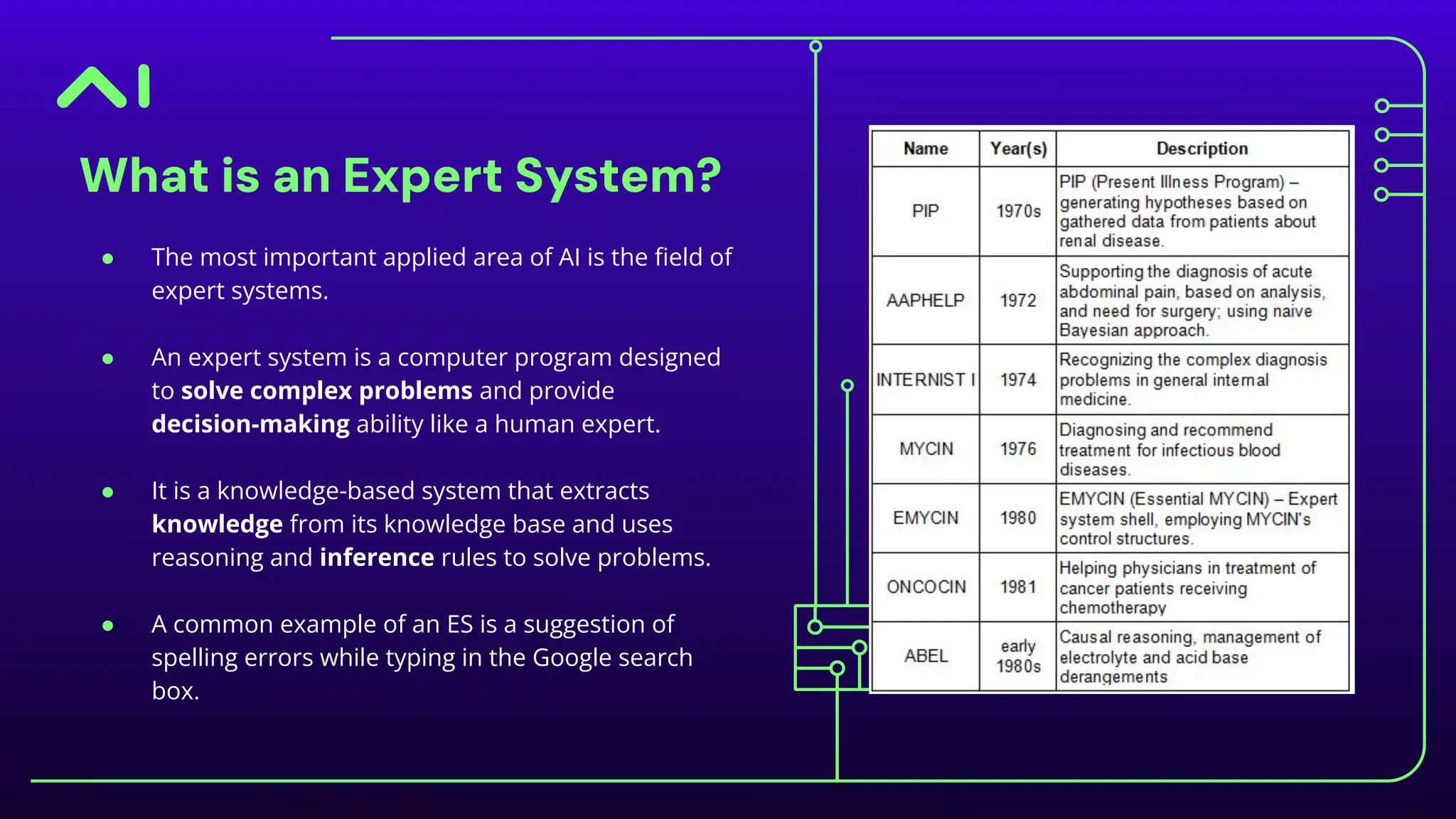
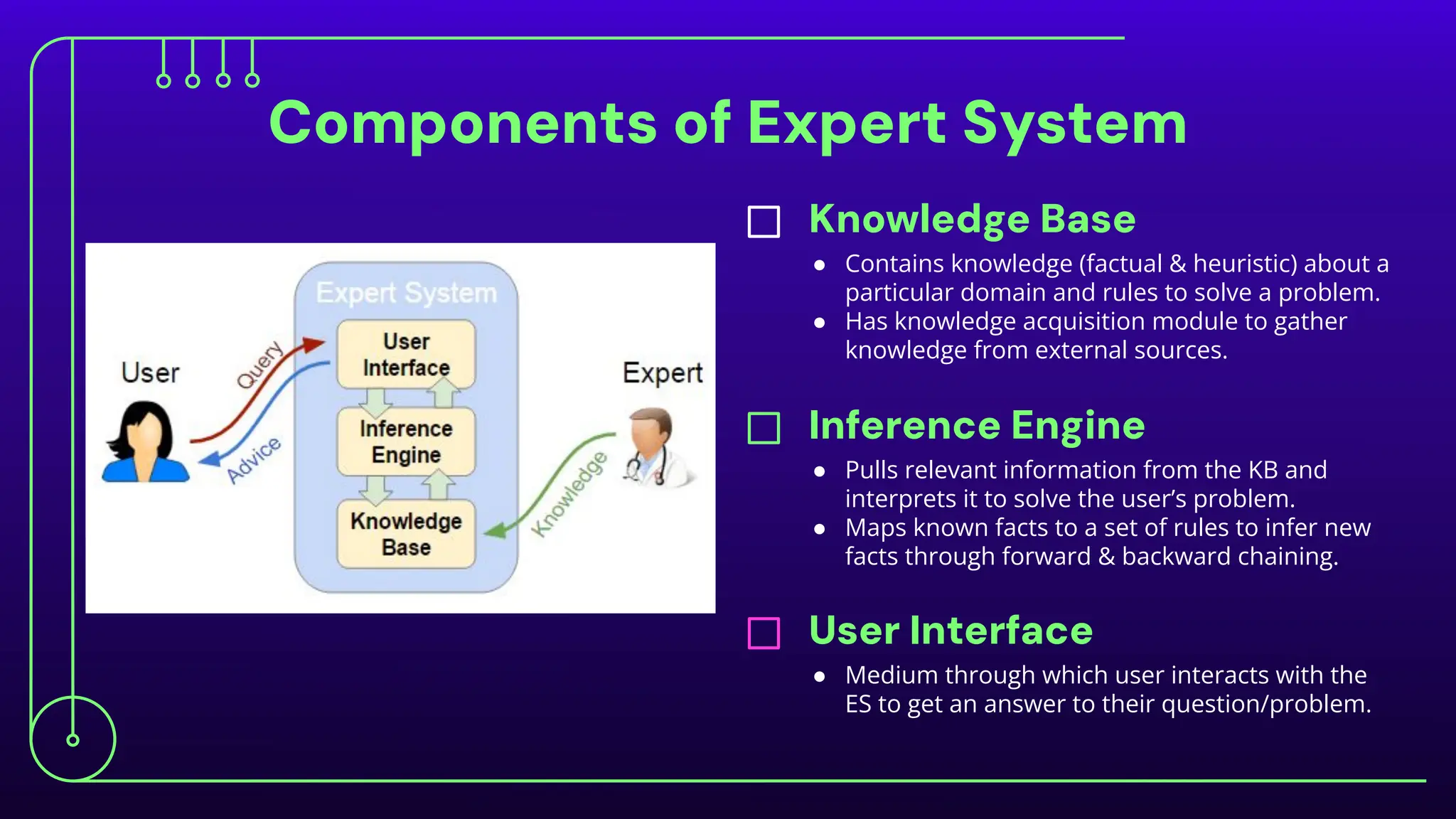
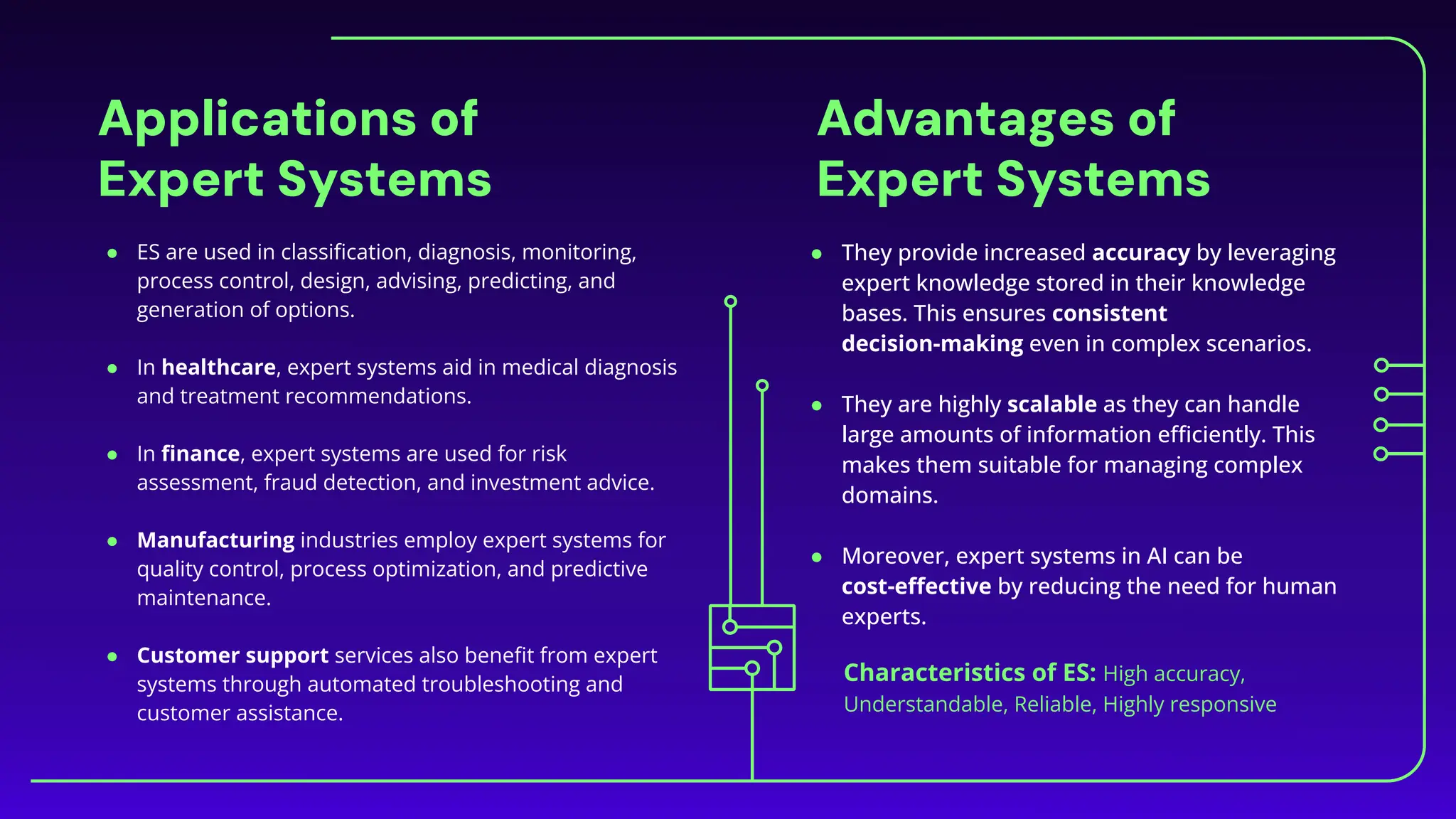
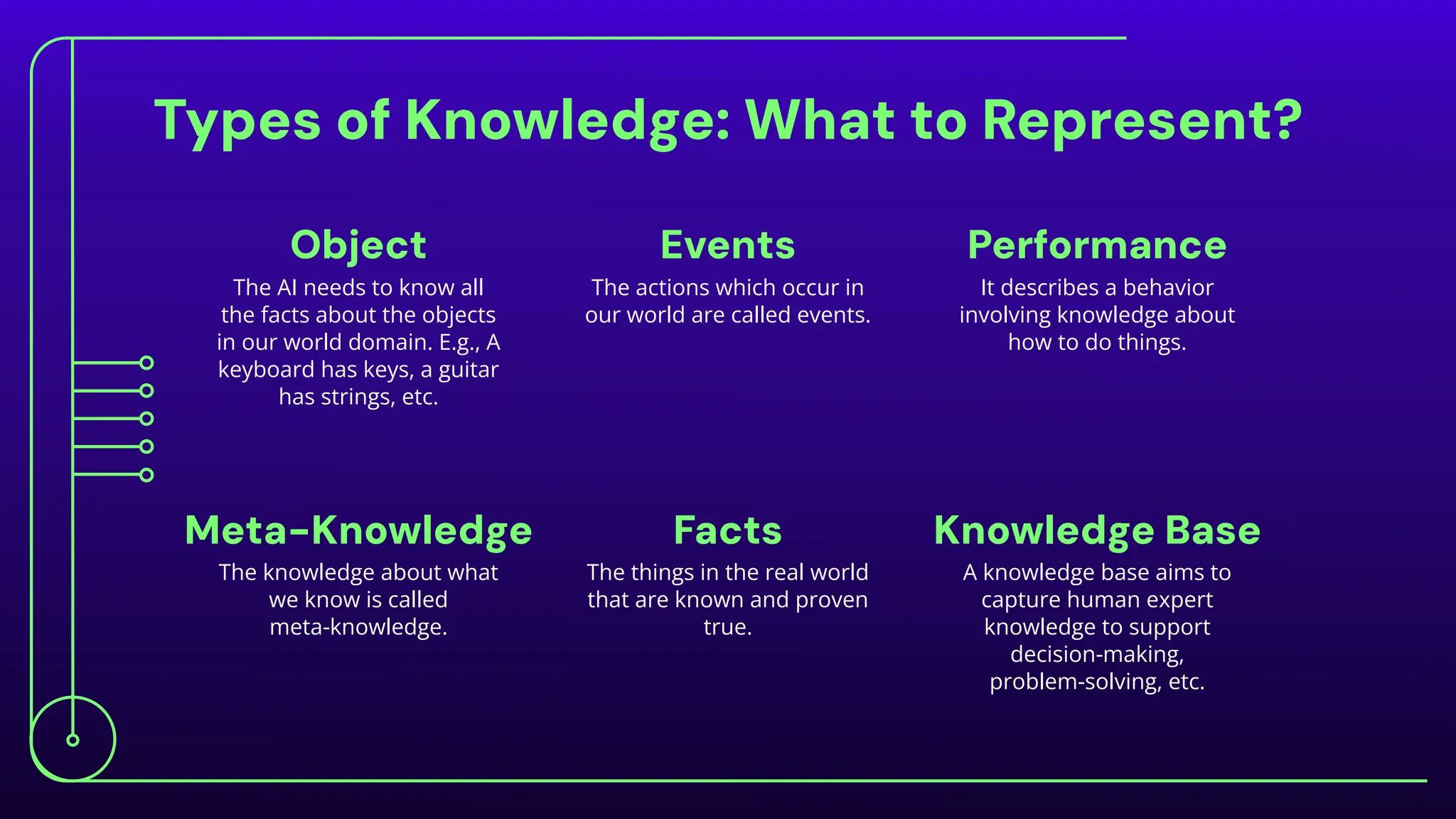
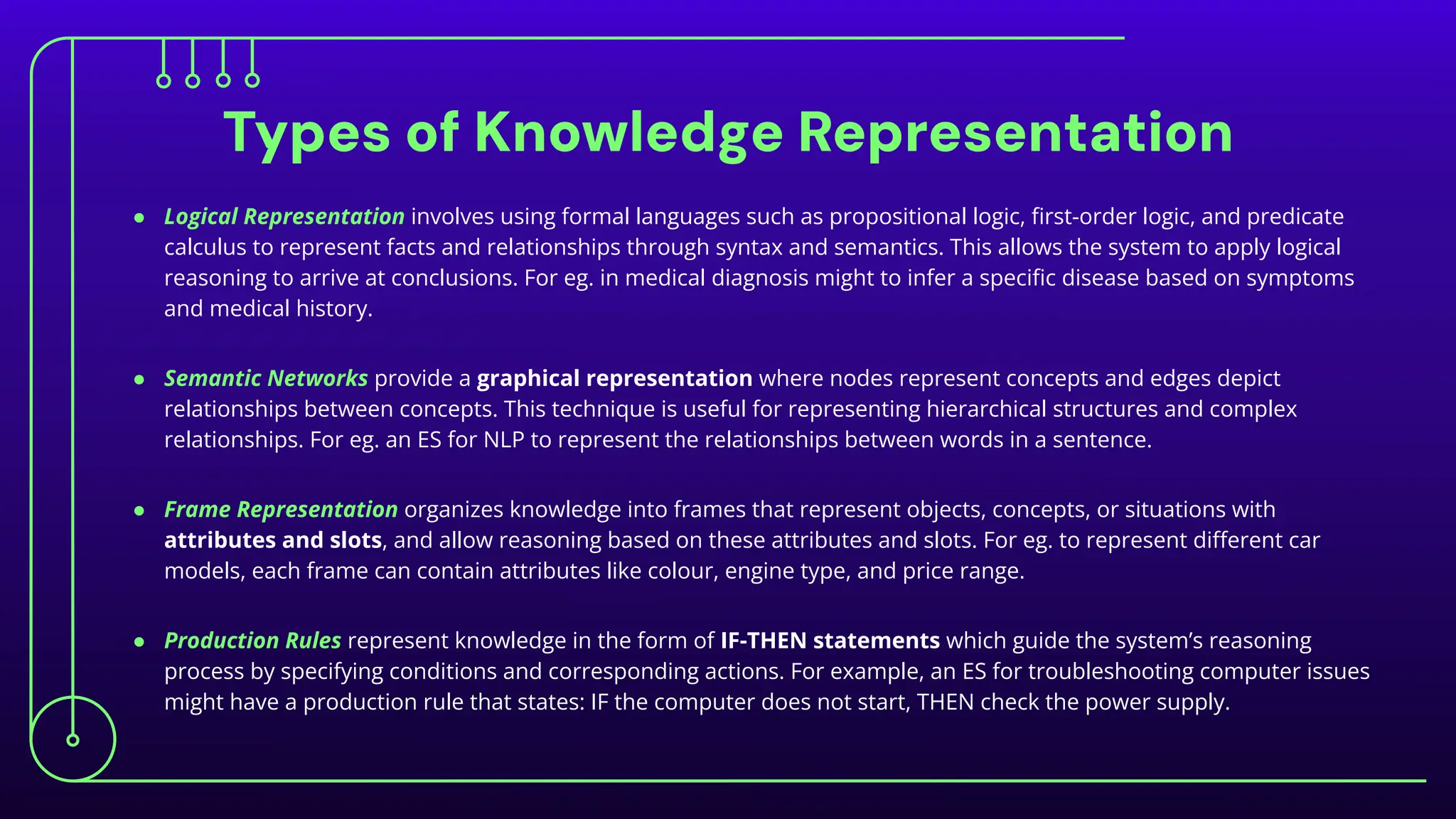
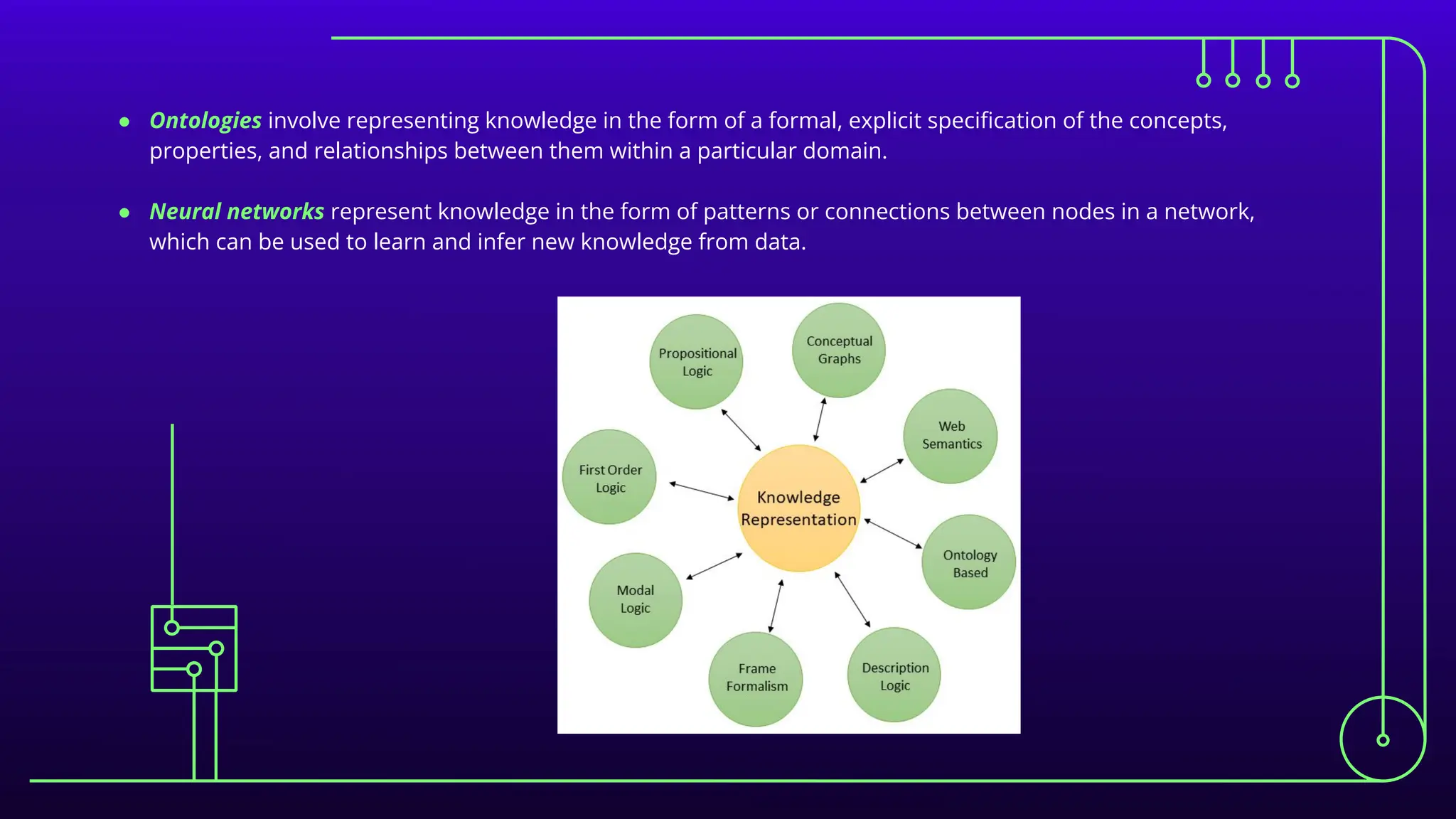
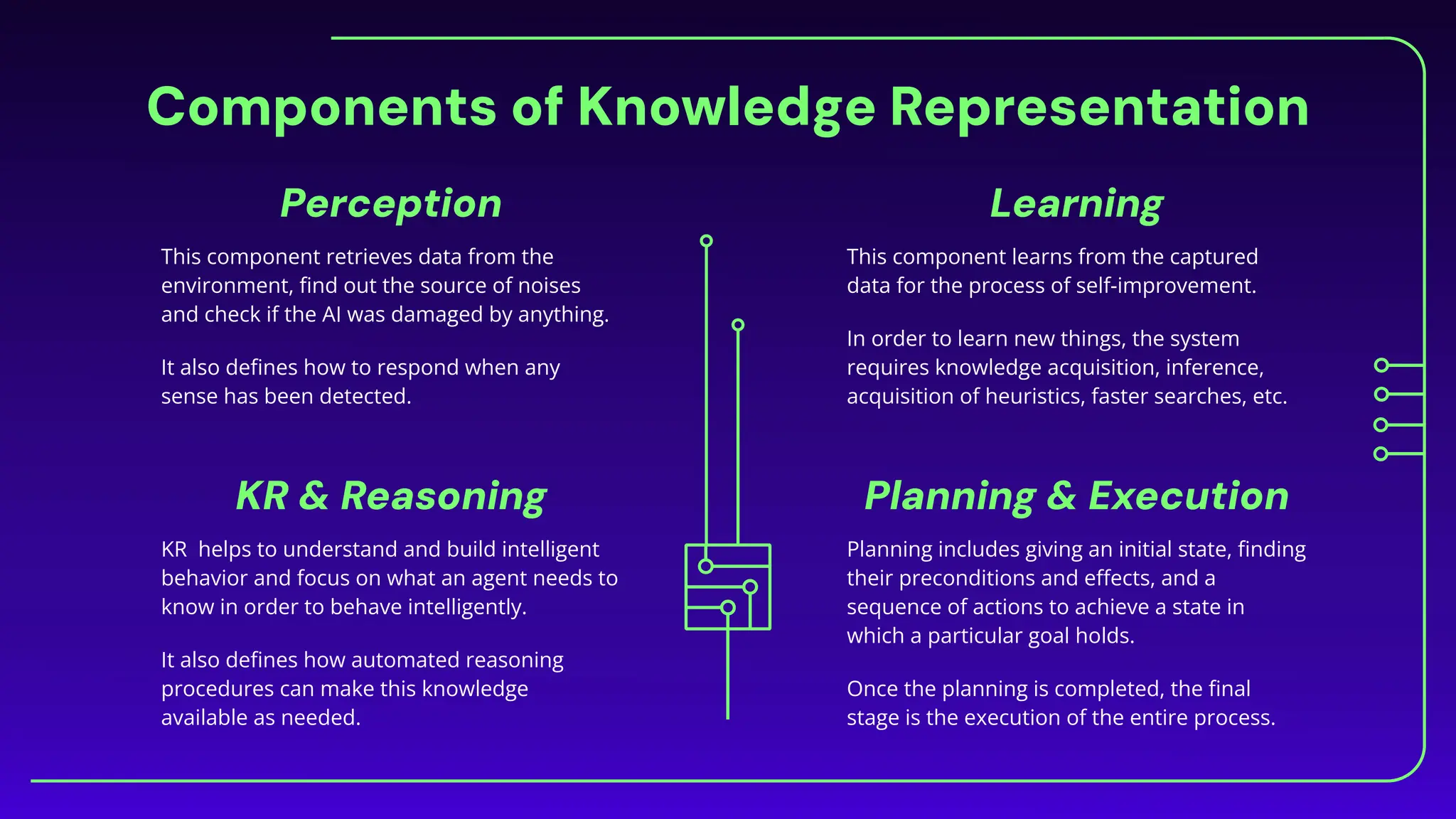
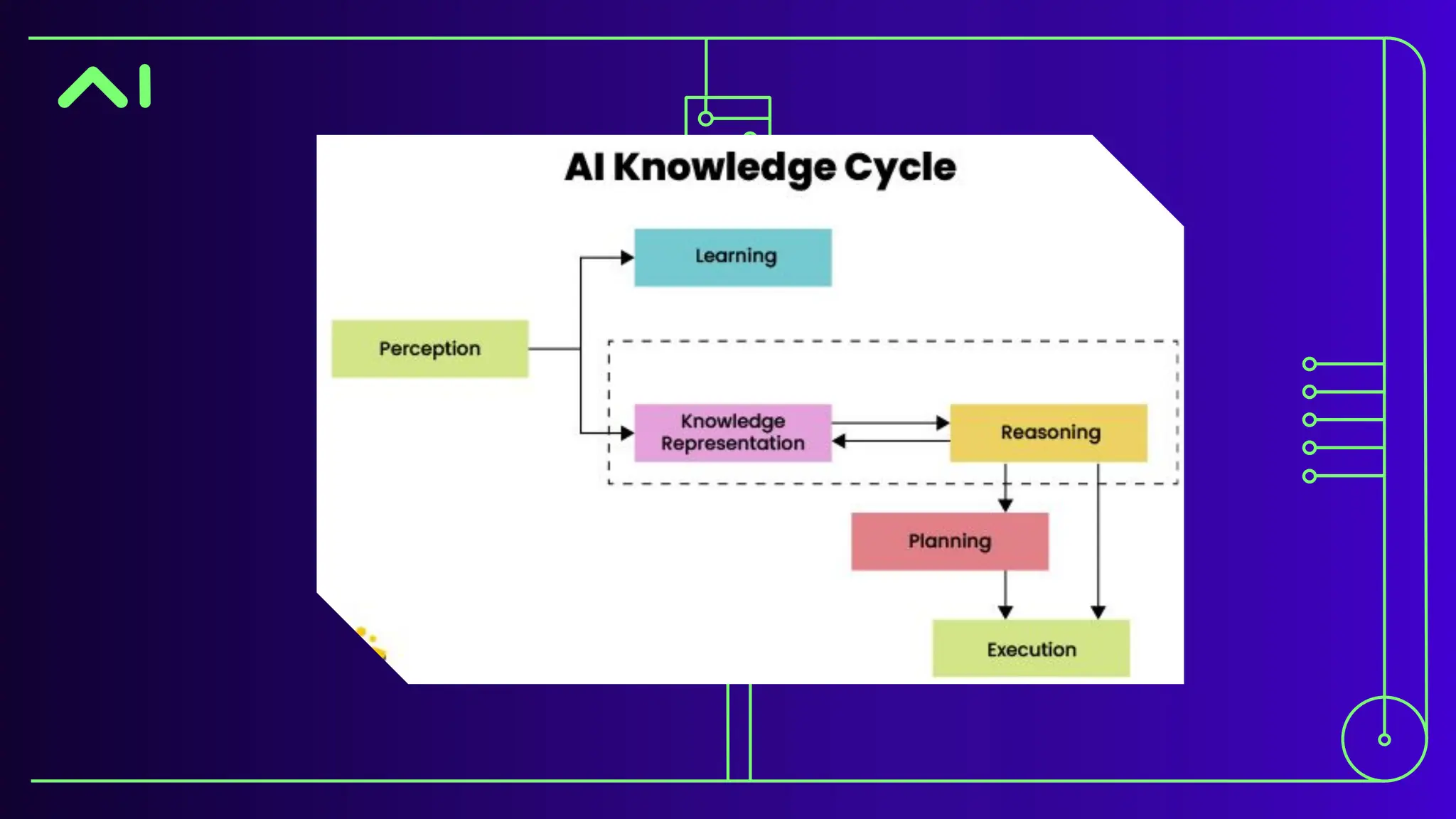
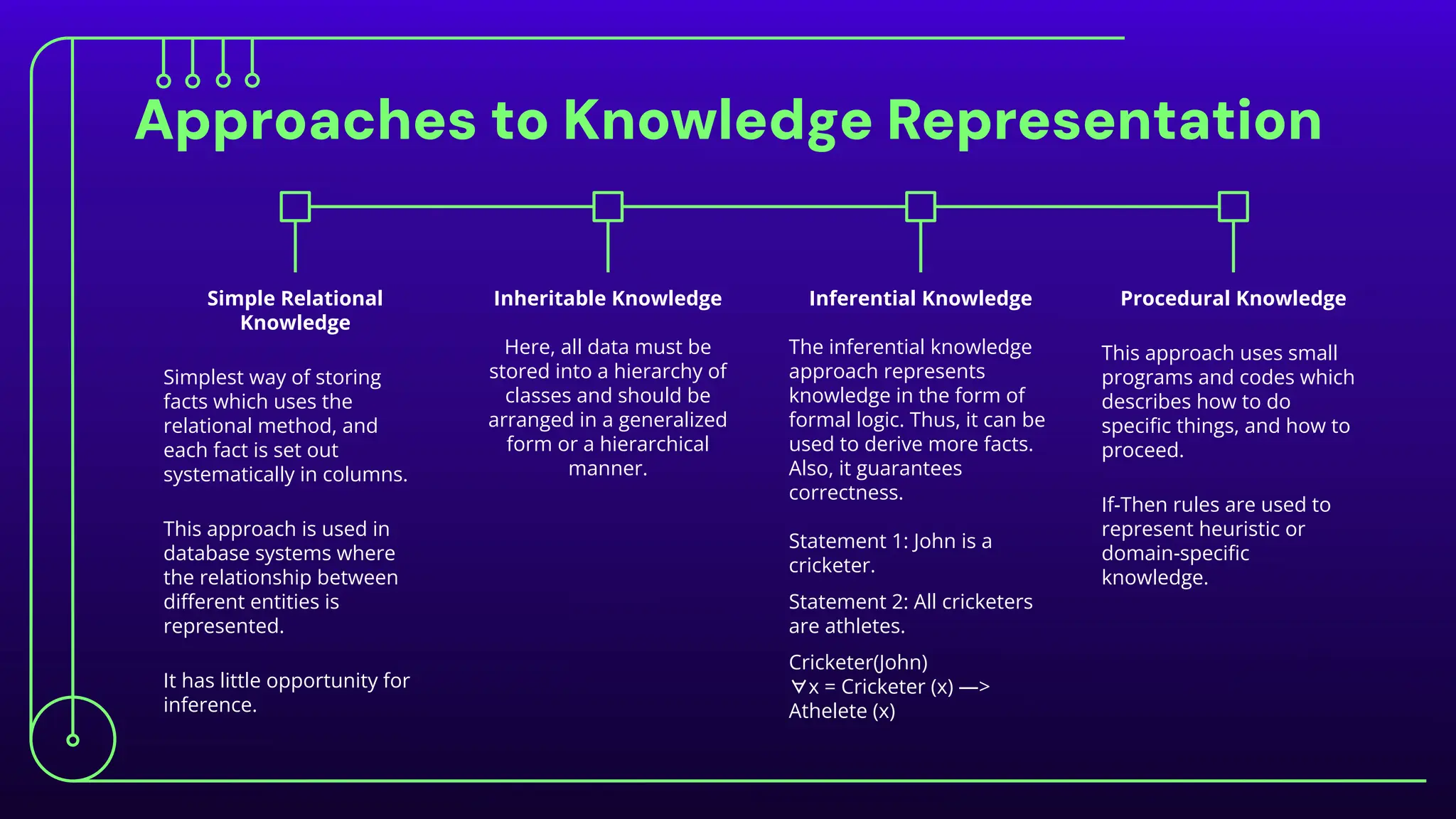
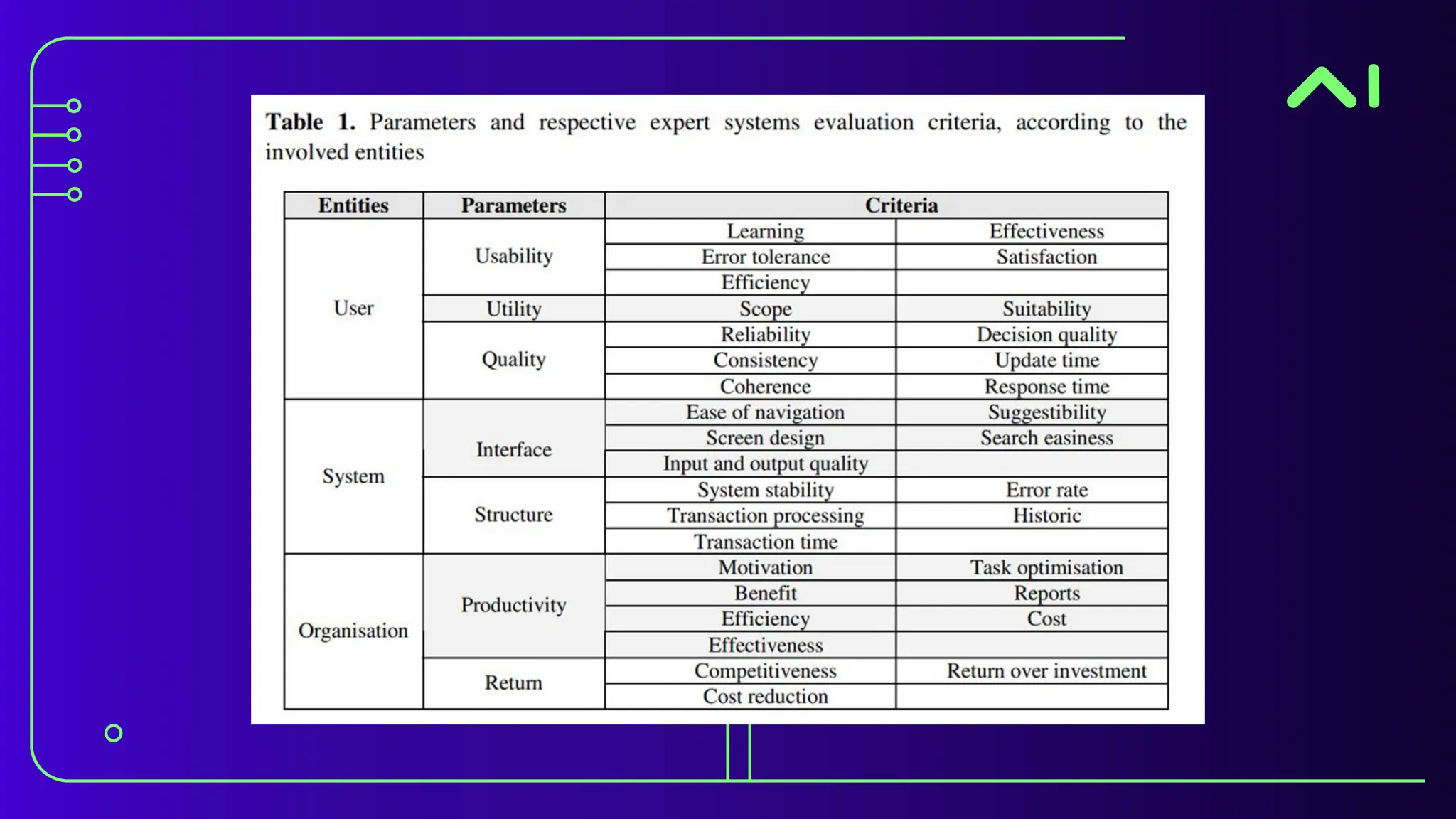
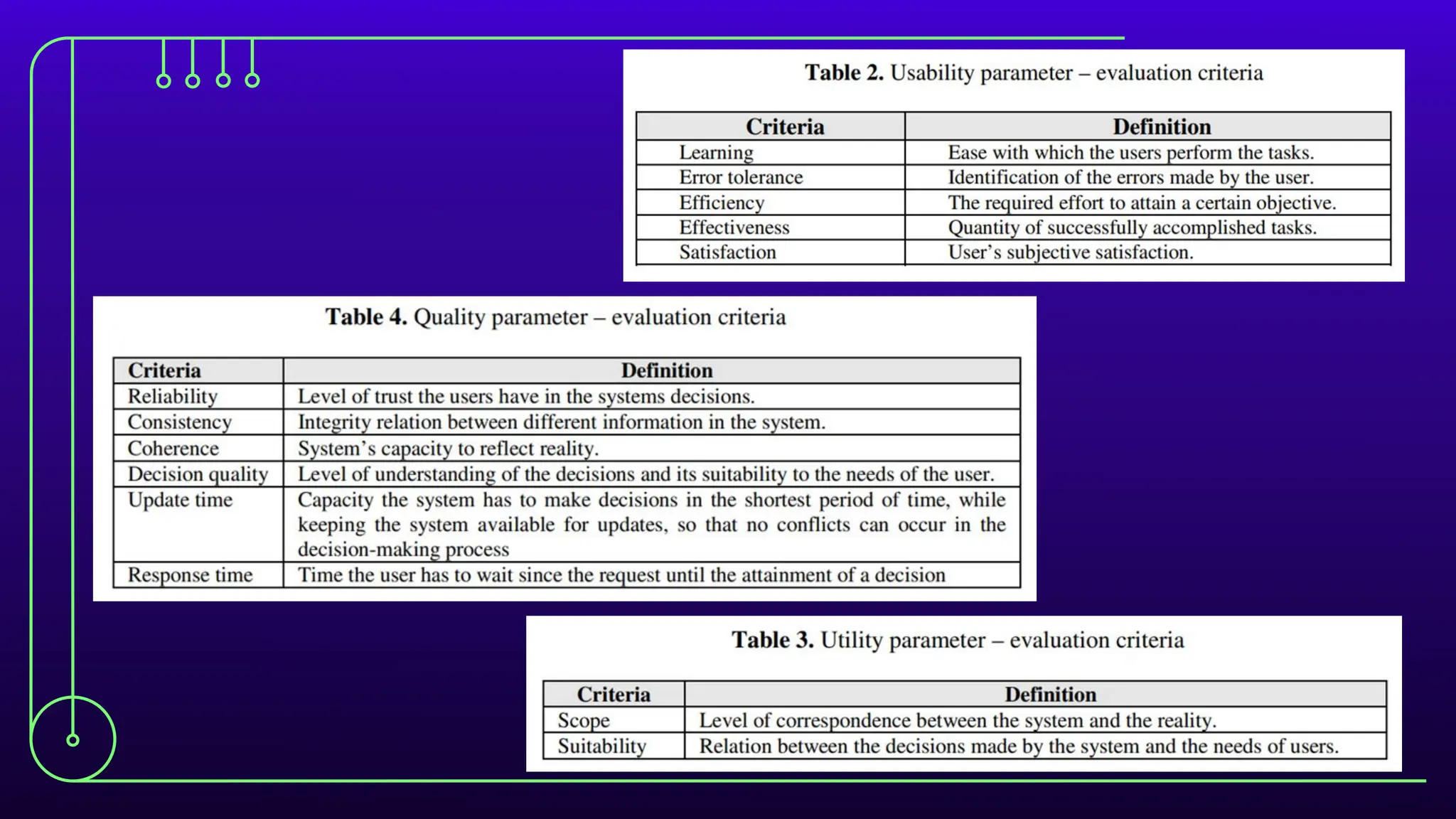
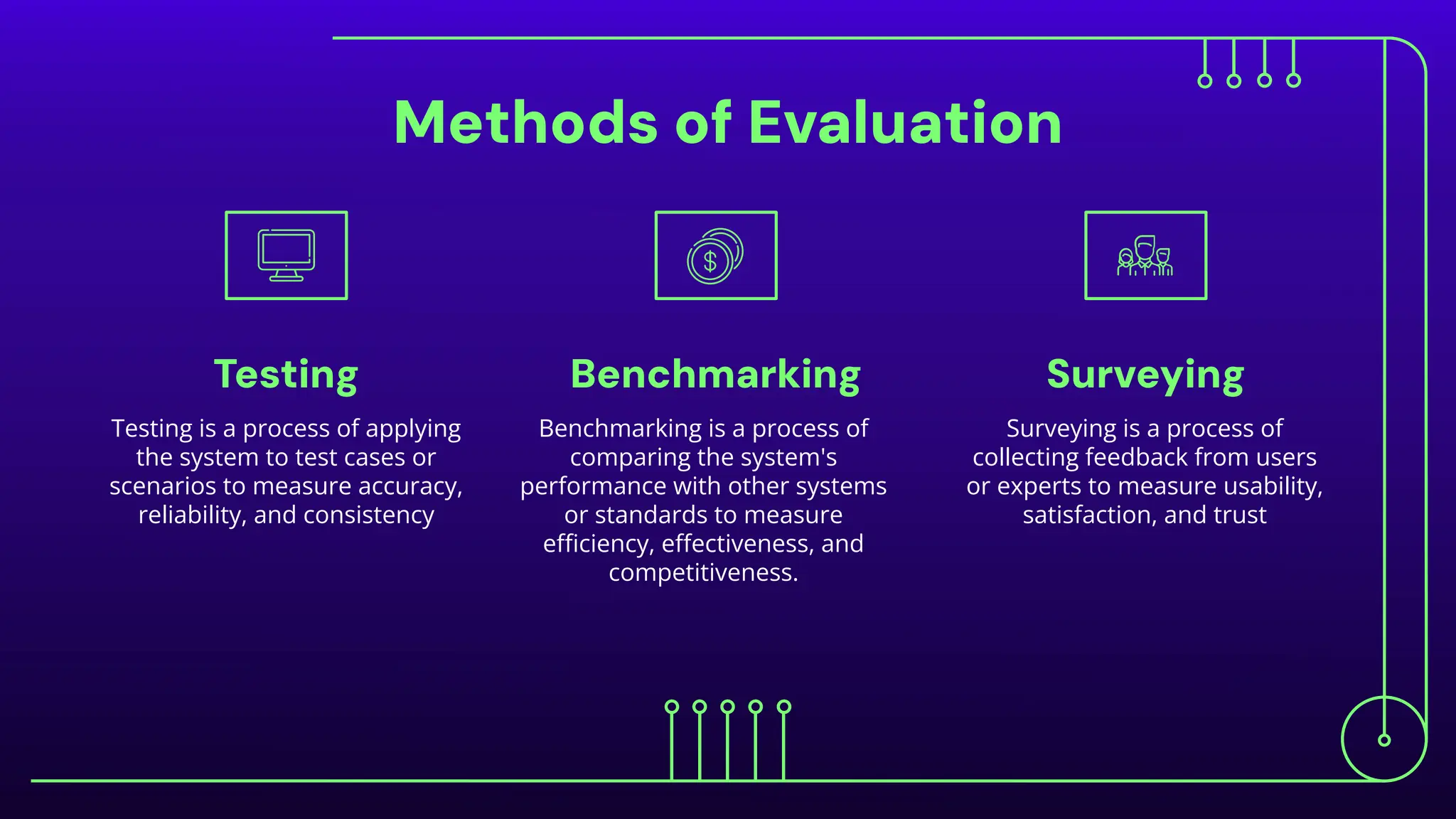
The document discusses expert systems, which are AI applications designed to solve complex problems through a knowledge base, inference engine, and user interface, enhancing decision-making in various fields like healthcare, finance, and customer support. It covers knowledge representation, detailing types such as logical representation, semantic networks, frames, production rules, ontologies, and neural networks, which help systems interpret and utilize real-world information. Finally, it addresses the evaluation of expert systems, emphasizing the need for assessing feasibility, functionality, performance, and user satisfaction throughout different stages of development and deployment.