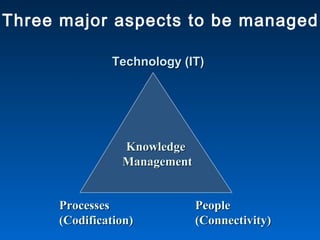
This document provides guidance on developing a knowledge management strategy for a library. It outlines several key steps: 1) Identify problems to be solved, such as knowledge decay or high staff turnover. 2) Prepare for change by getting sponsorship and studying the existing culture. 3) Create an implementation team with a range of expertise. 4) Perform a knowledge audit to understand current assets and gaps. 5) Identify human capital and information resources. 6) Create knowledge management solutions like access applications or a knowledge warehouse. 7) Link knowledge to people through communities, processes, and technology. An effective strategy requires managing people, processes, knowledge, and infrastructure.