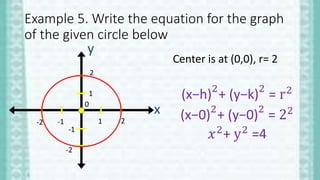
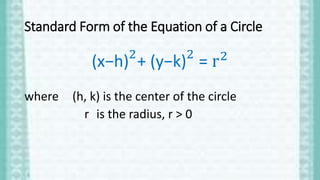
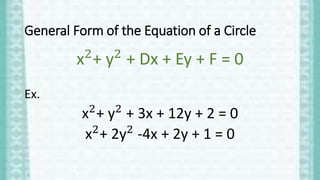Conic sections are shapes formed by the intersection of a plane and a double-napped cone. The four types of conic sections are circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas. A circle is defined as the set of all points equidistant from a fixed center point in a plane. The standard equation of a circle is (x-h)2 + (y-k)2 = r2, where (h,k) represents the center and r is the radius. This document provides examples of writing and graphing circle equations in standard and general form.



![Example 1. Determine the standard equation of
the circle given the coordinates of its center and
the length of its radius
a. center at (2, -3) and r= 3
(x−h)2
+ (y−k)2
= r2
(x−2)2
+ [y−(−3)]2
= 32
(x−2)2
+ (y+3)2
= 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1circle-230915032750-c102cfff/85/L1-Circle-pptx-7-320.jpg)
![Example 2. Given the standard form of the
equation below, find the coordinates of the center
and the radius.
a. (x+9)2
+ (y−1)2
= 25
Center is at (-9, 1) and r=5
(x+9)2
+ (y−1)2
= 25
[x− (−9)]2
+ (y−1)2
= 52](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1circle-230915032750-c102cfff/85/L1-Circle-pptx-8-320.jpg)