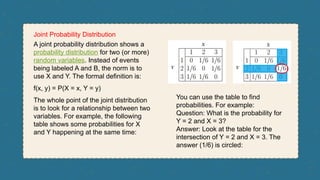
The document explains joint probability distribution, defining it as the likelihood of two independent events happening simultaneously. It details how to calculate joint probability using the formula p(a∩b) = p(a)×p(b) and provides examples, such as rolling dice and selecting colored balls, to illustrate the concept. Additionally, it introduces joint probability distribution, focusing on the relationship between two random variables.