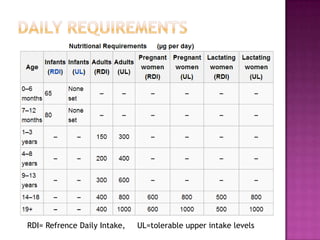
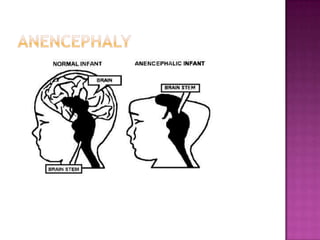
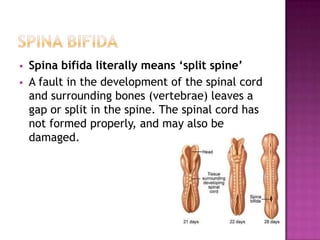
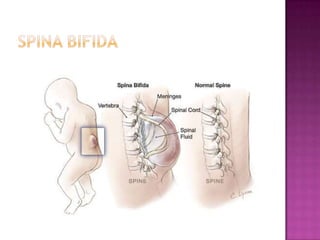
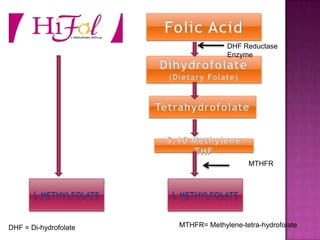
Folate, also known as vitamin B9, is a water-soluble vitamin found naturally in foods like leafy greens, fruits, beans and whole grains. It is essential for numerous bodily functions like DNA synthesis and repair. A lack of folate can cause health issues like megaloblastic anemia and neural tube defects in developing embryos. Symptoms of deficiency include diarrhea, weakness, nerve damage and cognitive declines. Anencephaly and spina bifida are neural tube defects where the brain and spinal cord do not properly form. Taking folic acid supplements before and during early pregnancy can help reduce the risk of spina bifida and other neural tube defects in babies. L-methylfolate is a biologically