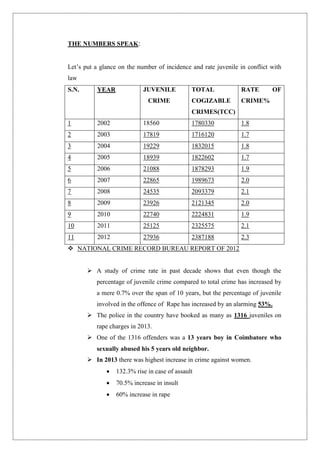
This document provides an abstract for a paper to be presented at a national seminar on juvenile justice and human rights. The paper will discuss the contemporary issues around setting a minimum age for criminal responsibility, particularly for serious crimes like rape and murder. It notes that in India, the 2012 Delhi gang rape case sparked debate around lowering the minimum age. The abstract outlines the historical development of juvenile laws in India and the current age of 18. It discusses the legal and scientific basis for setting the age. Global approaches are reviewed, and statistics on rising juvenile crime rates in India are presented. Arguments for and against revisiting the minimum age are summarized. The objective is to analyze the need to amend juvenile laws to curb rising delinquency while