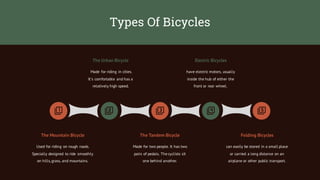
The document provides a comprehensive overview of transportation, detailing its definition, history, infrastructure, and types including land, water, and air transport. It emphasizes the importance of public transportation, energy usage, and environmental impacts while introducing various vehicles such as bicycles, motorcycles, automobiles, and trains. Furthermore, it discusses the evolution of air travel and shipping, highlighting the significance of these modes in global trade and commerce.