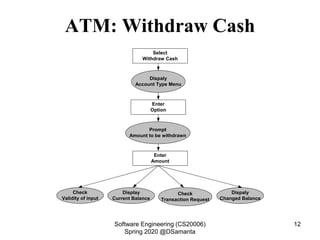
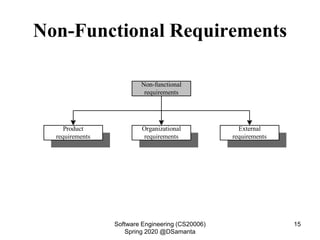
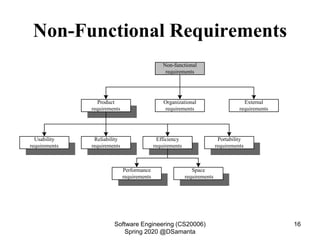
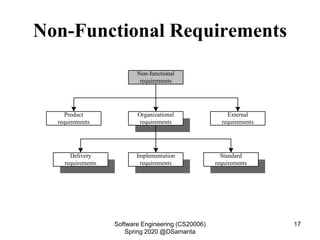
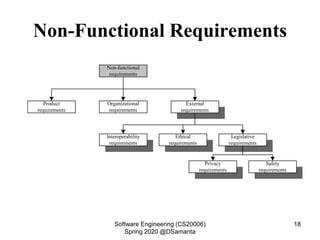
This document discusses requirement specification and system requirement specification (SRS) documents. It explains that SRS documents help avoid disputes by clearly outlining customer requirements. The document then provides templates for SRS documents, including sections for requirements gathering and analysis, functional requirements, non-functional requirements, and interface requirements. An example of functional requirements for an automated teller machine is also presented.