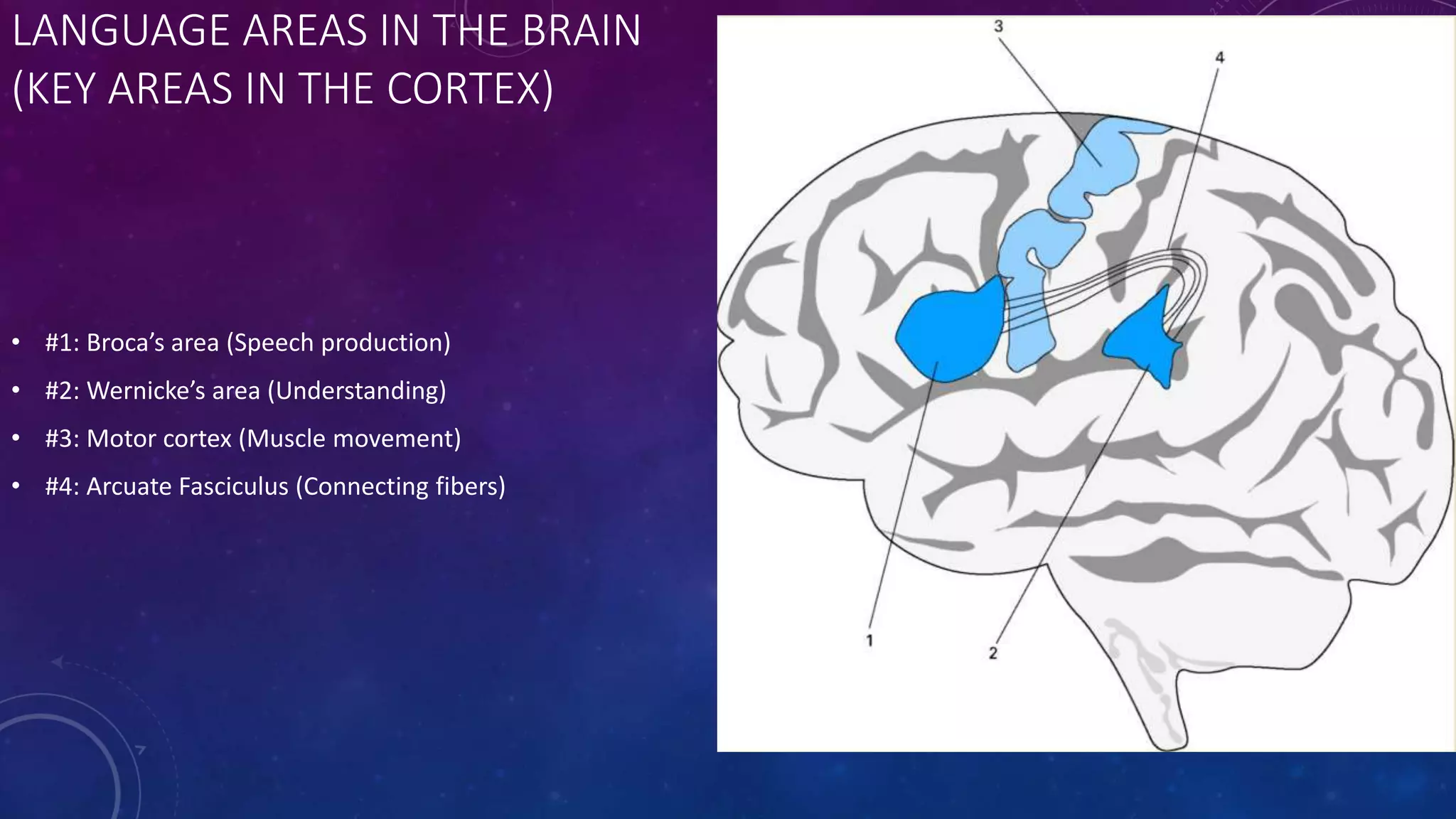
The document discusses language areas in the brain and different types of aphasia. It outlines four key language areas in the cortex: Broca's area for speech production, Wernicke's area for understanding, the motor cortex for muscle movement, and the arcuate fasciculus for connecting fibers. It also notes that the left hemisphere is dominant for language while the right hemisphere is for multi-tasking, visual-spatial skills, emotions, and music. There are three main types of aphasia: Broca's aphasia affects speech production, Wernicke's aphasia causes fluent but nonsensical speech, and the critical period hypothesis suggests there is a small window from ages 0-