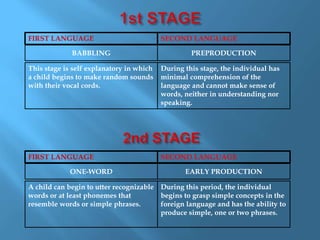
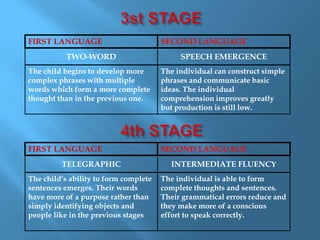
Language acquisition is the process by which humans develop the ability to understand and use language. There have been several theories that attempted to explain this process, including Skinner's theory of reinforcement and Chomsky's theory of universal grammar. Contemporary research has led to hypotheses such as the acquisition-learning distinction, the natural order hypothesis, the monitor hypothesis, the input hypothesis, and the affective filter hypothesis. Language acquisition occurs in stages from babbling to one-word utterances to telegraphic speech and finally fluency. First and second language acquisition follow similar stages but second language acquisition takes longer to progress through the stages.