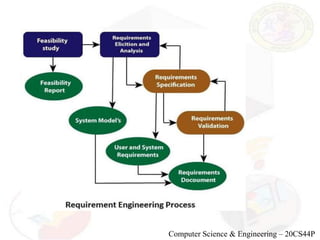
The document outlines the requirements engineering process, which consists of feasibility study, elicitation and analysis, specification, and validation. Each phase involves stakeholder interaction to discover, organize, and prioritize requirements while addressing conflicts. It emphasizes the importance of validating requirements to avoid costly errors during software development.