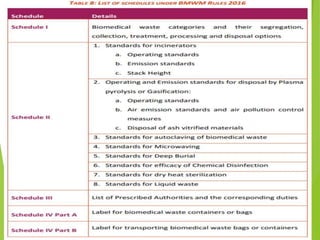
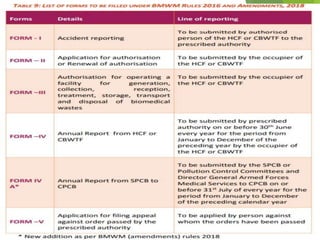
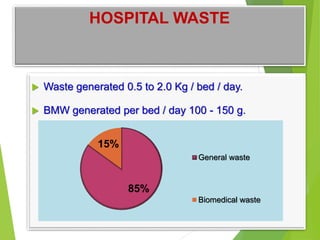
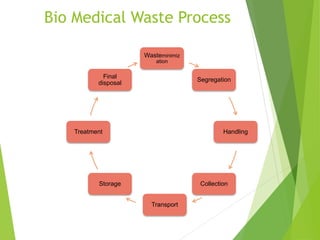
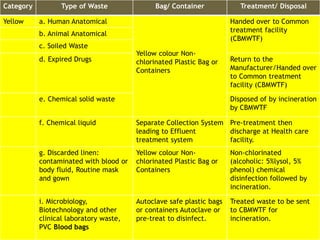
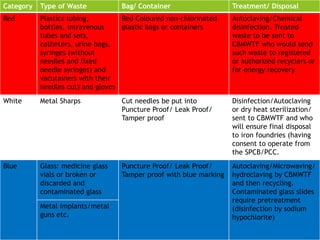
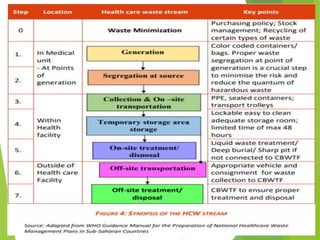
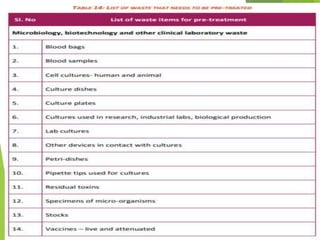
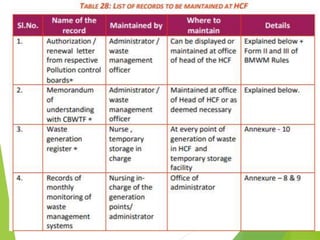
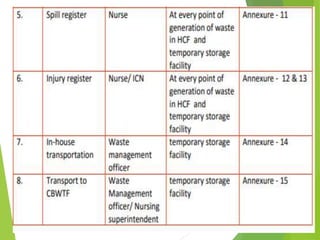
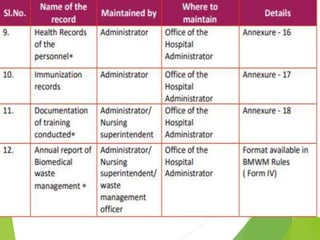
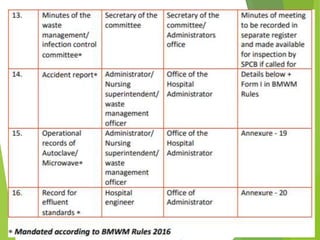
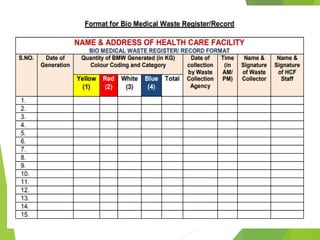
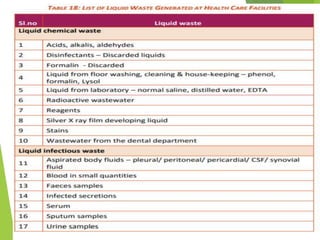
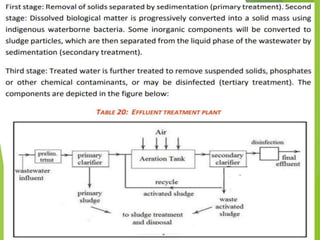
The Biomedical Waste Management Rules 2016, amended in 2018 and 2019, define biomedical waste and outline responsibilities and procedures for healthcare facilities regarding its management. Key provisions include segregation, safe storage, transportation, treatment, and disposal methods for different types of waste, as well as establishing accountability for violations which can result in legal actions. The rules emphasize the importance of minimizing hazardous waste and implementing specific protocols for handling and tracking biomedical waste effectively.