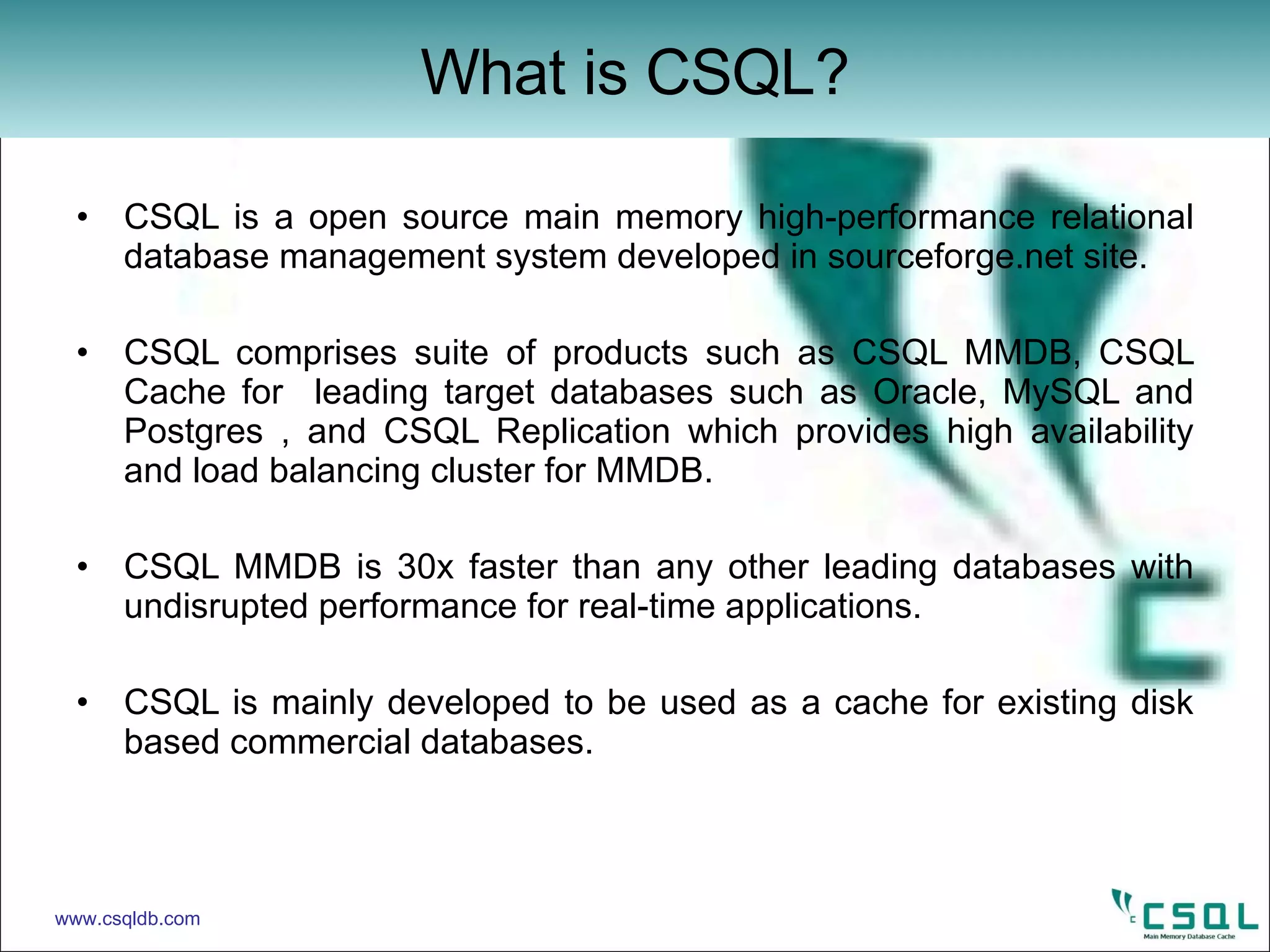
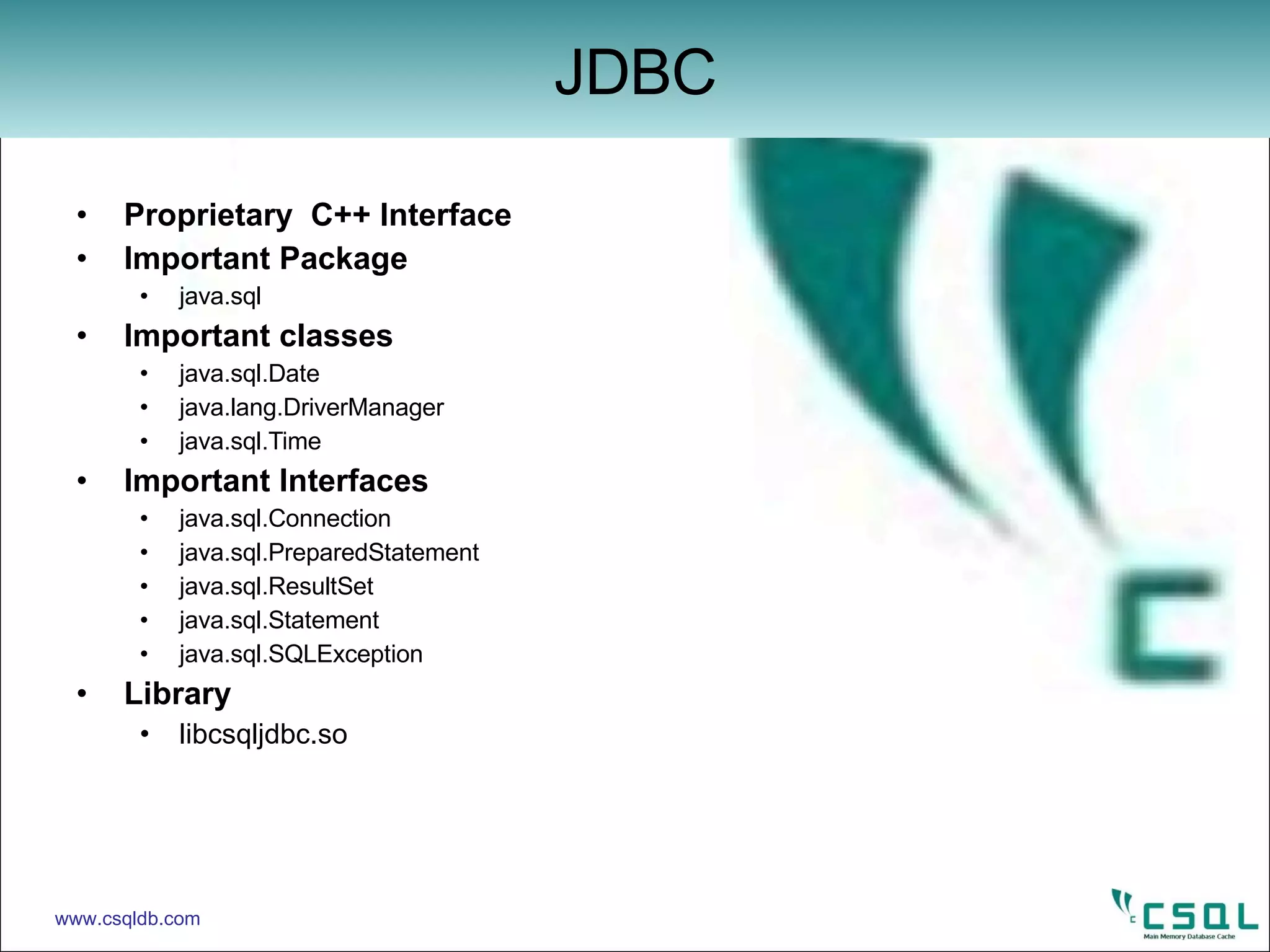
This document provides an overview of connecting to and interacting with a CSQL database using JDBC. It discusses loading the JDBC driver, establishing a connection, and executing SQL statements like CREATE, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and DROP using Statement and PreparedStatement objects. Example code is provided to demonstrate connecting to CSQL and performing common SQL operations through JDBC.
![CSQL - JDBC Jitendra Lenka Developer - Lakshya Solutions Ltd. [email_address] olutions.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdbc-12420385476-phpapp02/75/JDBC-for-CSQL-Database-1-2048.jpg)
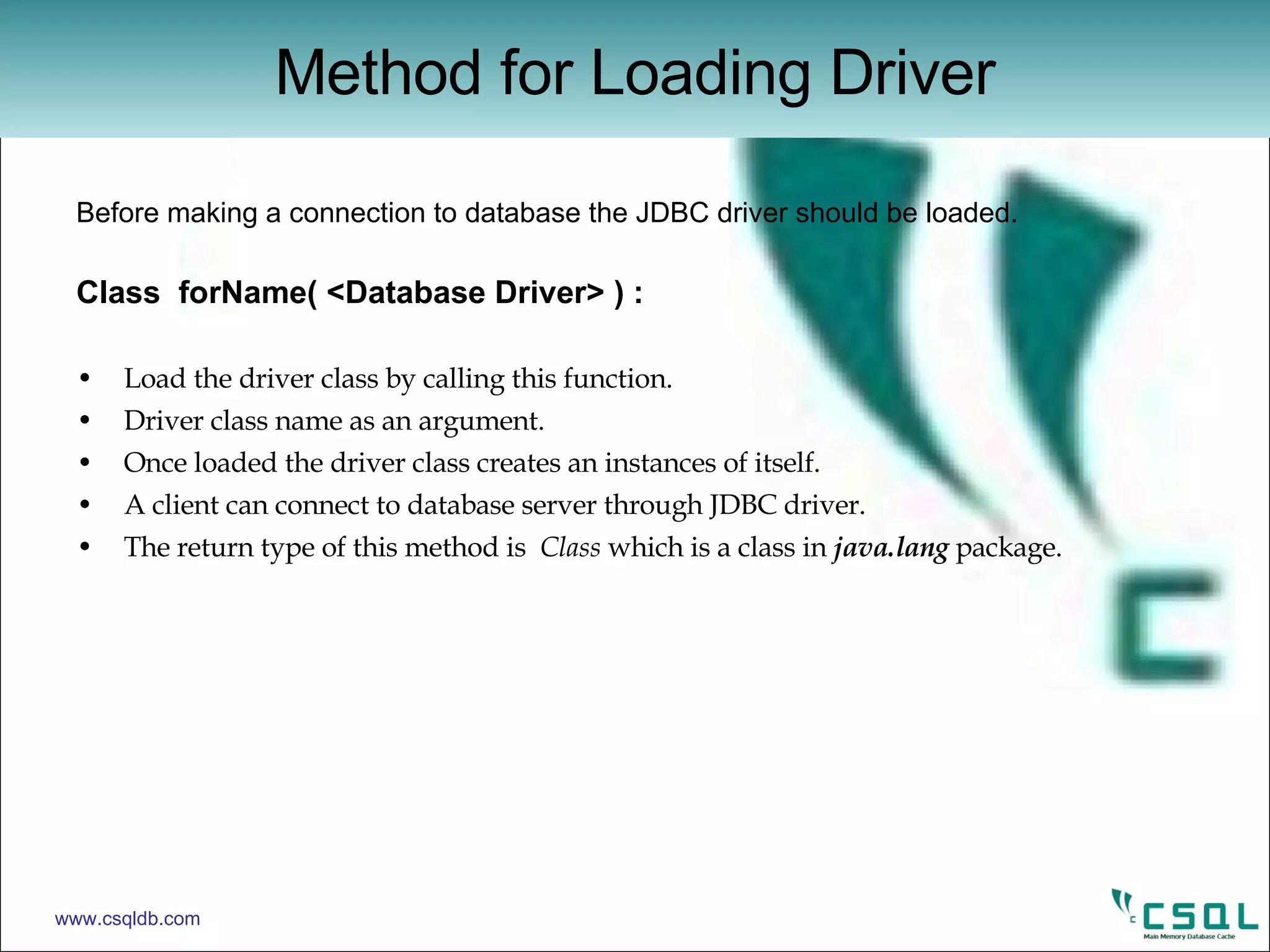


![Example : Connect to the CSQL through JDBC Driver. import java.sql.* ; public class ConnTest { public static void main( String argv[ ] ) { Connection con = null ; try { class.forName(“csql.jdbc.JdbcSqlDriver ”) ; Connection con = DriverManager . getConnection(“jdbc:csql” , “root” ,”manager”) ; if(con==null) System.exit(1) ; con.close() ; System.exit(0) ; } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(“Exception in Test :“ +e) ; e.getStackTrace(); System.exit(1) ; } } } Connection www.csqldb.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdbc-12420385476-phpapp02/75/JDBC-for-CSQL-Database-13-2048.jpg)



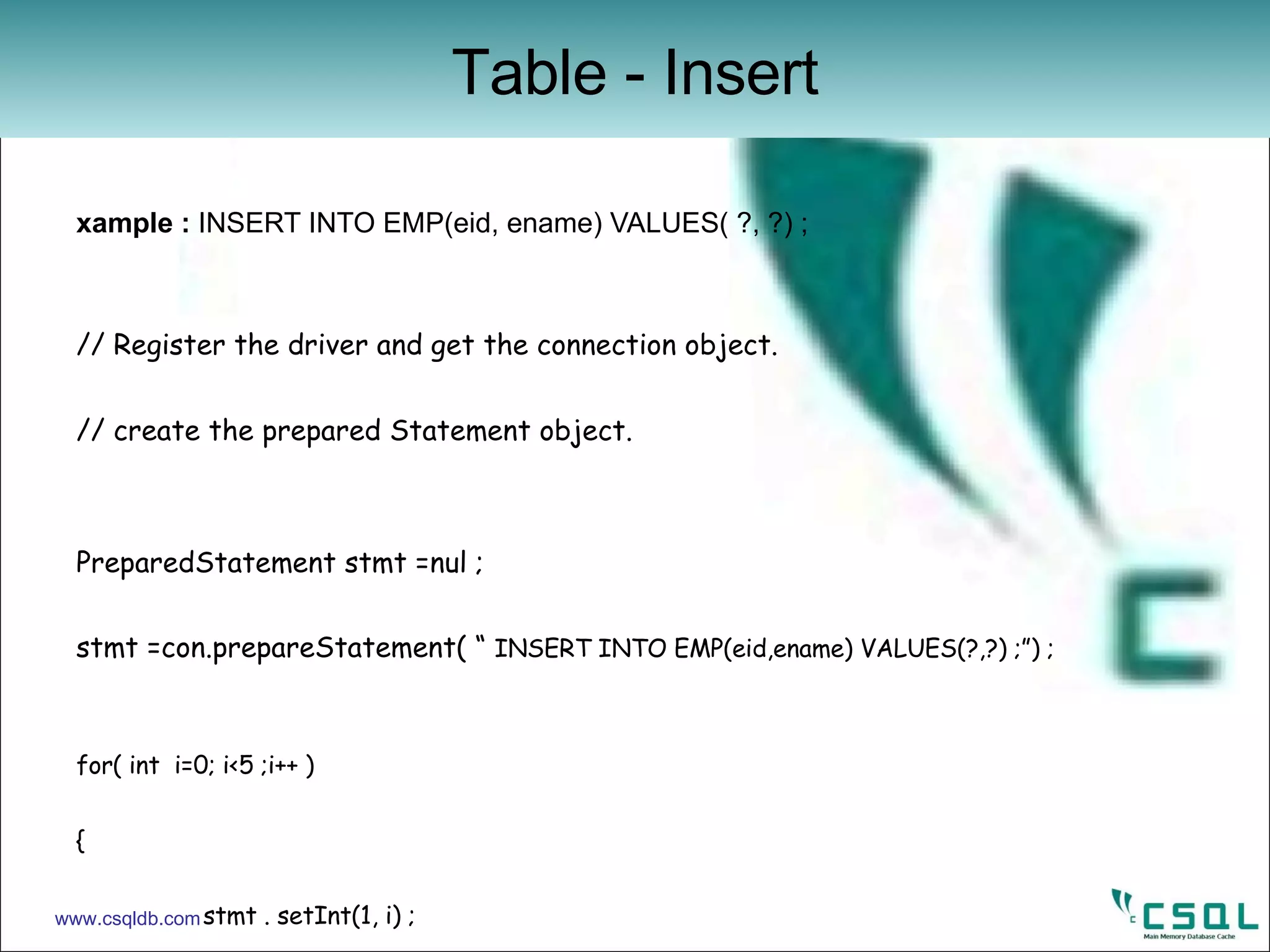
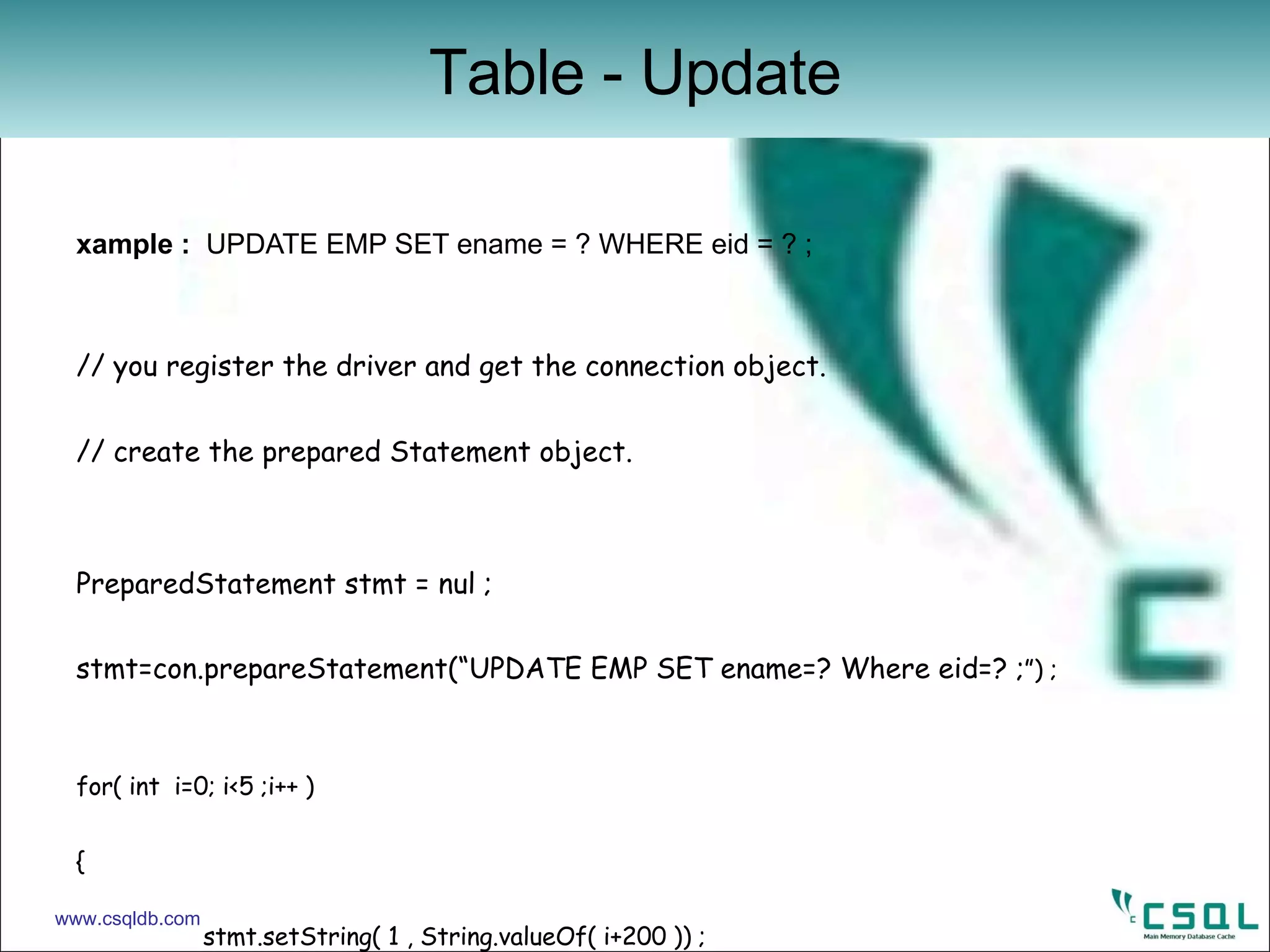


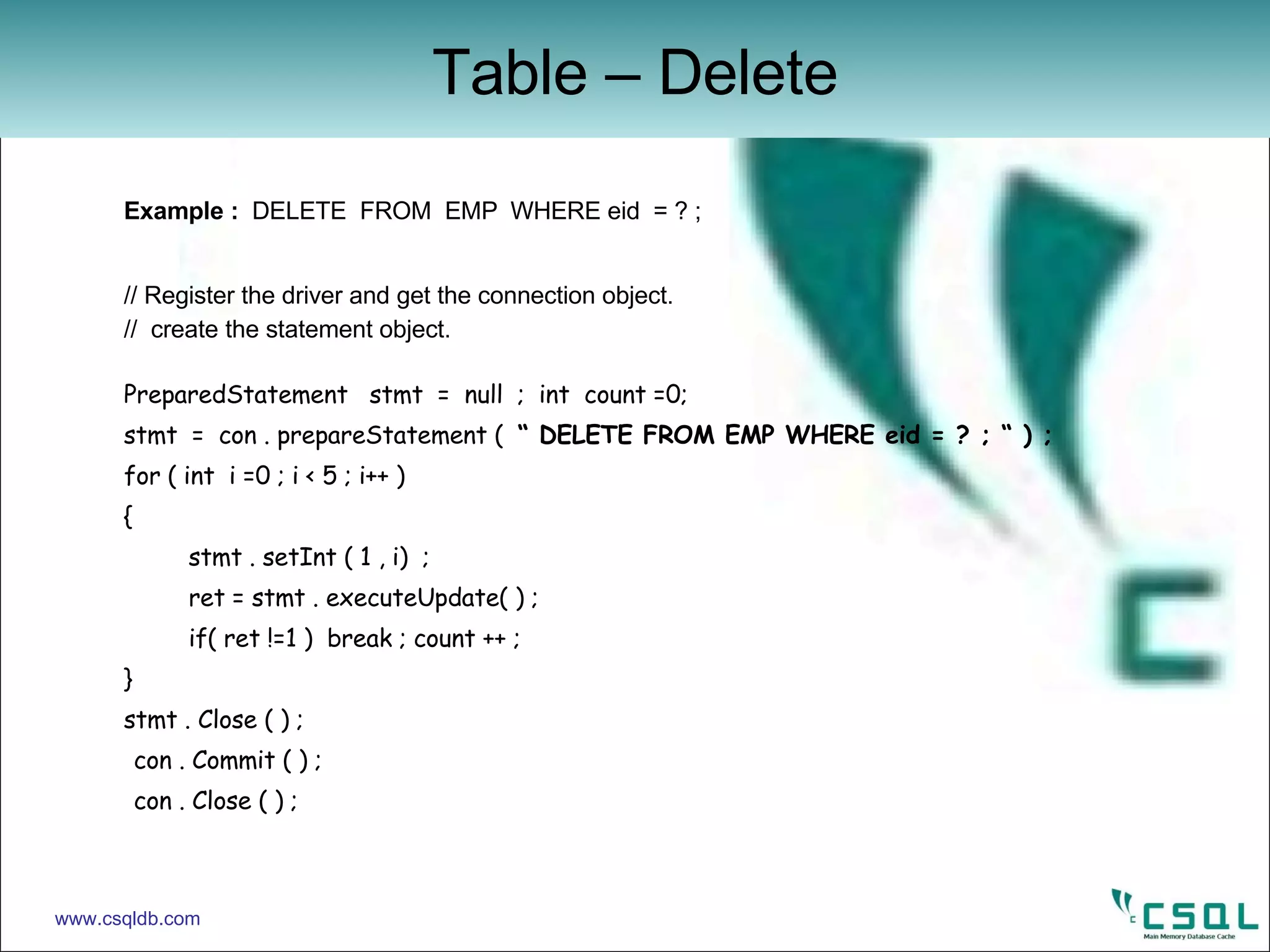
![Example : DROP TABLE EMP ; import java . Sql . * ; public class jdbcexample { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { try { // get the connection object ‘ con ‘ Statement cStmt = con . createStatement ( ) ; cStmt . execute ( “ DROP TABLE EMP ; “ ) ; cStmt . Close ( ) ; con . Close ( ) ; } catch ( Exception e ) { // print the error value here } } } Table – Drop www.csqldb.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdbc-12420385476-phpapp02/75/JDBC-for-CSQL-Database-24-2048.jpg)
![Example : set the auto commit false and commit the transaction. import java.sql.* ; public class ConnTest { public static void main( String argv[ ] ) { Connection con = null ; try { class.forName(“csql.jdbc.JdbcSqlDriver ”) ; Connection con = DriverManager . getConnection(“jdbc:csql” , “root” ,”manager”) ; con . setAutoCommit(false) ; // perform DML operations here con.commit() ; } // close the connection Transaction www.csqldb.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdbc-12420385476-phpapp02/75/JDBC-for-CSQL-Database-25-2048.jpg)

