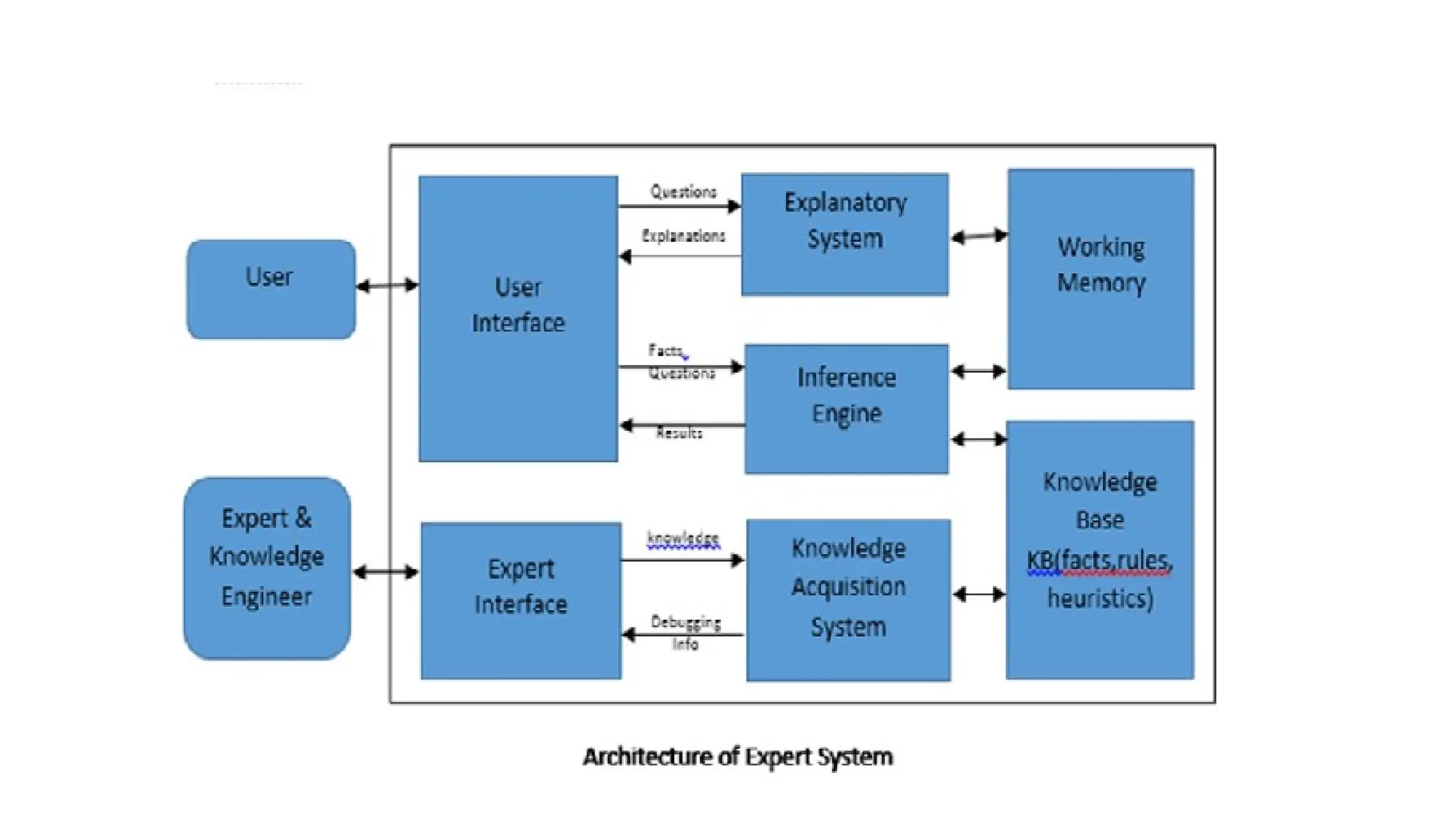
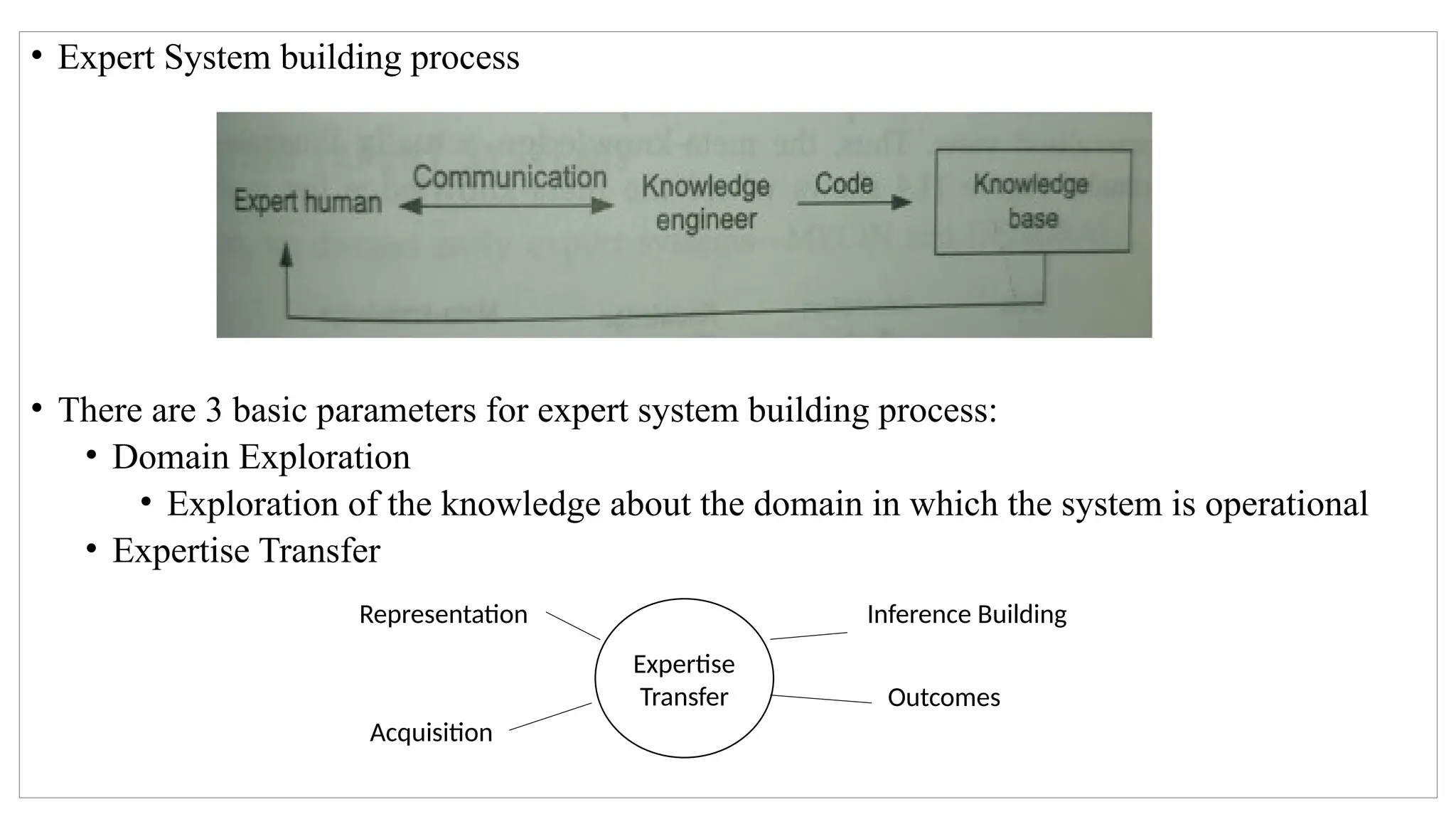
An expert system is a computer program that mimics human decision-making to solve complex problems, utilizing a knowledge base and an inference engine. They are domain-specific and consist of components such as working memory, explanation subsystem, and user interface. The document discusses various elements of expert systems, their architecture, building process, types, and notable existing systems like Mycin and Dendral.











![Example
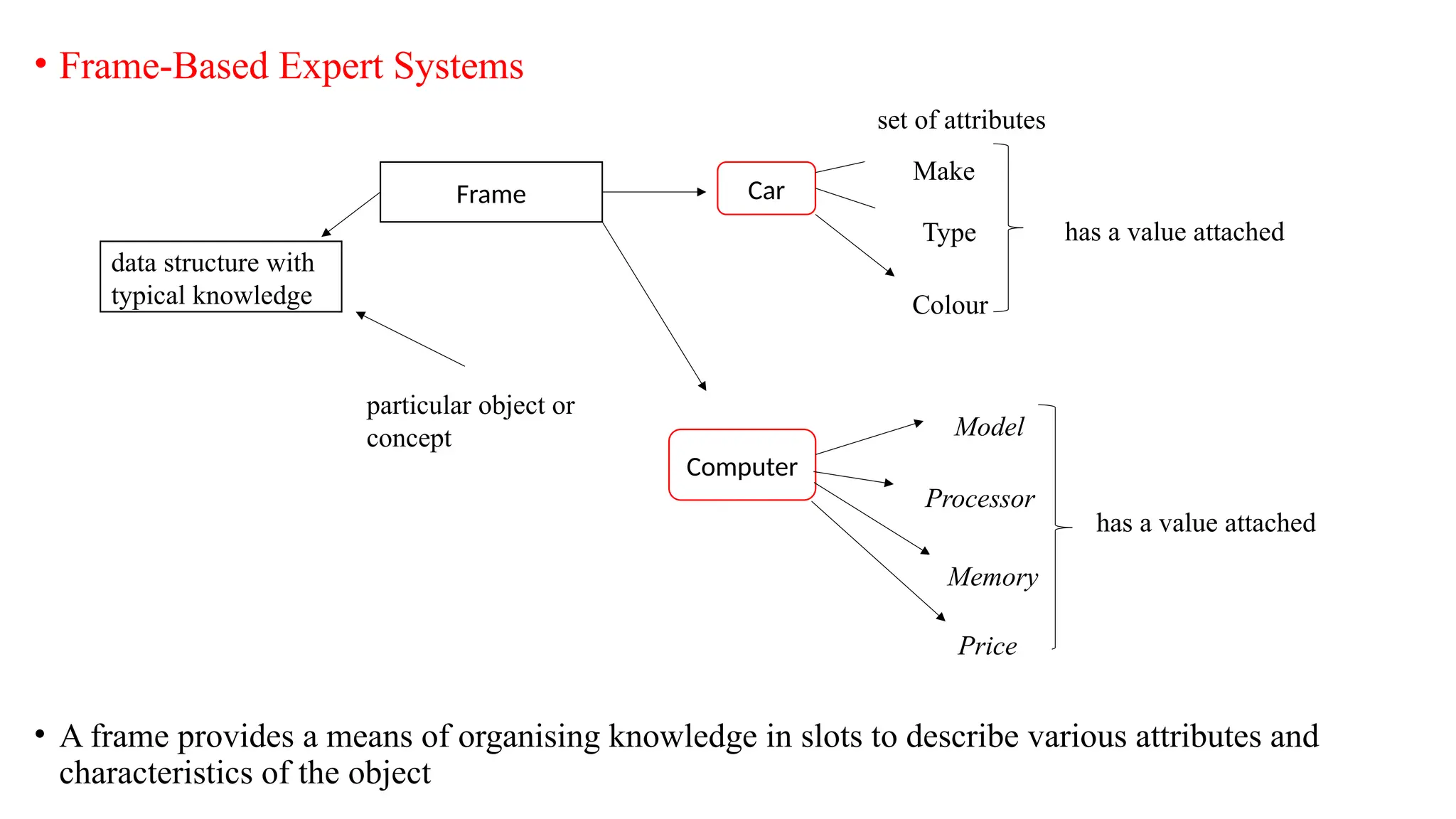
• Knowledge Base given as:
• If [X croaks and eats flies] Then [X is a frog]
• If [X chirps and sings] Then [X is a bird]
• If [X is a frog] Then [X is colored green]
• If [X is a bird] Then [X is colored yellow]
• [Fritz croaks and eats flies]
• Goal:
• [Fritz is colored Y]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsystems-241003172709-995ba821/75/Expert-Systems-in-Artificial-Inteligence-19-2048.jpg)
![• Workflow
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
[Fritz is a frog]
Knowledge Base
If [X croaks and eats flies]
Then [X is a frog]
If [X chirps and sings]
Then [X is a bird]
If [X is a frog]
Then [X is colored green]
If [X is a bird]
Then [X is colored yellow]
[Fritz croaks and eats flies]
Goal
[Fritz is colored Y]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsystems-241003172709-995ba821/75/Expert-Systems-in-Artificial-Inteligence-20-2048.jpg)