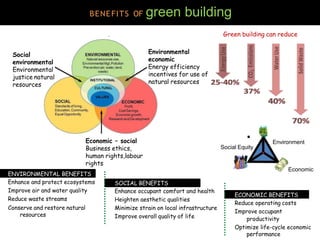
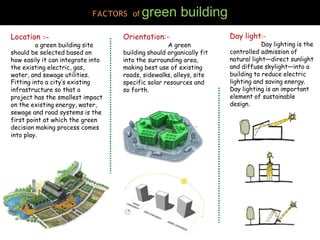
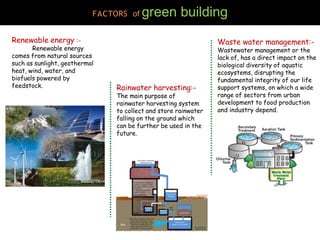
This document discusses green buildings. It defines green buildings as structures that are environmentally responsible and resource efficient throughout their lifecycle. It outlines the benefits of green buildings, which include social, environmental and economic benefits like enhanced occupant health and comfort, conservation of natural resources, and reduced operating costs. It also discusses factors to consider in green building like location, daylighting, orientation, materials used, and merits and demerits. Examples of green buildings in India that have received LEED certification are provided.