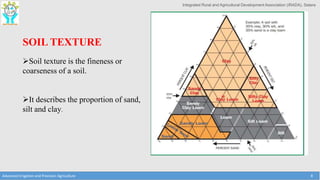
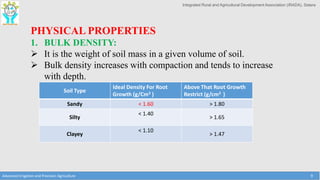
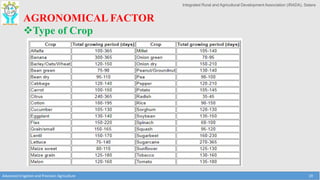
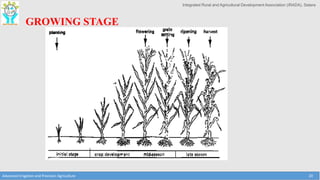
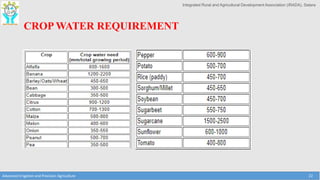
This document provides an overview of factors that must be considered for irrigation planning and management. It discusses the importance of understanding soil properties, water sources, topography, agronomic needs, and climate. Key factors that must be assessed include soil texture, structure, and physical properties; water quality and source type; slope and contours; crop water requirements based on type, growth stage, and spacing; and temperature, rainfall, and evaporation. Both soil and water testing are important to evaluate nutrient needs and water quality for effective irrigation. Understanding these primary data elements is essential for precision agriculture and maximizing the benefits of irrigation.