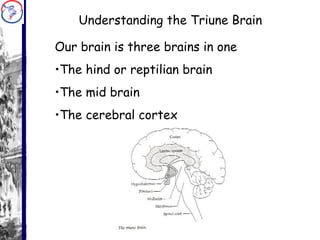
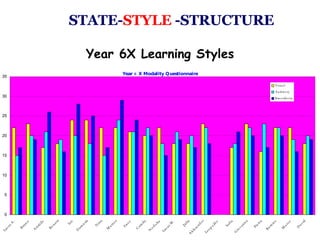
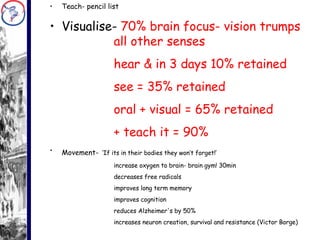
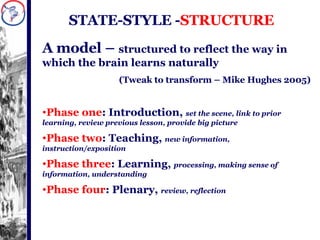
One School’s Journey from Good to Excellent outlines a school's process of improving from good to excellent through professional development and adopting a whole-school learning approach. The school underwent initial training in 2007 and 2009 and developed a roadmap. They then implemented whole-school continuous professional development focusing on learning styles, partnerships, observation, and management. Quotes emphasize the importance of growth, change, and learning. Photos show teachers collaborating on lesson planning, assessment, and developing their professional learning community.