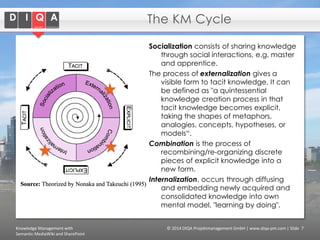
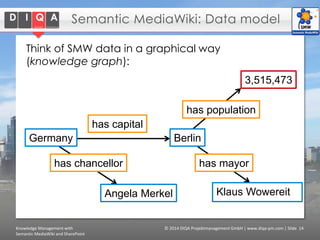
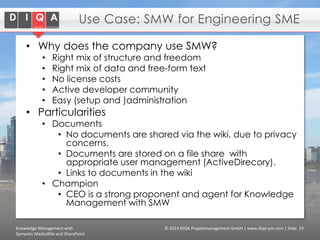
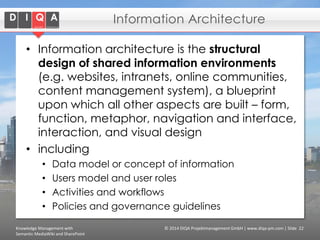
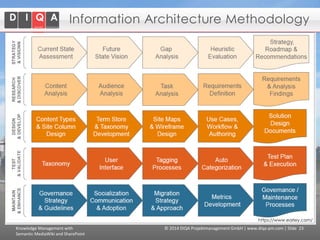
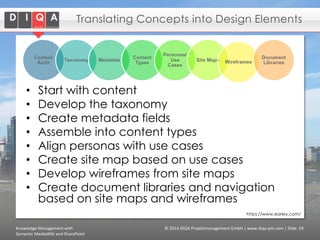
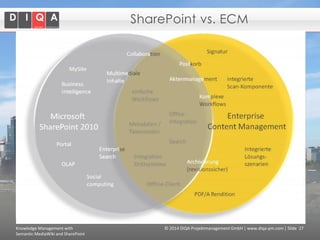
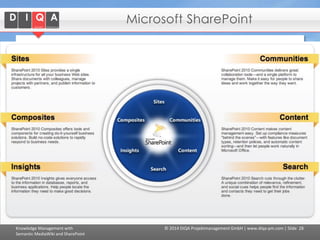
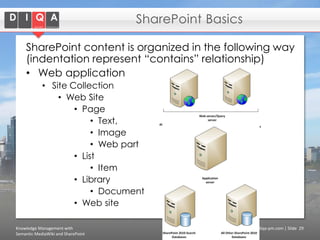
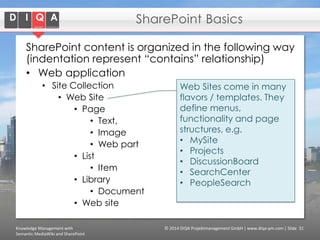
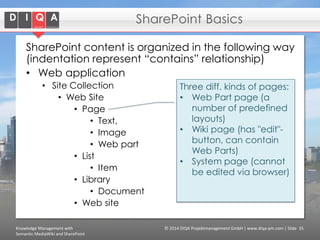
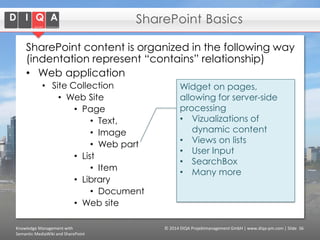
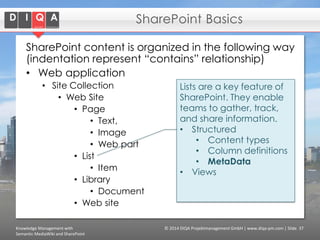
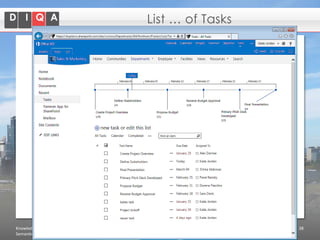
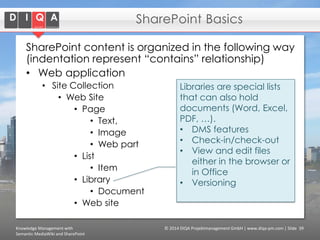
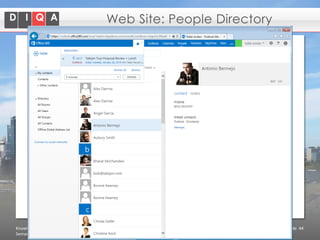
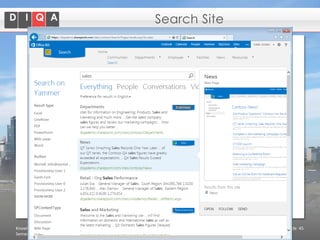
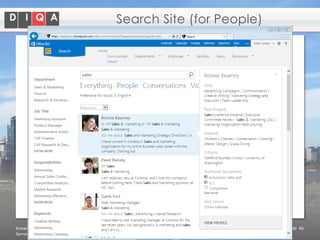
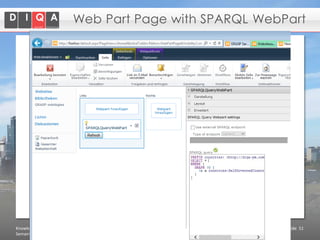
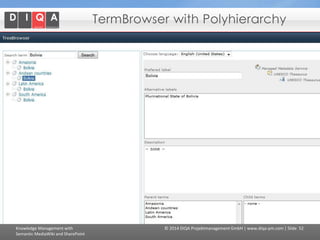
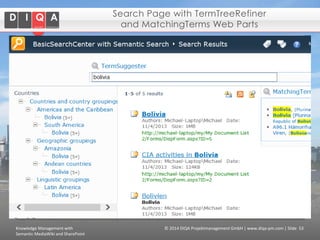
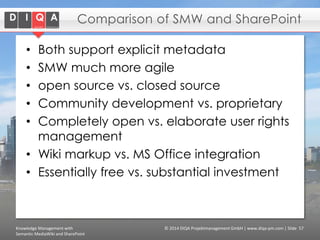
The document discusses knowledge management tools, specifically Semantic MediaWiki and SharePoint, highlighting their roles in enhancing information architecture and user collaboration. It outlines the goals of knowledge management, use cases for each platform, and the operational cycles involved in managing knowledge effectively. The conclusion emphasizes that while both tools offer valuable functionalities, organizational culture and tailored approaches are crucial for successful implementation.