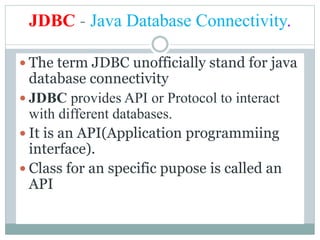
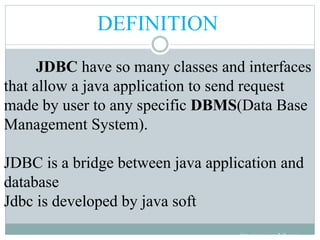
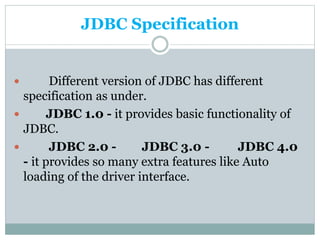
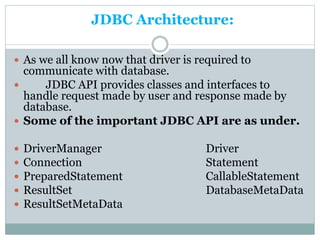
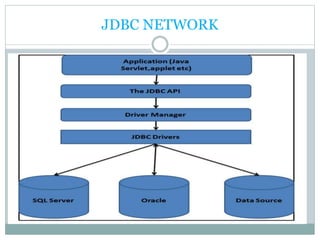
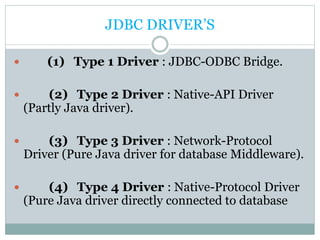
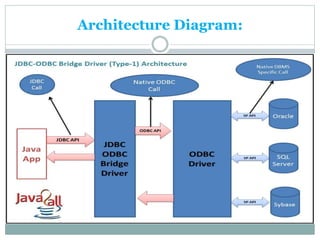
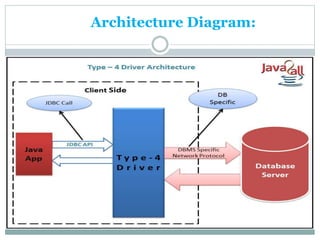
JDBC provides an API for connecting to and interacting with databases in Java. It defines interfaces and classes for establishing a connection with a database, issuing SQL statements, processing result sets, and handling exceptions. The key classes in JDBC include DriverManager, Connection, Statement, PreparedStatement, CallableStatement, and ResultSet. There are four types of JDBC drivers: Type 1 (JDBC-ODBC bridge), Type 2 (native API), Type 3 (network protocol), and Type 4 (native protocol). Connecting to a database in JDBC involves loading the driver, getting a connection, creating statements, executing queries, processing results, and closing the connection.















![Sample program
25
import java.sql.*;
class MyJdbcCode1
{ public static void main(String []args)
{ try
{ Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("Driver loadedd");
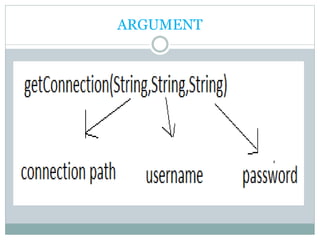
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@//sumit-
pc:1521/XE","hr","sati");
System.out.println("connected to the data base");
Statement st=conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs=st.executeQuery("select FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME from
EMPLOYEES");
while(rs.next())
{
String name1=rs.getString("FIRST_NAME");
String name2=rs.getString("LAST_NAME");
System.out.println(name1+"t"+name2);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdbc-sati-150922193331-lva1-app6892/85/Jdbc-new-25-320.jpg)

