Here are the definitions requested:
1. Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. A pollutant is a substance or thing that pollutes.
2. Land pollution is the accumulation of solid wastes and contaminants on land that cause harm to the environment or human health.
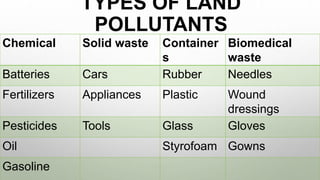
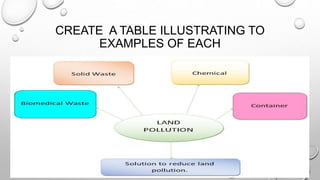
3. The main land pollutants are chemicals, solid waste, containers, and biomedical waste.
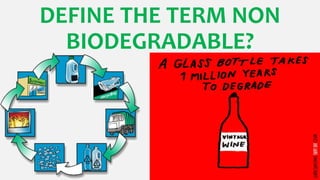
4. Biodegradable wastes come from plant or animal sources and break down naturally over time through decomposition. Non-biodegradable wastes like plastics do not break down and can persist for thousands of years.
5. Methods to control land pollutants include