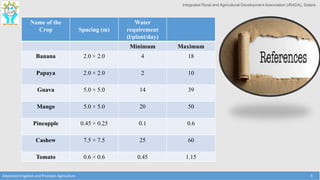
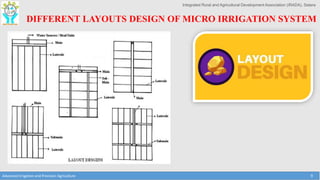
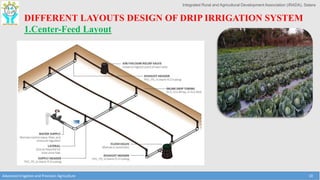
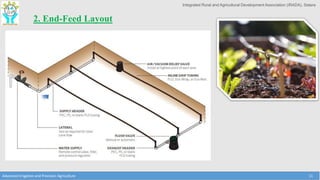
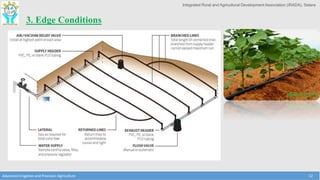
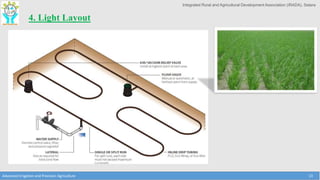
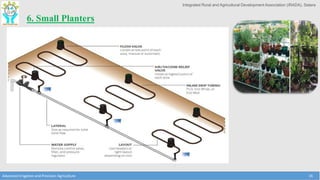
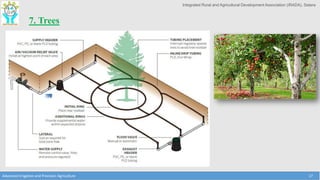
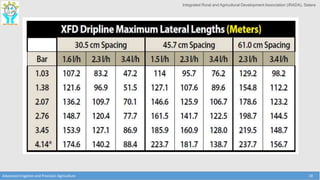
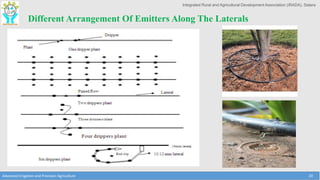
This document discusses the layout and design of drip irrigation systems. It describes the key steps in the design process, which include collecting data on water resources, land, climate and crops. It also covers computing peak crop water requirements, selecting appropriate emitters, and hydraulically designing the pipe network and determining the required pump horsepower. The document provides examples of different drip irrigation system layouts and considerations for selection of emitters and arrangement along laterals. It aims to explain how to plan and design drip irrigation systems for uniform crop irrigation while minimizing costs.