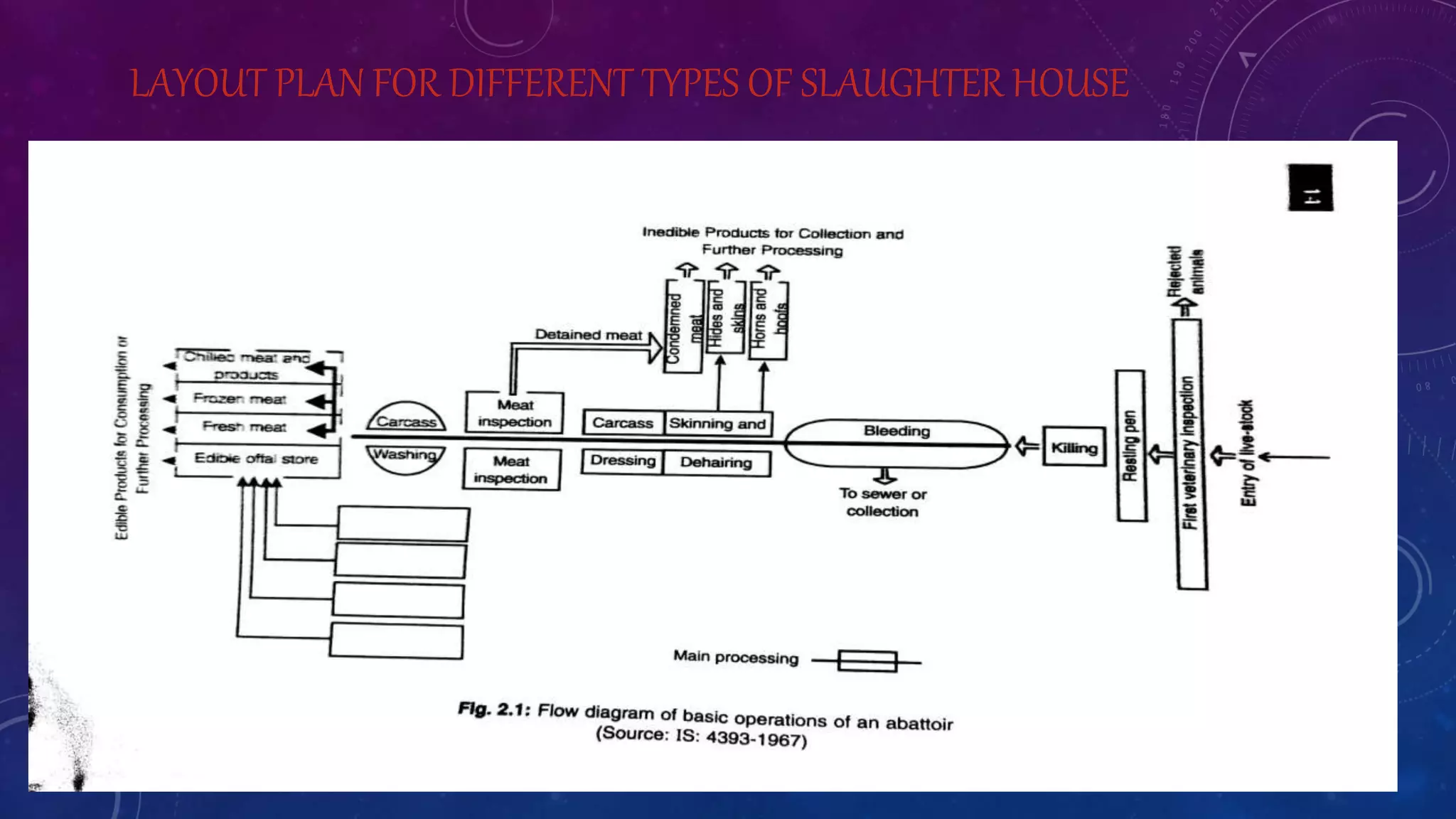
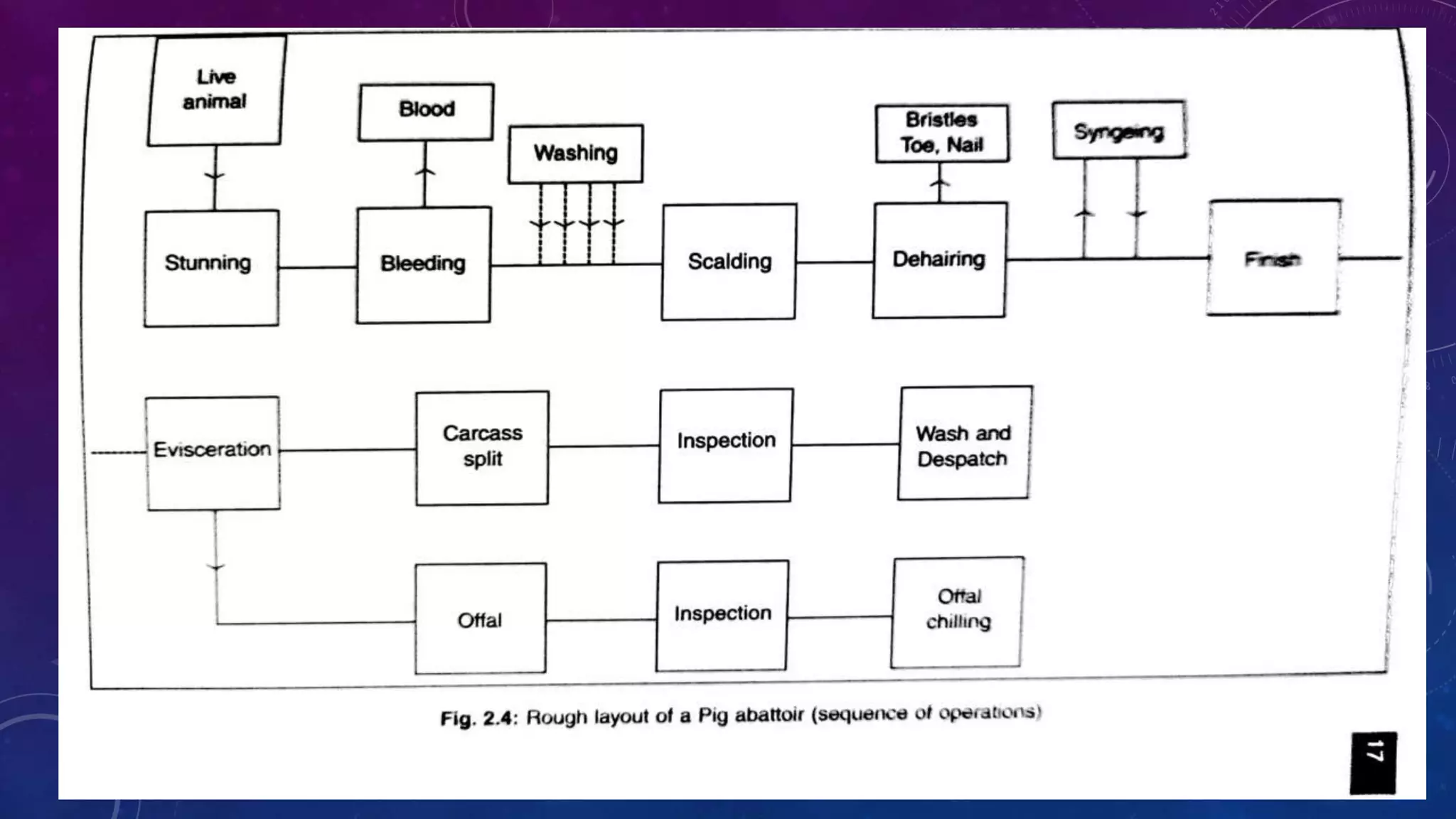
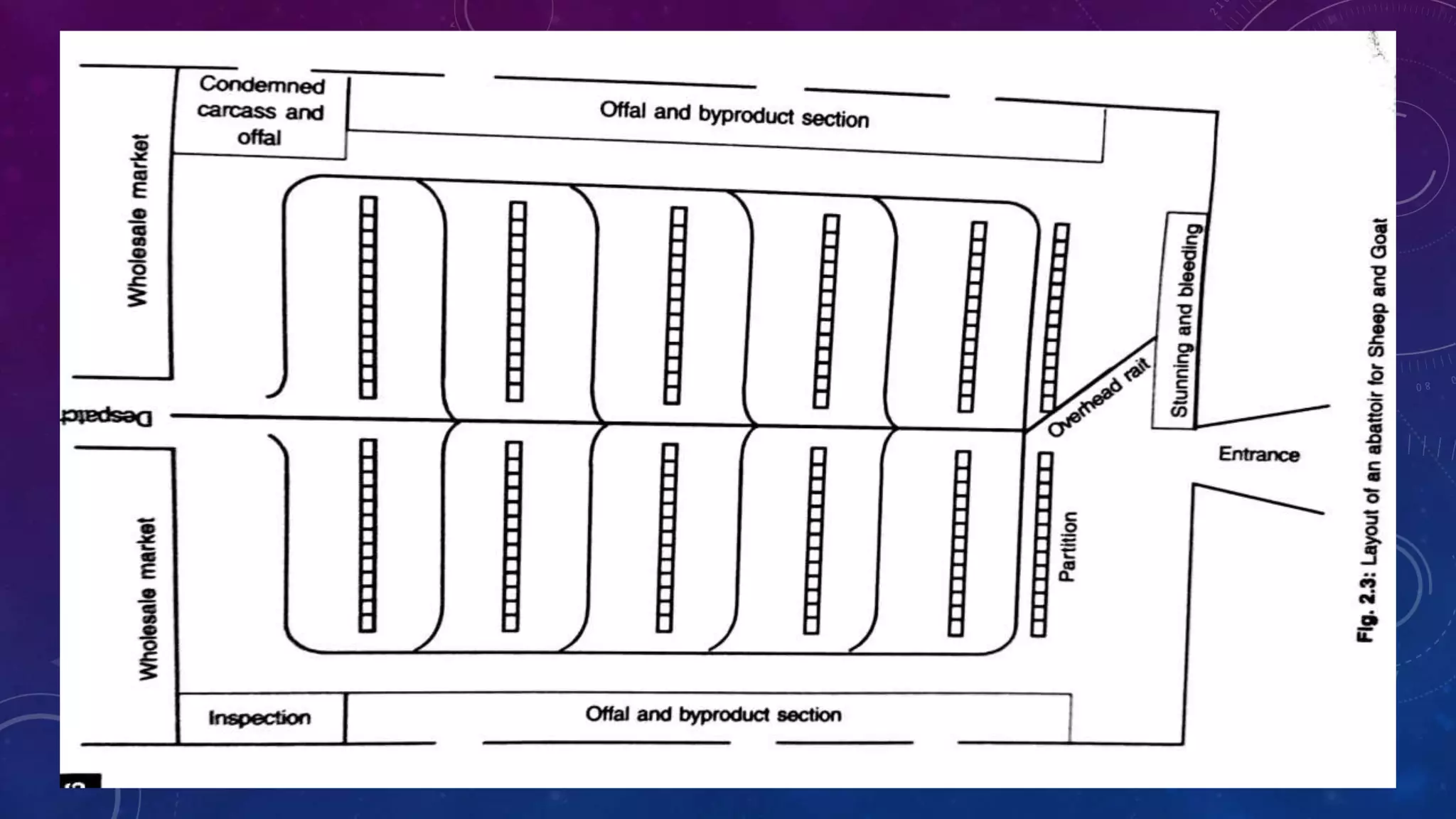
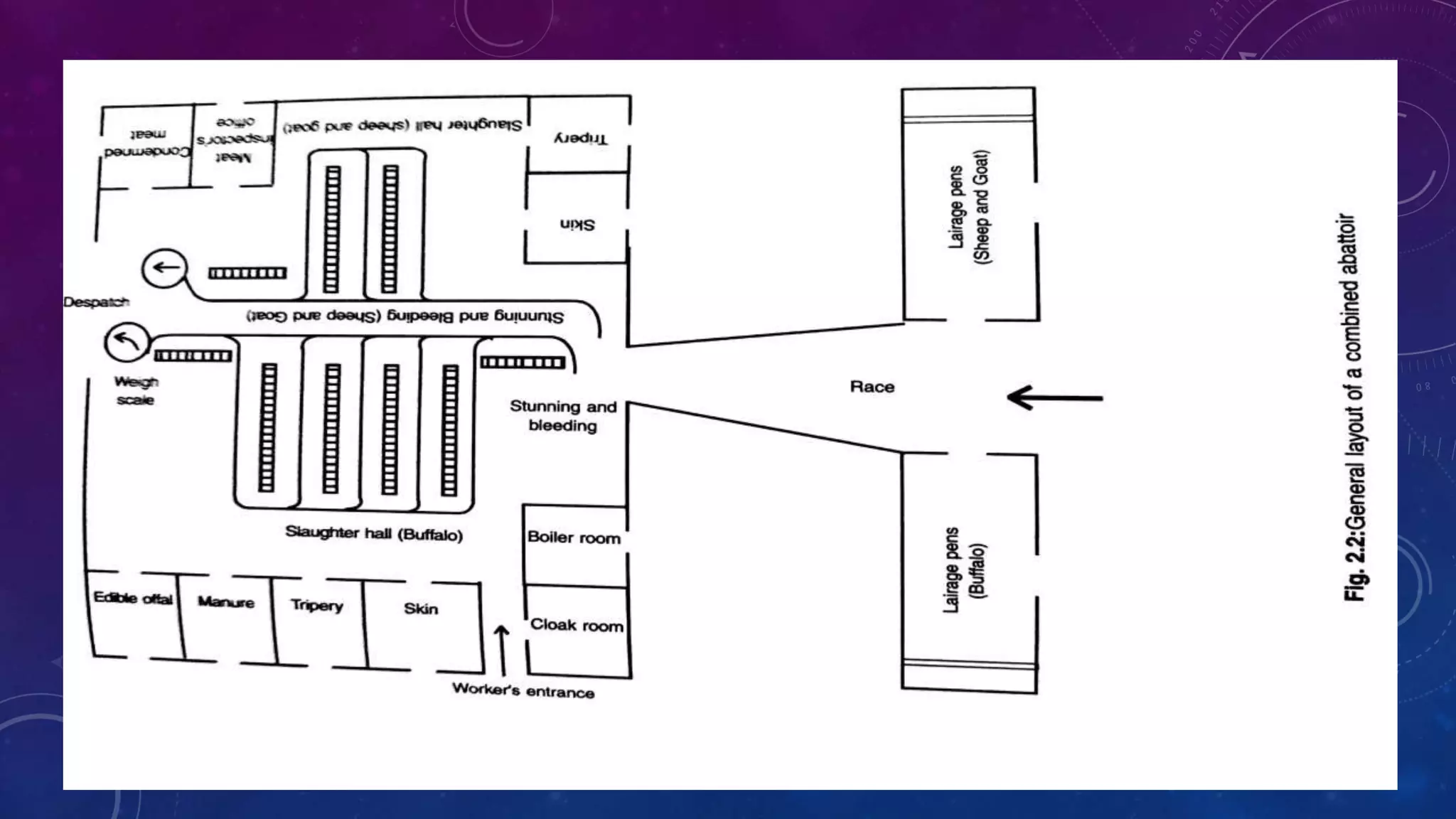
The document outlines the layout design and essential components of a modern abattoir, detailing its engineering aspects, site selection criteria, and operational considerations for effective animal slaughter and waste management. It emphasizes the importance of social acceptance, specialized facilities, and adherence to hygiene standards. Additionally, it provides specifications for the physical design, including minimum space requirements and height regulations for different areas within the slaughterhouse.