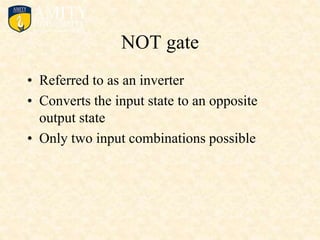
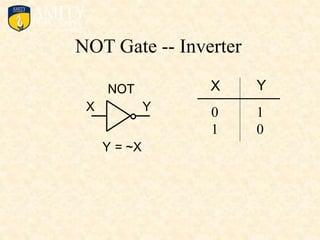
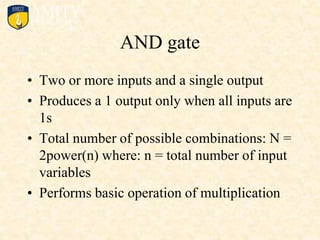
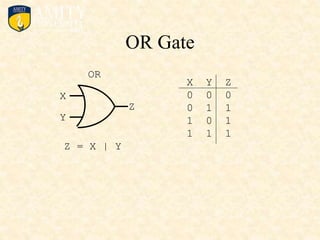
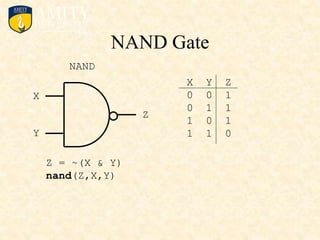
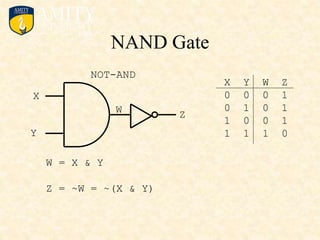
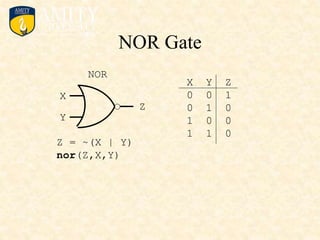
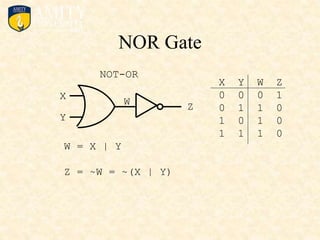
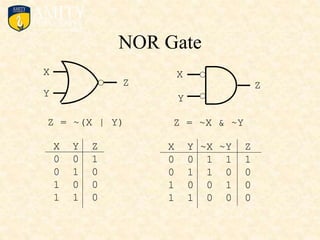
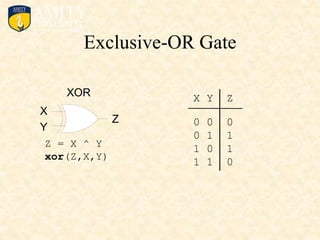
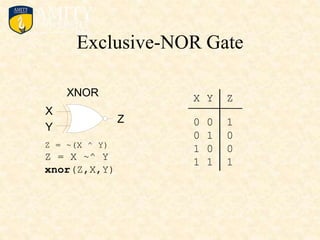
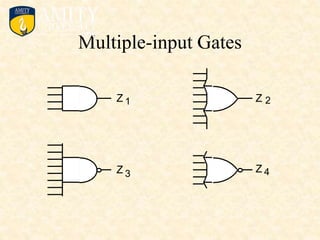
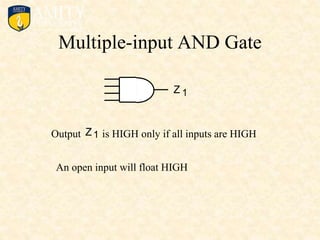
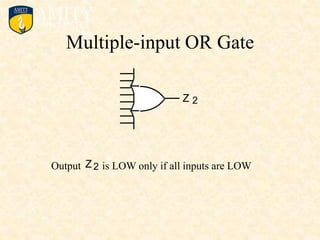
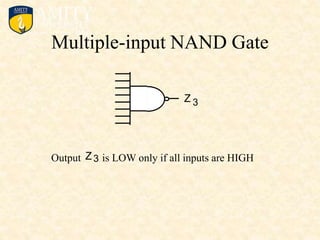
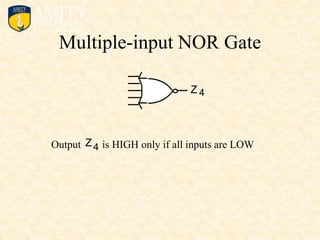
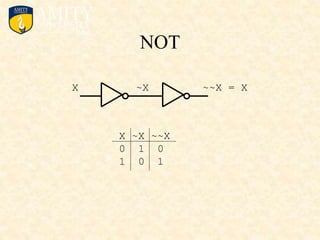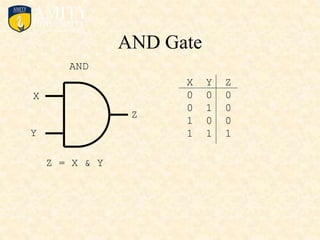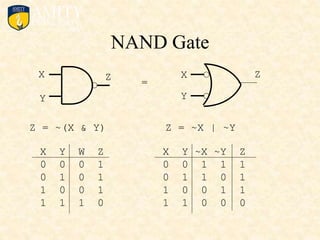This document outlines the syllabus for a Digital Electronics & Computer Organization Lab course. The syllabus includes simulations of basic logic circuits like half adders, full adders, and arithmetic logic units using ORCAD software. It also covers the study of the 8085 microprocessor instruction set and basic logic gates like AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR gates. Multiple-input logic gates are also discussed.