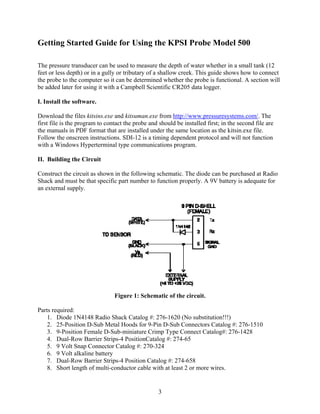
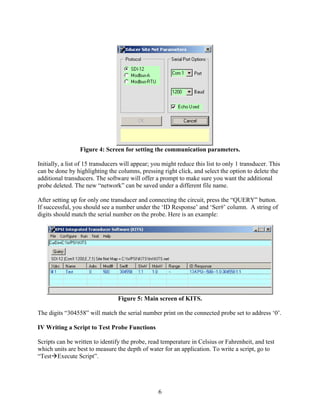
This document serves as a guide for using the KPSI transducer probe model 500, detailing software installation, circuit construction, probe reading, and script writing for probe function testing. It also includes calibration instructions, care guidelines for the probe, and a reference to using the probe with a Campbell CR205 datalogger. Key instructions are provided with accompanying figures for clarity and troubleshooting advice.