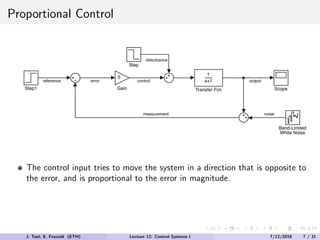
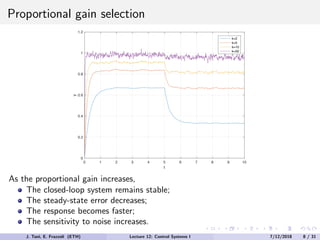
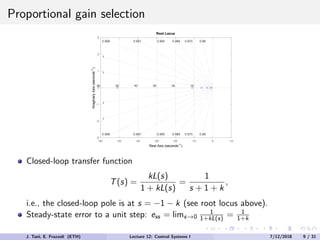
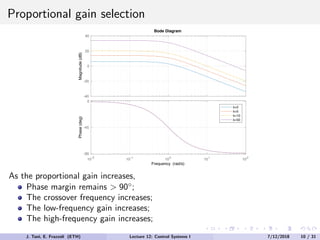
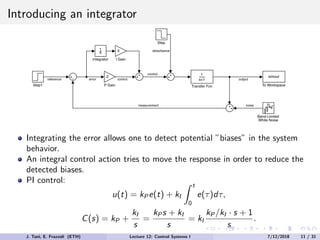
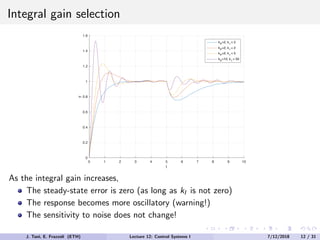
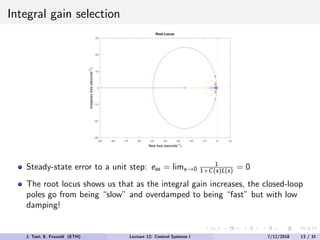
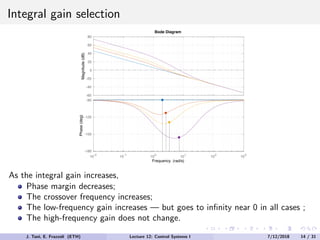
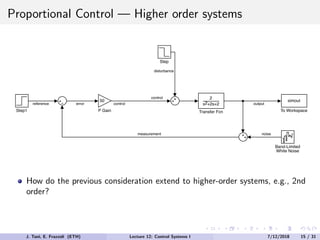
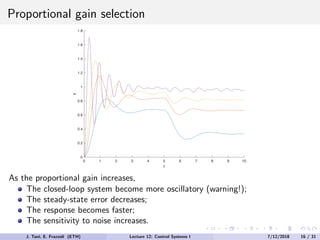
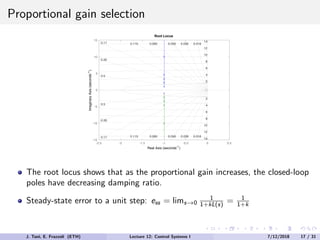
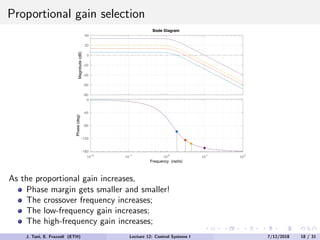
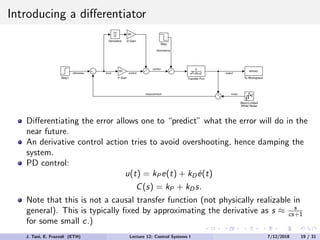
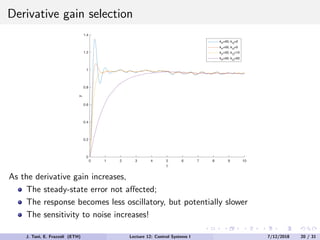
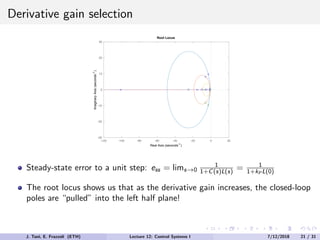
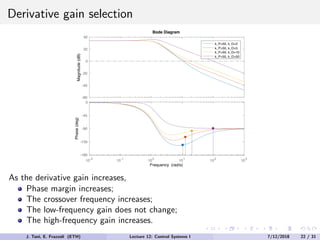
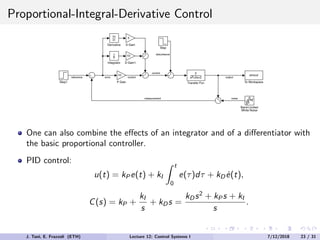
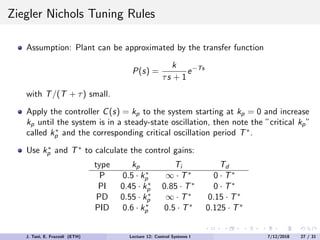
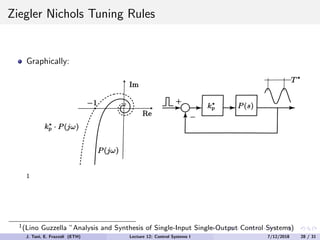
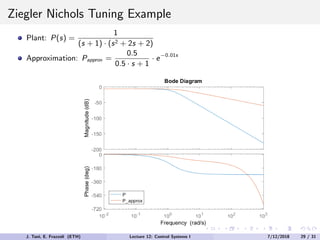
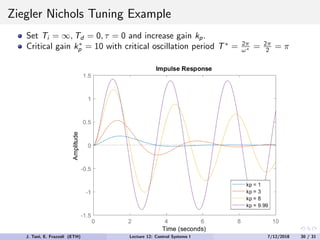
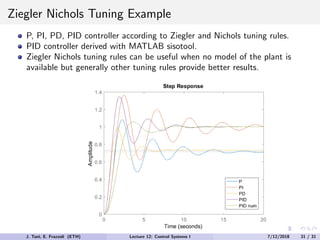
The document discusses PID control, which combines proportional, integral and derivative control actions. It explains each control action and its effects on the system response and stability. Proportional control reduces steady-state error but can cause oscillation. Integral control eliminates steady-state error but also causes oscillation. Derivative control reduces overshoot and damping but increases sensitivity to noise. PID controllers combine these actions to achieve desired response without oscillations or steady-state error. The document provides examples of tuning the gains of each action.