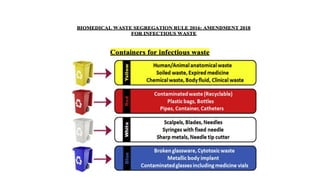
The document discusses biomedical waste management rules established in 2016, outlining the responsibilities of healthcare facilities in the handling of medical waste. Key features include the classification of waste into four categories, strict guidelines for treatment and disposal, and protocols for training healthcare workers. The rules emphasize safe storage practices and the establishment of a bar-code system for tracking waste, with various reporting requirements to ensure compliance with environmental standards.