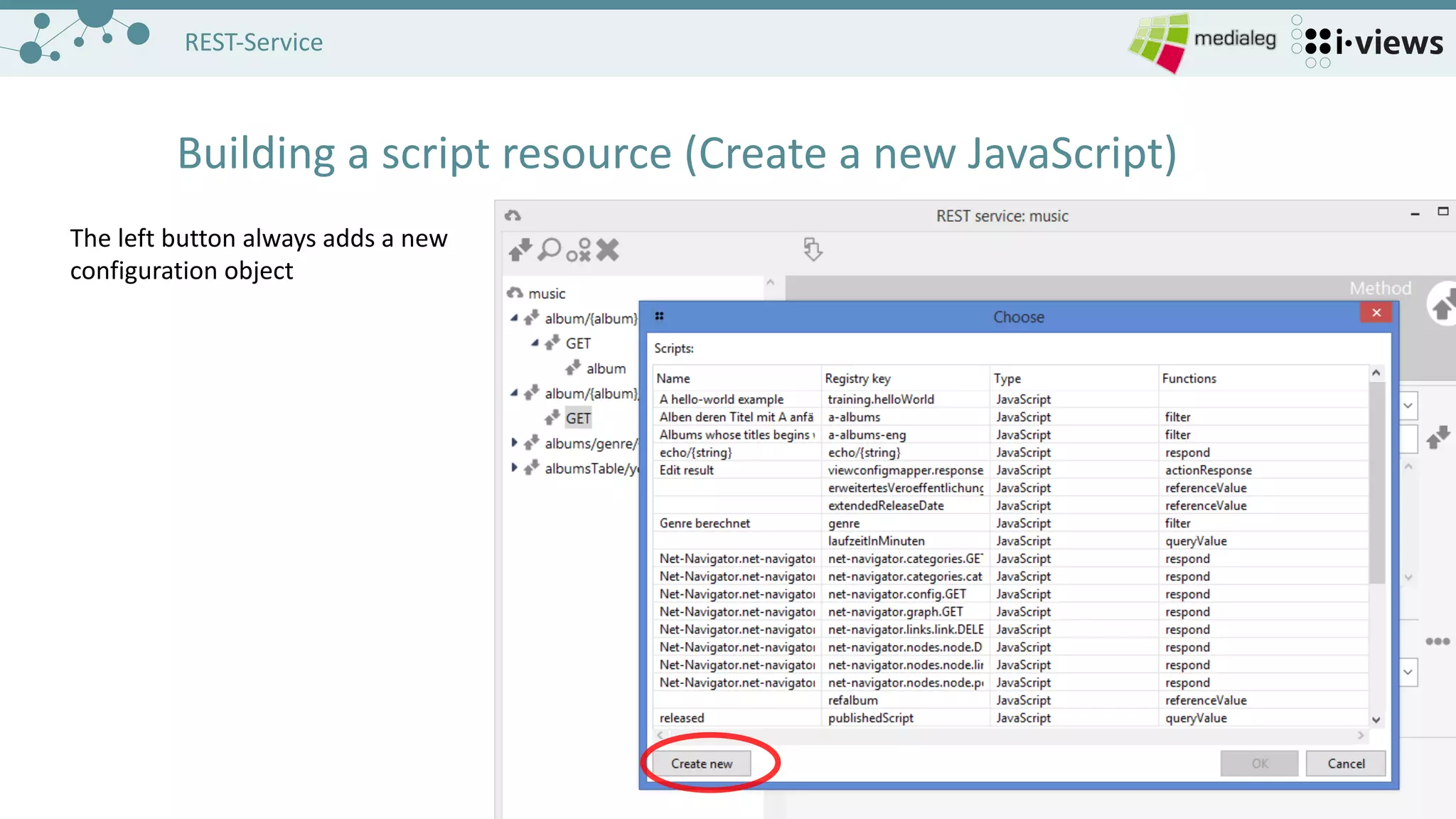
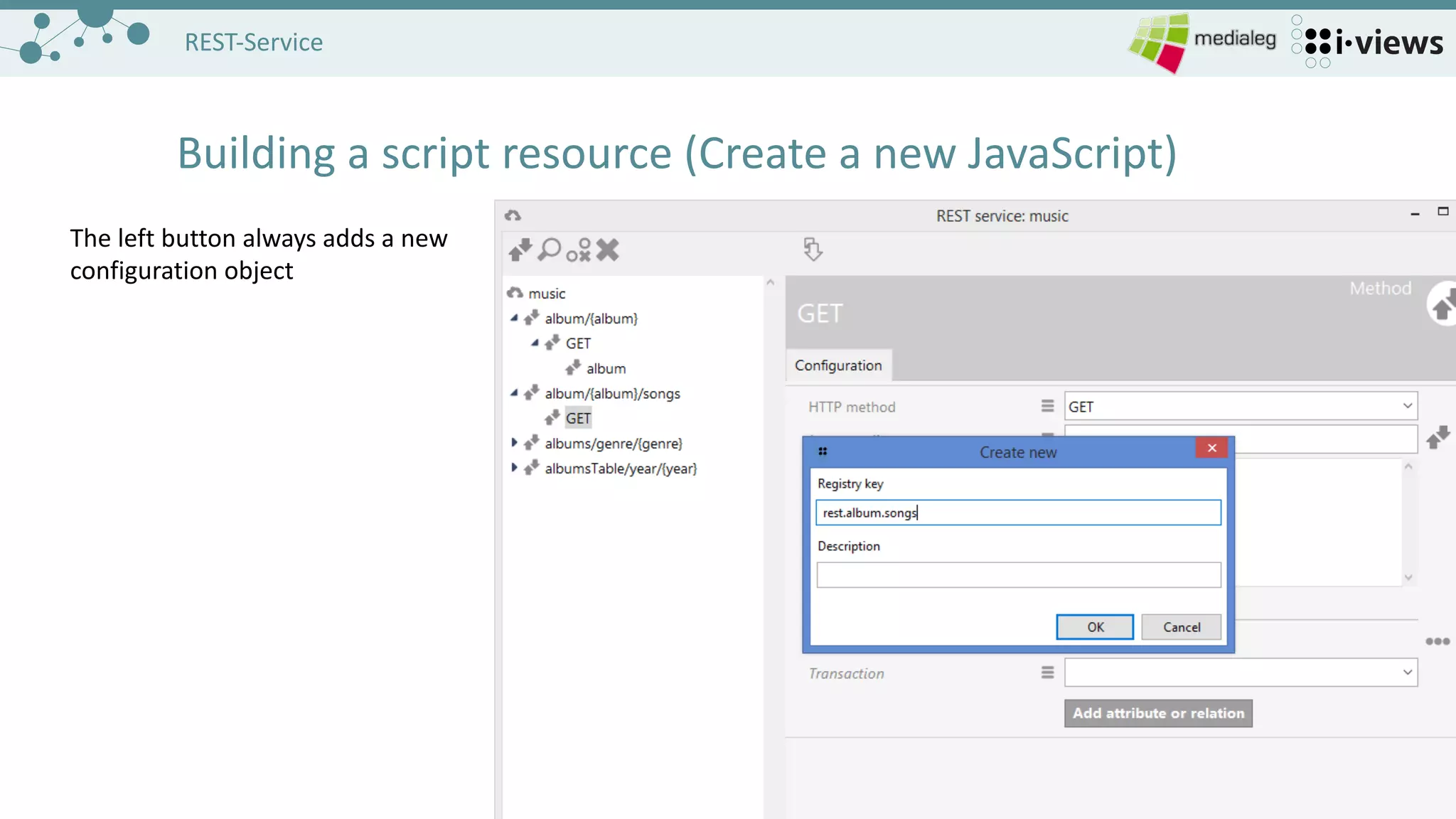
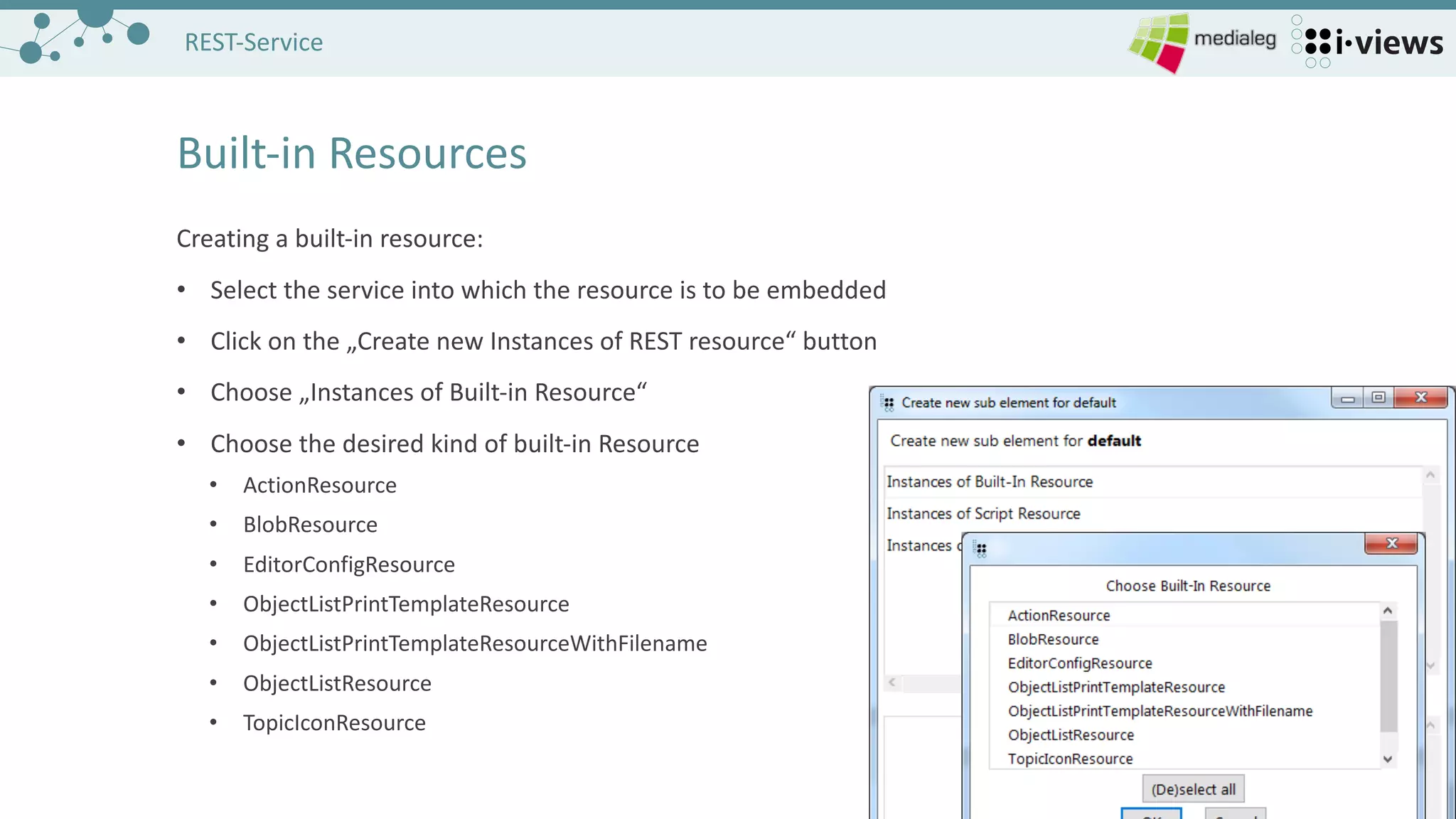
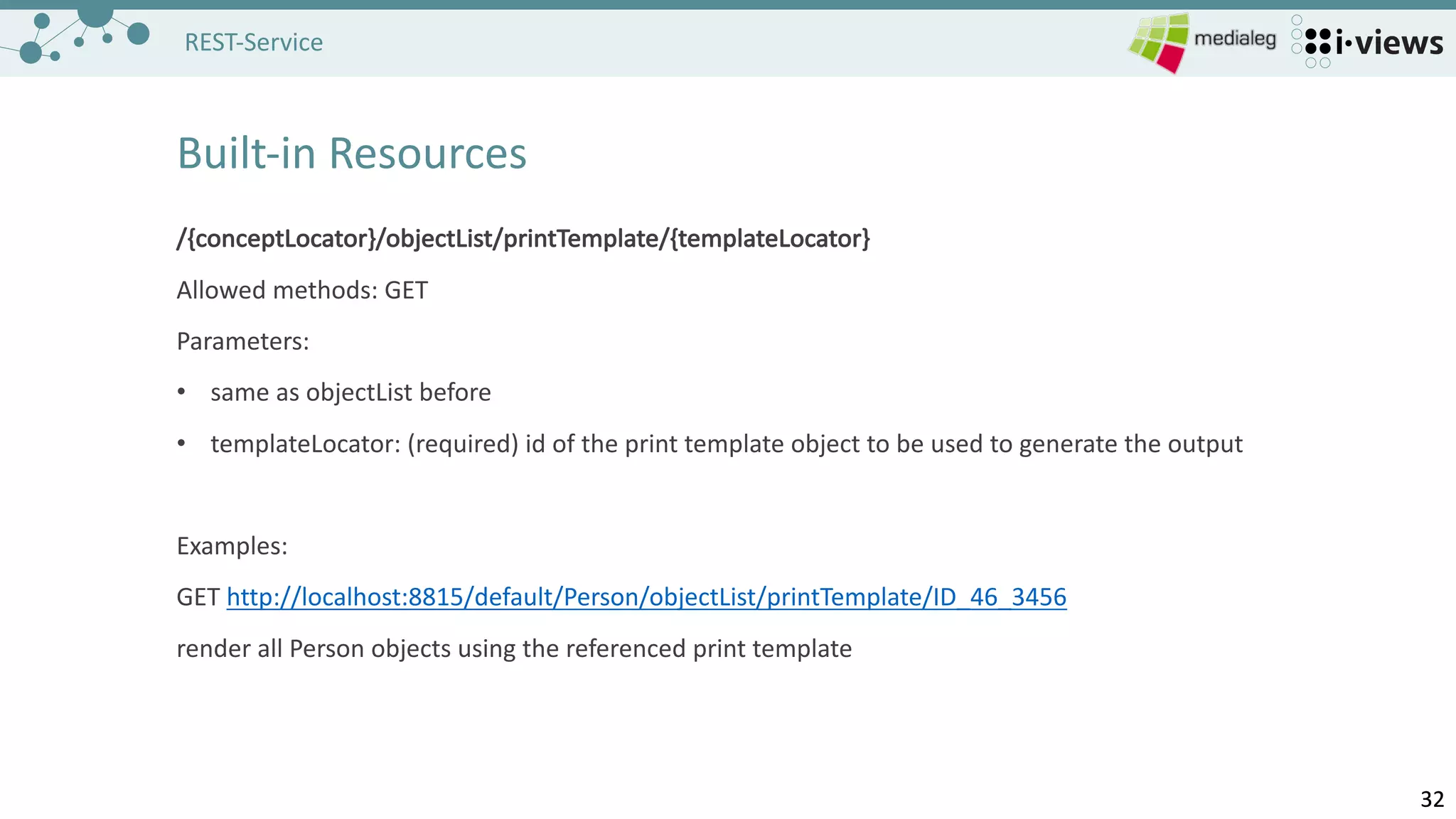
The document outlines the setup and configuration of REST services for accessing and editing a semantic graph database. It covers the necessary components, including server configuration, service and resource creation, and methods for handling HTTP requests. It also provides examples for built-in resources and homework tasks to reinforce the learning of REST service implementation.





![77
REST-Service
Set-up issues
• Configuration of REST-bridges: configuration file bridge.ini is needed to specify which services are
going to be provided by the application
• Define the host [and port] of the server of the semantic graph database
• Define the name of the volume to be accessed
• Define the port over which the services will be available
• Define the services this instance of REST-bridge is going to serve](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l12restservice-170407072746/75/L12-REST-Service-7-2048.jpg)

![1010
REST-Service
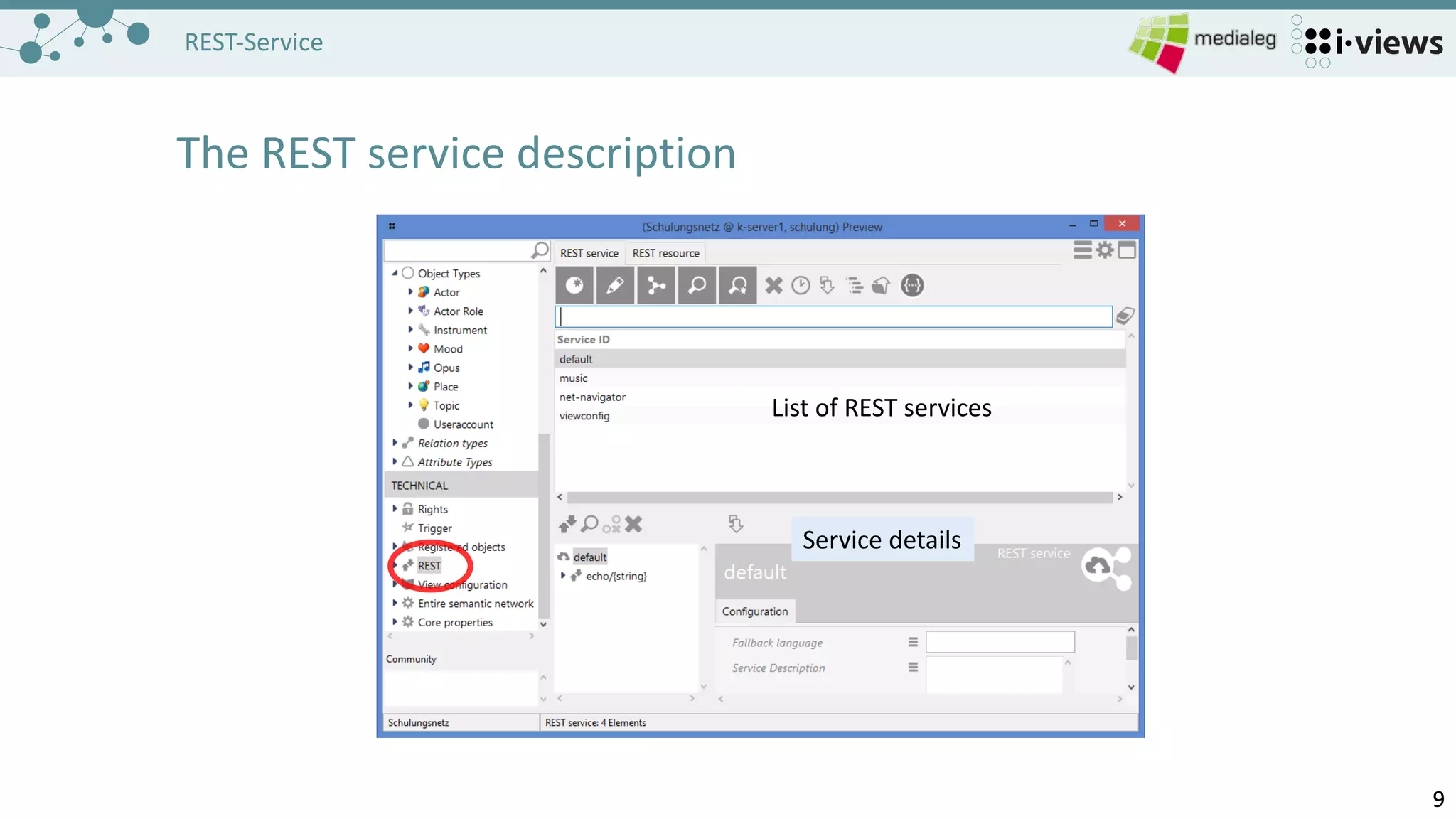
Building blocks (REST service)
- Collection of resources
- Start of the URL path
- Services are configured in the
bridge.ini
[Default]
host=localhost
loglevel=10
[KHTTPRestBridge]
volume=Schulungsnetz
port=8815
services=music](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l12restservice-170407072746/75/L12-REST-Service-10-2048.jpg)