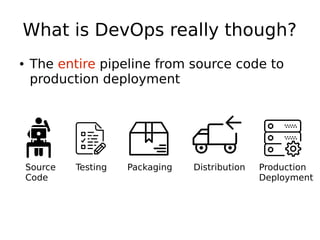
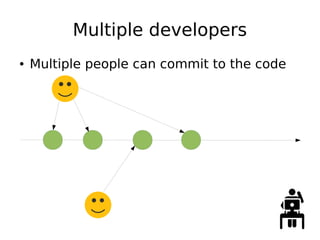
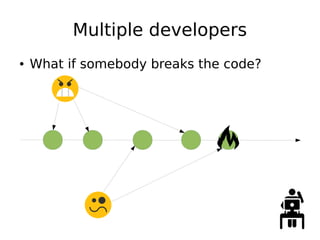
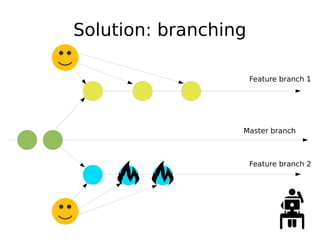
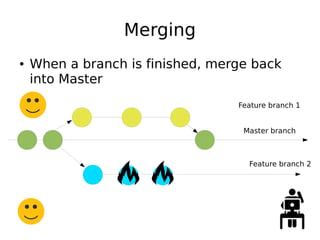
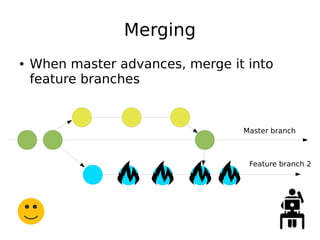
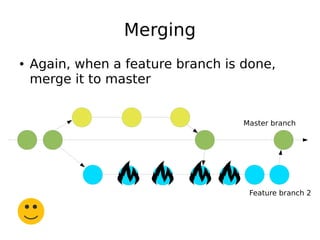
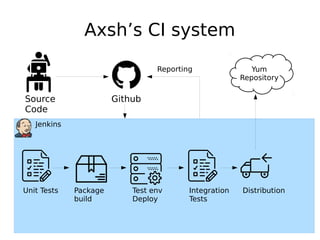
DevOps aims to streamline the process from writing code to deploying applications by encouraging collaboration between developers and operations teams. It utilizes tools that automate the integration, testing and deployment of code changes. The key aspects are using version control systems like Git for code management, branching to allow parallel work without disrupting the main code, and continuous integration pipelines that automatically build, test and deploy code changes. This helps catch bugs early and allows rapid yet stable releases.