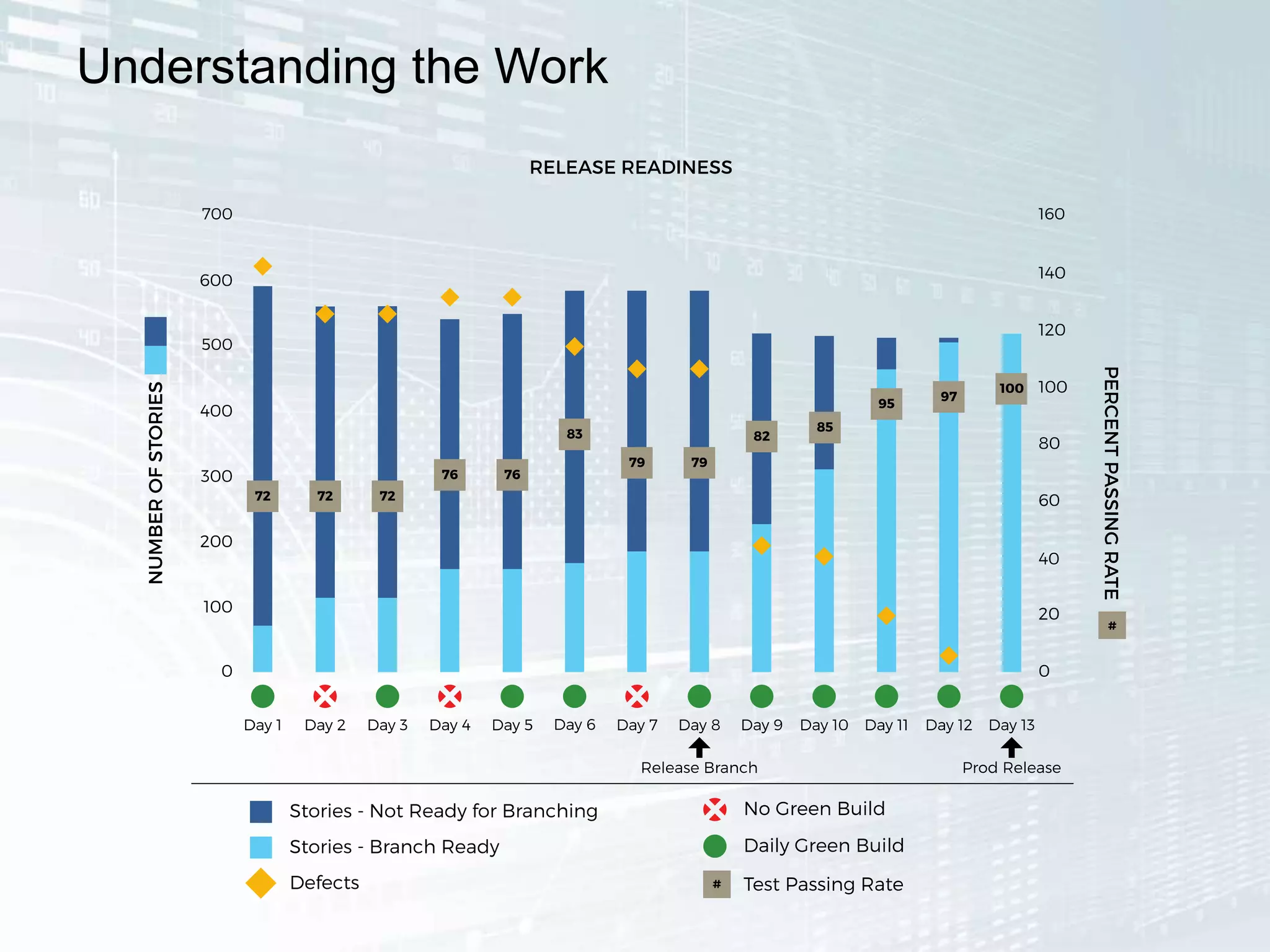
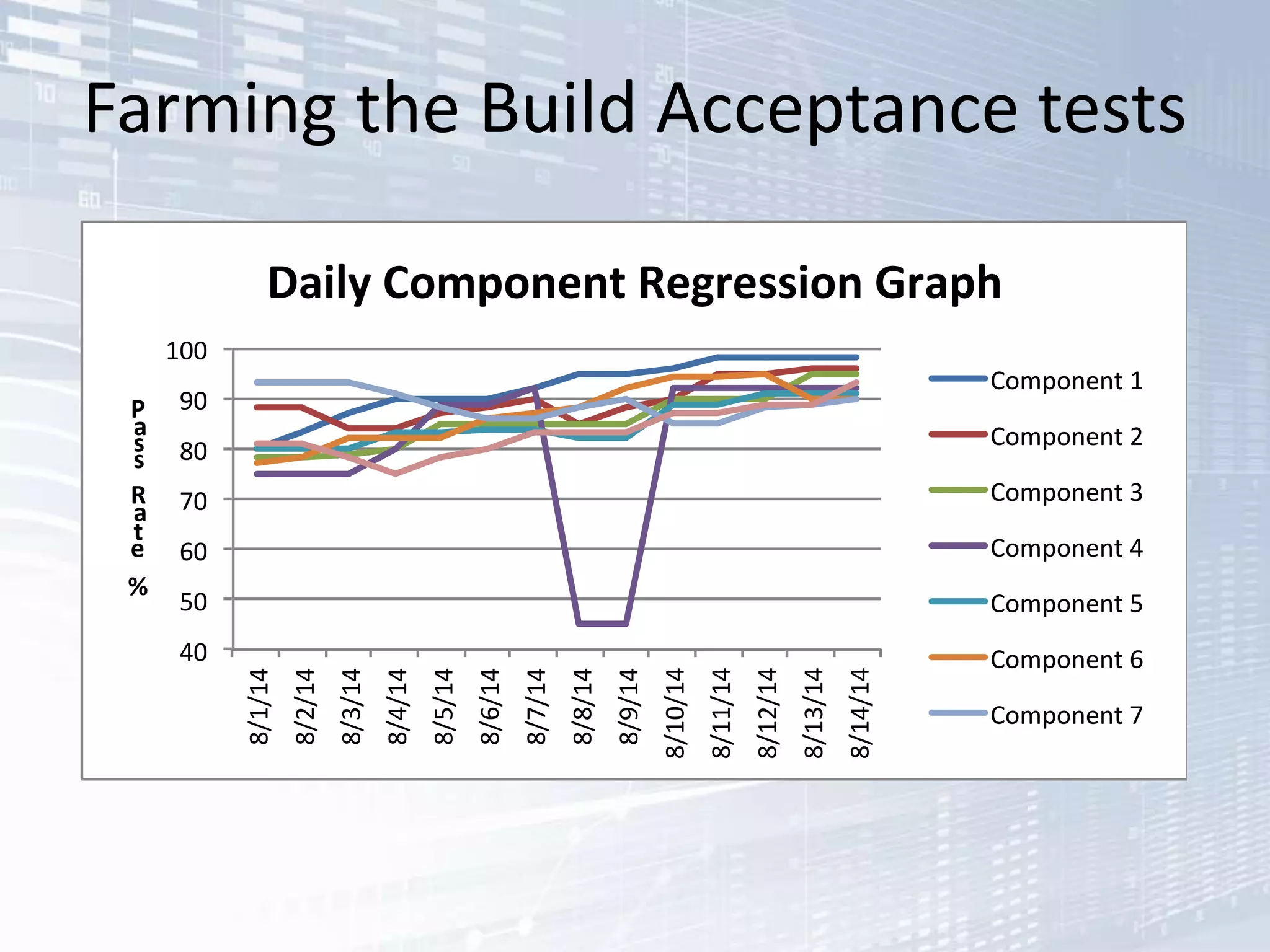
The document outlines the successful application of DevOps and Agile principles at scale, significantly reducing development costs from $100 million to $55 million annually, and increasing product development capacity by 140%. It emphasizes continuous improvement, the importance of feedback, and enhancing deployment stability, while also highlighting the cultural shifts necessary within organizations to achieve these objectives. Ultimately, it showcases the transformation leading to a substantial increase in innovation capacity from approximately 5% to 40%.