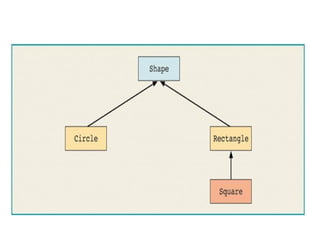
This document discusses inheritance in Java programming. It defines inheritance as an "is-a" relationship between a superclass and subclass where the subclass is a more specific version of the superclass. The key concepts covered are method overloading, which allows methods to perform different tasks based on parameters; method overriding, which provides different implementations of methods in subclasses; and dynamic method dispatch, which determines which version of an overridden method to execute based on the object type at runtime.











![class OverloadDemo
{
public static void main (String arr[])
{
Area11 ar= new Area11();
ar.area(10);
ar.area(10,5);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l7-inheritance-150408005400-conversion-gate01/85/L7-inheritance-13-320.jpg)



![class OverrideDemo
{
public static void main(String arr[])
{
Override o = new Override();
o.display();
Override1 o1 = new Override1();
o1.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l7-inheritance-150408005400-conversion-gate01/85/L7-inheritance-17-320.jpg)


![class Dispatch {
public static void main(String args[]) {
A a = new A(); // object of type A
B b = new B(); // object of type B
C c = new C(); // object of type C
A r; // obtain a reference of type A
r = a; // r refers to an A object
r.callme(); // calls A's version of callme
r = b; // r refers to a B object
r.callme(); // calls B's version of callme
r = c; // r refers to a C object
r.callme(); // calls C's version of callme
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l7-inheritance-150408005400-conversion-gate01/85/L7-inheritance-20-320.jpg)
