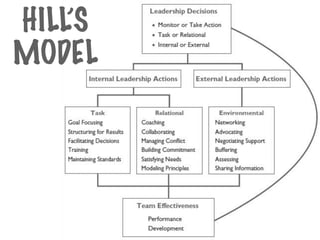
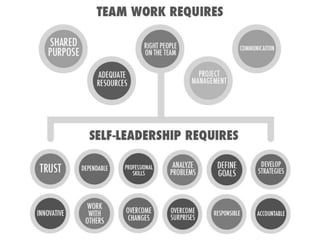
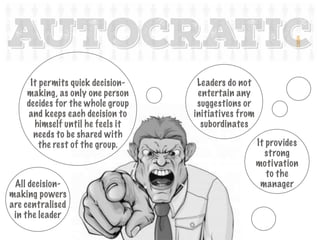
Definitions of leadership are varied but it involves influencing others. It is a reciprocal relationship where leaders and followers influence each other. Self-leadership involves intentionally influencing one's own thinking, feelings, and behaviors to achieve goals. Becoming a self-leader through behaviors like self-awareness and goal-setting benefits both individuals and organizations. There are different leadership styles such as autocratic, where all power is centralized; democratic, where decisions are shared; and laissez-faire, where subordinates have freedom. Narcissistic leadership prioritizes the leader over group members through arrogance and dominance. Toxic leadership leaves groups worse off. Task-oriented leaders focus on goals while relationship-oriented leaders focus on relationships and