This article introduces the Job Content Questionnaire (JCQ) as a tool for assessing psychosocial job characteristics. Part I describes the development and theoretical basis of the JCQ scales, which measure job demands, decision latitude, social support, physical demands, and job insecurity. These scales assess the job strain model and its predictions about stress risk and behavioral responses under conditions of high psychological demands and low decision control. Part II reports on the cross-national validity of the JCQ scales based on studies of over 10,000 men and 6,000 women across multiple countries. Part III reviews comparisons of intercountry and interoccupation differences in JCQ scale scores.



![Decision l
L'tit:dAichite_Lc
t
Engineer
• Natural Programmer Farmer
O
Scientist • ~]~ Teacher--H.S.
• Publc
WIFManager-trade
• Officials • Physician
+0.50 Bank Officer
• Lineman • Clerk
• Foreman Supervisor
O Repairman..~ O Nurse
I I
o_Machinist • Carpenter
050
/
+0.5~
Psychological
Demands
k-
1
I I I il~ Fireman
t
Stationary • Health • Off. Computer
• EngineerA~ I Technician Operator
_ WBilling Clerk
~lhDeliveryman
• Watchman WSales Clerk
I
• Dispatcher
-0.5o-
• Gas Station
O Janitor Attendant
• Cutting tWaitress
• Miner - OperativeO Nurse's Aide
O • Freight handler
Construction • Telephone
Laborer Operator/,f--~
" " Keypuncher / Si t n t ~
~ /Gm a '~gh O
ae
r~
stitcher,-,,~.,~
O Assembler-
electric/trans, mfg.
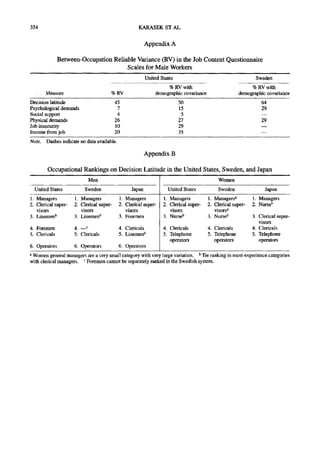
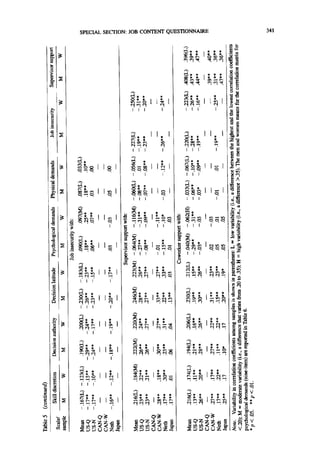
Figure I. The occupational distribution of psychological demands and decision latitude
(U.S. male and female workers; N = 4,495). From "The Political Impfications of Psychosocial
Work Redesign: A Model of the Psychosocial Class S~ucture" (p. 177), by R. A. Karasek, in
J. V. Johnson and G. Johansson (Eds.), The Psychosocial Work Environment: Work
Organization, Democratization, andHealth, 1991, Amityville, N-Y:Baywood. Copyright 1989
by Baywood Publishing Company. Reprinted with permission.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jcq-120618163639-phpapp01/85/JCQ-SCALE-4-320.jpg)



![SPECIAL SECTION: JOB CONTENT QUESTIONNAIRE 329
pressures are too much for me" are replaced by The same occupational basis that provides the
questions that emphasize simple assessments of standardized scores is also the basis of an often
environmental conditions only, such as: "I have utilized occupational score linkage system (Schwartz
freedom to make decisions about my job" and "My et al., 1988). The JCQ job characteristic scales can be
job requires I work fast." Such linguistic distinctions linked to other databases through U.S. three-digit
have been considered quite significant in other census occupation codes (1970) and also to four-digit
psychological research contexts: for example, state- U.S. Standard Industrial Classification (industry
trait response differentiations based on phrasing classification) codes. This database linkage system
differences such as "Today I feel angry" versus "I allows psychosocial job content scores to be associ-
usually feel angry." ated with health and productivity outcomes in
Sources of difficulty remain, however. Self- national or company databases already in existence
reflexive judgments remain in two psychological (such as U.S. Census, Commerce, or U.S. National
demand questions: "work hard" and "work fast" (see Center for Health Statistics data), for which direct
Appendix A). Also, the JCQ goal of broad coverage questionnaire data collection would not be feasible.
on jobs characteristics with a short set of questions
means that many questions elicit summary judgments
Aggregate Scoring Methods for Work Groups
about some quality of the job (skill requirements,
decision possibilities). Questions about more specific Bias of findings could potentially occur with
job situations could avoid this problem, but would self-reported psychosocial work environment and
likely make the questionnaire longer or the questions dependent variables such as depression, exhaustion,
unjudgable by some respondents, and therefore the and dissatisfaction (see the Implications for Broad
responses difficult to compare across groups. Interpretability of Psychosocial JCQs section). One
remedy is to aggregate self-report responses by work
groups with similar work situations, thus diluting
Occupation-Based Analysis
individual biases (Kristensen, 1996). This is, of
and Score Standardization course, the basis of the occupation database linkage
In addition to direct administration of JCQ system suggested above, but systems of mixed
questionnaires to workers, the JCQ system offers a self-report and work-group aggregated assessment
second set of occupation-based methodologies. There have also been successfully applied (Vahtera, Pentti,
is an extensive system of JCQ scores scales by & Uutela, 1996).
detailed occupation and gender in several countries The alternative of expert observations is certainly
that is the basis of (a) the JCQ occupational score theoretically desirable, but in practice it has problems.
standardization system and (b) the occupational Expert observations are costly, time consuming, and
linkage system. in assessment of social interactions do not obviously
Detailed scoring procedures for the JCQ scales are generate more accurate measures resulting in low
described in the JCQ Questionnaire and User's Guide interrater reliability. There are also theoretical biases
(Karasek, 1985). Most of the scales have been involved in the very concept of standard "expert"
standardized by detailed occupation codes for several measures: It is much easier to measure the easily
national populations (for the U.S. population: Karasek observed, repetitive quality of the low-status assembly-
& Theorell, 1990, Appendix; Schwartz et al., 1988; line jobs than the diverse tasks of nigh-status
with related scales standardized in Sweden [work managers or professionals. Thus, measurement reli-
exposure matrix: Johnson & Johansson, 1991; ability for the most potent set of psychosocial job
Johnson & Stewart, 1993]). The JCQ questions can be characteristics (decision latitude, skill, and decision
compared to national scale scores for detailed census autonomy) is probably correlated with scale level--a
code by sex and by four-digit industry code. This complex confounding of content and validity (for all
allows unique assessment of differences between a methodologies, not just the JCQ).
target group and "national norms" for psychosocial
job dimensions. This allows JCQ users involved in Scale Statistical Validity
practically oriented job analyses, small populations,
or single-plant studies to compare their findings with The most substantial compilation of reliability
national averages on the scales (broken down by sex, findings is presented in the following section (Part II).
occupation, and industry). However, previous reliability analyses of the scales](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jcq-120618163639-phpapp01/85/JCQ-SCALE-8-320.jpg)
![330 KARASEK ET AL.
very similar to the JCQ scales have been published update has cataloged 41 studies of the major coronary
for the U.S. national populations (Q.E.S. database: heart disease risk factors (blood pressure, serum
Karasek & Theorell, 1990, Appendix 1; Schwartz et cholesterol, and smoking) testing associations with
al., 1988). Kawakarni and Fujigaki (1996) and job strain. In over a dozen studies of blood pressure
Kawakami, Kobayashi, Araki, Haratani, and Furui using sophisticated ambulatory assessment technolo-
(1995) published the first studies on the reliability of gies, all show either positive or mixed positive
recommended format JCQ scales (omitting physical results. However, less-sophisticated blood pressure
demands and job insecurity). The study concluded measurement technologies show no consistent associa-
that the JCQ is reliable for Japanese populations and tions, and smoking and cholesterol have mixed
found Japanese occupation scale ratings that are positive and null associations.
similar to those in the United States (see Appendix A). Consistent associations between mental strain and
Brisson et al. (in press) showed JCQ scale reliabilities JCQ-like scales are also reported (see Bourbonnais,
to be good and confirmed the scale structure Busson, Moisan, & Vezina, 1996; Karasek &
(Larocque, Brisson, & Blanchet, in press) from both Theorell, 1990), but differential effects of job
random population survey and a white-collar survey characteristics are noted. Measures of exhaustion and
from Quebec, Canada. A 1993 large-scale sample in burnout are more consistently associated with high
the United States (Amick, Mangione, & Wu, 1998) psychological demands, whereas depression and
reported JCQ scales to be reliable, as well as scale anxiety measures are more strongly associated with
structure confirmation, but some scales differ signifi- low decision latitude.
cantly from the recommended JCQ format. Sante Occupational musculoskeletal injury prediction is
Quebec (1994) showed acceptable JCQ scale reliabili- reviewed by Bongers, de Winter, Kompier, and
ties in the Netherlands, but some factor structure Hildebrandt (1993), who found support for the
differences arose. predictive utility of the demand/control/support model,
particularly for upper extremity disorders. Many
additional studies using the demand/control model
Predictive Validity and JCQ scales have been undertaken since then,
including associations with pregnancy disorders
It is beyond the scope of this article to review the
(Brandt & Neilsen, 1992; Fenster et al., 1995)and
extensive research literature using the JCQ and
immune system disfunctions (Kawakami & Fujigaki,
JCQ-like scales to predict illness (much research is
1996; Peters et al., 1998).
based on similar, but not exactly equivalent scales).
Comprehensive reviews are presented by Marmot and
Theorell (1988), Kristensen (1989), Schnall and
JCQ Measurement and Administrative Issues
Landbergis (1994), Kristensen (1995), Kasl (1996),
and Tbeorell and Karasek (1996). However, in
summary, it can be stated that the JCQ scales and JCQ Administration
JCQ-like scales demonstrate substantial predictive
validity with respect to stress-related chronic disease The JCQ is designed for self-administration and
in international and U.S. research. has often been included as a section in other
Job strain and heart disease associations constitute questionnaire instruments in which a short introduc-
the broadest base of empirical support for the model. tory sentence about how to respond to the questions is
JCQ scales or similar scales associate significantly included. The completion time is short, approxi-
with cardiovascular mortality using a wide range of mately 15 min for the full recommended version.
methodologies. Landsbergis (augmenting his earlier Professional assistance, such as the research person
review [Schnall & Landsbergis, 1994] by personal reviewing the instructions, has also often occurred.
communication, December 1997) tabulated 72 pub- In addition to the standard JCQ questions, JCQ
lished studies of cardiovascular disease (CVD) or users are encouraged to add their own specific
CVD risk factors testing associations with job strain "umbrella questions" that refer to the measurement
using JCQ-like scales. Of the 36 studies investigating of specific job conditions in the surveyed work sites.
CVD or mortality, over two thirds showed positive Although the umbrella questions would differ be-
associations (i.e., either all significant or mixed tween studies, they could be factor analyzed with the
significant positive results) with job strain, and many other JCQ questions and correlated with the standard
of these were positive cohort studies. Landsbergis's JCQ scales used as reference points.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jcq-120618163639-phpapp01/85/JCQ-SCALE-9-320.jpg)












![SPECIAL SECTION: JOB CONTENT QUESTIONNAIRE 349
debate about self-report bias in the use of question- availability of vocabulary about precise category
naire-based job assessment. The issue is whether boundaries in each area of job experience.
self-reported variations on the scales correspond to However, the critique of potential bias in the scales
the "objective reality" that other knowledgeable (Brief, Burke, George, Robinson, & Webster, 1988;
observers would also report, or whether there is Ganster & Schaubroek, 1991) can also easily be
something idiosyncratic about the observer himself or overdone, leading to Type II statistical errors. The
herself that make such reports unreliable as an current form of this critical position claims that
assessment of the external environment--wbether JCQ-like job assessment methodologies really tap a
this be due to demographic status (e.g., aging or personality-based "negative affect factor" that ac-
gender), national culture, or enduring characteristics counts for both respondents' negative descriptions
of the personality. As an estimate of these person- about their job and their negative emotional state.
based effects, demographic status adds an average of Take, for example, a common but potentially
7% of the variance in the job scales (as covariates to misleading application of the "triviality trap." In this
occupation in U.S. national studies; Schwartz et al., trap, the typical associations between the job
1988). In Table 3 we showed interstudy differences characteristics and mood states, when assessed by
that could be presumed to reflect national differences questionnaires, are spuriously inflated by common
in culture with respect to work explain an average of questionnaire response behavior for both sets of
5% of the scale variance. The suggestion of the variables, which then accounts for the observed
present study, then, further narrows down the associations. The recommended solution proposed in
alternative, person-based explanations to the prima Brief et al. (1988) and Watson and Pennebaker (1989)
facie claim that the job scales measure the work and endorsed by Ganster and Schanbroeck (1991) is
environment. The question now remains whether the that these associations should be controlled for
vast remaining portion of the variance in the scales person-based measures of negative affect. This cure is
exists due either to the job or to pure personality. worse than the problem itself. It potentially creates a
problem by overcontrolling the associations. Claim-
There is no doubt much random error variance in the
ing the negligible remaining relationship is clear
scales (assessed in Table 4), but this is not of
evidence of a no-job/well-being association and is a
consequence to this debate because it will not
"triviality turnaronnd."
contribute to causal associations in either direction.
Consider application of this trap with specific
Because the debate seems to have come down on the
questions used in JCQ research: "My job requires
side of psychological characteristics attributed to
working fast" and "There is little decision freedom
persons as the source of such scale variance, we now
on my job" in the job measure category; and, in the
reassess the self-report bias critique.
dependent variable category, psychological strain and
The critique of self-reports begins with cautions
mood reports such as "The future looks hopeless"
about methodological weaknesses of questionnaire
and "I have sleeping difficulties" (of course, the
reports. Two problems in particular limit causal
alternative outcome for much of the above-cited
interpretations in this area: (a) individual differences
research is quite objective coronary heart disease
in perceptions of stressors exist and (b) common- diagnoses).
method variance could inflate associations between The negative affect control solution is often based
job measures and self-reported well-being measures. on other questionnaires that assess trait-based nega-
This later problem varies by scale, however: poten- tive affect (often trait anxiety has been used) that have
tially significant for psychological demand scales very much in common with m o o d state measurement
(where Hackman and Lawler, 1971; Frese and Zapft, instruments, which are the studies' primary dependent
1988; and Kirmeyer and Dougherty, 1988, show variable. In fact, they are often based on the very
worker-observer reliabilities of .32, .35, and .35, same questionnaire items with different formats and
respectively), and probably insignificant for decision instructions (Spielberger, Gorsuch, Lushene, Vagg, &
latitude scales (where Hackman and Lawler, 1971; Jacobs, 1983; Spielberger & Sydeman, 1994, p. 296).
Frese and Zapft, 1988; and Caiffm, 1983, show For illustrative purposes, consider the trait measure
worker-observer reliabilities of .71, .54, and .65 to of anger: I am [generally feel] quick tempered" and
.75, respectively). This limitation may relect the "feel infuriated when I do a good job and get a poor
magnitude of cognitive assessment required by the evaluation." Suppose the state anger questions: "I am
questionnaire format (Frese & Zapft, 1988), and also furious [right now]" and "I am mad" measure the
the degree of worker familiarity with or the dependent variable. In the negative-affect adjustment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jcq-120618163639-phpapp01/85/JCQ-SCALE-28-320.jpg)
![350 KARASEK ET AL.
solution, job/well-being and state associations are states and reporting pattern. Given the systematic and
controlled with trait measures of this type. In this objectively linked associations between job character-
example, an association between "My job requires istics and occupation around the world in findings
working fast" and "[Right now], I am furious," such as those reviewed above, and negative well-
controlled by "[Generally] I feel mad" used as a being associations in literature of many of the same
measure of negative affect. Finding that most of the countries cited in Part I, this critique necessarily takes
association disappears, researchers in this tradition on further implication that may represent a heavy,
have often concluded that most of the variance can be unexpected burden of proof for its advocates. The
accounted for by negative affectivity--a personality implicationis that the industrial world's low-decision-
trait--and not by job conditions. However useful latitude populations are generally afflicted with the
such trait measures may be as approximations in other consistent, social-class-based personality deficit of
research contexts, for the close cause-and-effect negative affectivity--which compels such people to
simultaneous control of this research context, we systematically complain--but who have "objec-
would not endorse the validity of claims to "pure tively" nothing to complain about--in their similar
state" and "pure trait" measurement status, even jobs in the United States, in Japan, in Canada, in
when other research has confirmed state-trait differen- Sweden, in the Netherlands, and so on.
tiation, as in the case of Spielberger et al.'s scales. It is The critiques of self-report job analysis scales may
certainly not clear that they have been endorsed by be having the unfortunate effect of taking the heat off
their originators for such purposes. The trait measures the world's business leaders to humanize work
can easily include state components that overcontrol environments. Humane-sounding work-design
the associations and cause "I3rpeII errors. The result is buzzwords were commonly used in many "reengineer-
an underestimation of job effects, an understatement ing" job change programs in the United States in the
of "valid" disease state prevalence, and a false early 1990s. However, these changes appear to have
attribution of disease state to person characteristics. had very negative impacts on broad groups of
Indeed, recent research (Dollard & Winefield, workers, particularly because of unexamined psycho-
social consequences. The discussion of these topics,
1998) that explicitly test for the possibility of such
sometimes emanating from U.S. business schools,
overcontrol with negative affectivity, using job
which in particular should know the dangers, seems
experience cohorts to test whether negative affectivity
instead to be preoccupied with the above critique of
is itself associated with duration of exposure to
psychosocial research.
stressful job circumstances, finds that it is. This type
In conclusion, psychosocial researchers have admit-
of finding even further undermines the interpretation
ted to limitations of these measures. It is now time for
that controlling for such measures should be used as a
the detractors to reassess them in light of broad
basis for rejecting associations between job and
workplace reality that is presently evolving. Research-
well-being: The presumably "pure" traits are not pure
ers in this area need to do as much as they can to
methodologically but are also impure in that short-
validate a social and political discussion, as well as
term measurements can be partly the long-term
scientific discussion of these topics, which are
results of environmentalexperience at work (longitu-
affecting so many people, now on a global scale.
dinal effects noted in Johnson et al., 1996; Karasek &
Theorell, 1990). Certainly, many of these personality
trait measures are at least as contaminated by References
common-method variance problems as the job
Amick, B., Mangione, T., & Wu, V. (1998). Work
characteristics they attempt to purify. They are also organization and drinking: A test of two psychosocial
usually assessed in samples in which there is limited exposure models. Manuscriptsubmittedfor publication.
variance in environmental stressors, which also Berggren, C. (1992). Alternatives to lean production: Work
undermines associations with job measures. For good organization in the Swedish auto industry. Ithaca, NY:
ILR Press.
reasons, ethical committees ensure that laboratory Bongers, P. M., de Winter, C. R., Kompier, M. A. J., &
stressors are far from the potency of truly difficult Hildebrandt, V. H. (1993): Psychosocialfactors at work
work situations, which also limits the likelihood of and musculoskeletal disease. Scandinavian Journal of
discovery of social environmenteffects here. Work, Environment and Health, 19, 297-312.
The negative affect critique of job and well-being Bosma, H., Peter, R., Siegrist,J., & Marmot,M. (1998). Two
alternative job stress models and the risk of coronary
associations, of course, implies its own causal heart disease. American Journal of Public Health, 88,
hypothesis: Personality causes the negative emotional 68-74.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jcq-120618163639-phpapp01/85/JCQ-SCALE-29-320.jpg)
![SPECIAL SECTION: JOB CONTENT QUESTIONNAIRE 351
Bourbonnals, R., Brisson, C., Moisan, J., & Vezina, M. automobile industry. International Journal of Industrial
(1996). Job sla'ain and psychological distress in white- Ergonomics, 20, 371-388.
collar workers. Scandinavian Journal of Work Environ- Ganster, D. G., & Schaubroeck, J. (1991). Work stress and
ment and Health, 22, 139-145. employee health. Journal of Management, 17, 235-271.
Brandt, L. P., & Neilsen, C. V. (1992). Job stress and adverse Gleckman, H. (1995, November 20). Rewriting the social
outcome of pregnancy: A causal link or recall bias? contract. Business Week, p. 70.
American Journal of Epidemiology, 135, 302-311. Griffen, R. W. (1983). Objective and social sources of
Brief, A., Burke, M., George, J., Robinson, B., & Webster, J. information in task redesign: A field experiment.
(1988). Should negative affectivity remain an unmea- Administrative Science Quarterly, 28, 184-200.
sured variable in the study of job stress? Journal of Habermas, J. (1984). Theory of communicative active action
Applied Psychology, 73, 207-214. (Vol. 1). Cambridge, England: Polity Press.
Bfisson, C., Dion, G., Blanchet, C., Moisan, J., Guinont, C., Hackman, J. R., & Lawler, E. E. (1971). Employee reactions
& Vezina, M. (1998). Reliability and validity of the to job characteristics. Journal of Applied Psychology, 55,
French version of the 16-item psychological demand and 259-286.
decision latitude scale of the Karasek Job Content Hall, E. M. (1994). Women, work, and health: Employment
Questionnaire in white-collar workers. Manuscript sub- as a risk factor for coronary heart disease. Journal of
mitted for publication. Preventive Cardiology, 4, 365-384.
Brisson, C., Laroque, B., Bourbonnais, R., Dion, G., Haratani, T., Kawakami, N., Kobayashi, E, Ishizaki, M.,
Moisan, J., Blanchet, C., Guimont, C., Vinet, A., Vezina, Hayashi, T., Masumoto, T., Hiro, H., Aizawa, Y.,
M., Dagenais, G., & Laflamme, N. (1998, August). The Hashimoto, S., & Araki, S. (1997, August). Work stress,
Job Content Questionnaire (JCQ) in the Canadian depression, accidents and sick absence: Preliminary
samples. Paper presented at the First International findings from the Japan Work Stress Cohort Study. Paper
Conference on Psychosocial Factors at Work, Copenha- presented at the 15th Asian Conference on Occupational
gen, Denmark. Health, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Cannon, W. B. (1914). The emergency function of the Hochschild, A. (1983). The managed heart: Commercializa-
adrenal medulla in pain and the major emotions. tion of human feeling. Berkeley: University of California
American Journal of Physiology, 33, 356-372. Press.
de Jonge, J., & Kompier, M. A. J. (1997). A critical Houtman, I. (1995, May). Reliability and validity of the
examination of the demand-control-support model from a Dutch version of the Karasek Job Content Questionnaire.
work psychological perspective. International Journal of Paper presented at the NIOSH/APA Conference on
Stress Management, 4, 235-258. Stress, Work and Health, Washington, DC.
Dhondt, S. (1994). Monitoring occupational health and Johansson, S. (1971). Om LevnadsnivdandersOkningen [On
safety in Europe: Time constraints and its implications. the national survey of level of living]. Stockholm:
Leiden, The Netherlands: TNO-Gezondheidsonderzoek Allmamma F6flaget.
(Netherlands Institute for Health and Prevention). Johnson, J. V. (1986). The impact of workplace social
Dhondt, S. (1998). Time constraints and autonomy at work support, job demands and work control upon cardiovascu-
in the European Union. Dublin, Republic of Ireland: lar disease in Sweden. Unpublished doctoral dissertation,
European Foundation for the Improvement of Living and Johns Hopkins University.
Working Conditions. Johnson, J. V. (1989). Collective control: Strategies for
Dollard, M. E, & Winefield, A. H. (1998). A test of the survival in the workplace. International Journal of
demand-control/support model of work stress in correc- Health Services, 19, 469--480.
tional officers. Journal of Occupational Health Psychol- Johnson, J. V., & Hall, E. M. (1988). Job strain, work place
ogy, 3, 243-264. social support, and cardiovascular disease: A cross-
Fenster, L., Schaefer, C., Mathur, A., Hiatt, R. A., Pieper, C., sectional study of a random sample of the Swedish
& Hubbard, A. E. (1995). Psychologic stress in the working population. American Journal of Public Health,
workplace and spontaneous abortion. American Journal 78, 1336-1342.
of Epidemiology, 142, 117-183. Johnson, J. V., & Johansson, G. (Eds.). (1991). The
Fox, M. L., Dwyer, D. J., & Ganster, D. G. (1993). Effects of psychosocial work environment: Work organization,
stressful job demands and control on physiological and democratization and health. In Essays in memory of Bertil
attitudinal outcomes in a hospital setting. Academy of Gardell. Amityville, NY: Baywood.
Management Journal, 36, 289-318. Johnson, J. V., & Stewart, W. (1993). Measuring work
Frankenhaeuser, M., & Johansson, G. (1986). Stress at work: organization exposure over the life course with a
Psychobiological and psychosocial aspects. International job-exposure matrix. Scandinavian Journal of Work,
Review of Applied Psychology, 35, 287-299. Environment and Health, 19, 21-28.
Frese, M., & Zapft, D. (1988). Methodological issues in the Johnson, J. V., Stewart, W., Friedlund, P., Hall, E. M., &
study of work stress: Objective vs. subjective measure- Theorell, T. (1990). Psychosocial job exposure matrix:
ment of work stress and the question of longitudinal An occupationally aggregated attribution system for
studies. In C. L. Cooper & R. Payne (Eds.), Causes, work environment exposure characteristics (Stress Re-
coping and consequences of stress at work (pp. 375-411). search Report No. 221). Stockholm: National Institute for
New York: Wiley. Psychosocial Factors and Health.
Frieling, E., Freiboth, M., Henniges, D., & Saager, C. Johnson, J. V., Stewart, W., Hall, E. M., Fredlund, P., &
(1997). Effects of team work on the working conditions of Theorell, T. (1996). Long-term psychosocial work
short cycled track work: A case study from the European environment and cardiovascular mortality among Swed-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jcq-120618163639-phpapp01/85/JCQ-SCALE-30-320.jpg)
![352 KARASEK ET AL.
ish men. American Journal of Public Health, 86, telecommunication and electric power companies in
324-331. Japan: Reliability and validity of the Japanese version of
Karasek, R. A. (1976). The impact of the work environment Job Content Questionnaire. International Journal of
on life outside the job. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Behavioral Medicine, 2, 358-375.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Kawakami, N., Tanigawa, T., Araki, S., Nakata, A., Sakurai,
Karasek, R. A. (1979). Job demands, job decision latitude, S., Yokoyama, K., & Morita, Y. 0997). Effects of job
and mental strain: Implications for job redesign. Adminis- strain on helper-inducer (CD4 +CD29 + ) and suppressor-
trative Science Quarterly, 24, 285-308. inducer (CD4+CIMSRA+) T cells in Japanese blue-
Karasek, R. A. (1985). Job Content Questionnaire and collar workers. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, 66,
user's guide. Lowell: University of Massachusetts 192-198.
Lowell, Department of Work Environment. Kirmeyer, S. L., & Dougherty, T. W. (1988). Workload,
Karasek, R. A. (1990). Lower health risk with increased job tension, and coping: Moderating effects of supervision
control among white-collar workers. Journal of Occupa- support. Personnel Psychology, 41, 125-139.
tional Behaviour, 11, 171-185. Kristensen, T. S. (1989). Cardiovascular diseases and the
Karasek, R. A. (1991). The political implications of work environment: A critical review of the epidemiologic
psychosocial work redesign: A model of the psychosocial literature on chemical factors. Scandinavian Journal of
class structure. In J. V. Johnson & G. Johansson (Eds.), Work, Environment and Health, 15, 245-264.
The psychosocial work environment: Work organization, Kristensen, T. S. (1995). The demand-control-support
democratization, and health (pp. 163-190). Amityville, model: Methodological challenges for future research.
NY: Baywood. Stress Medicine, 11, 17-26.
Karasek, R. A. (1997). Demand/control model: A social, Kristensen, T. S. (1996). Job stress and cardiovascular
emotional, and physiological approach to stress risk and disease: A theoretical critical review. Journal of Occupa-
active behavior development. In ILO encyclopedia of
tional Health Psychology, 1, 246-260.
occupational health and safety. Geneva: ILO.
Landsbergis, P. A., Schnall, P. L., Warren, K., Schwartz,
Karasek, R. A. (1998). The new work organization,
J. E., & Picketing, T. (1994). Association between
conducive production, and work quality policy. In M.
ambulatory blood pressure and alternative formulations
Marmot (Ed.), Labor market changes and job insecurity:
of job strain. Scandanavian Journal of Work Environment
A challenge for social weUfare and health promotion (pp.
and Health, 20, 349-363.
78-105). Copenhagen: WHO/Europe.
Karasek, R. A., Baker, D., Marxer, F., Ahlbom, A., & Larocque, B., Brisson, C., & Blancbet, C. (in press).
Theorell, T. (1981). Job decision latitude, job demands, Coherence interne, validite factorielle et validite discrimi-
and cardiovascular disease: A prospective study of nante de la traduction francaise des EcheUes de demande
Swedish men. American Journal of Public Health, 71, psychologique et de latitude decisionnelle du "Job
694-705. Content Questionnaire" de Karasek [Internal consistency,
Karasek, R. A., Schwartz, J., & Pieper, C. (1983). Validation factorial validity, and discriminant validity of the French
of a survey instrument for job-related cardiovascular version of the Karasek Job Content Questionnaire]. Revue
illness. New York: Columbia University, Department of d'Epidemiologie et de Sante Publique.
Industrial Engineering and Operations Research. Lohr, S. (1996, December 29). Though upbeat on the
Karasek, R. A., & TheoreU, T. (1990). Healthy work: Stress, economy, people still fear for their jobs. New York I~mes, p.
productivity, and the reconstruction of working life. New 26.
York: Basic Books. Marmot, M. G., Bosma, H., Hemingway, H., Brunner, E., &
Karasek, R. A., Theorell, T., Schwartz, J., Schnall, P., Pieper, Stansfeld, S. (1997). Contribution of job control and other
C., & Michela, J. (1988). Job characteristics in relation to risk factors to social variations in coronary heart disease
the prevalence of myocardial infarction in the U.S. HES incidence. Lancet, 350, 235-239.
and HANES. American Journal of Public Health, 78, Marmot, M. G., & Tbeorell, T. (1988). Social class and
910-918. cardiovascular disease: The contribution of work. Interna-
Karasek, R. A., Triantis, K., & Chaudhry, S. (1982). tional Journal of Health Services, 18, 659--674.
Co-worker and supervisor support as moderators of Marshall, N., Barnett, R., & Sayer, A. (1997). The changing
associations between task characteristics and mental workforce, job stress, and psychological distress. Journal
strain. Journal of Occupational Behavior, 3, 147-160. of Occupational Health Psychology, 2, 99-107.
Kasl, S. V. (1989). An epidemiological perspective on the Meshkati, N., Hancock, P., & Rahami, M. (1990). Tech-
role of job control in health. In S. Sauter, J. J. Hun~ll, & niques in mental workload assessment. In Ergonomic task
C. L. Cooper (Eds.), Job control and worker health analysis (pp. 65-93). London: Taylor & Francis.
(pp. 161-189). New York: Wiley. Nunnally, J. C., & Bernstein, I. H. (1994). Psychometric
Kasl, S. V. (1996). The influence of the work environment on theory (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
cardiovascular health: A historical, conceptual, and Orth-Gomer, K. (1979). Iscbemic heart disease and psycho-
methodological perspective. Journal of Occupational logical stress in Stockholm and New York. Journal of
Health Psychology, 1, 42-56. Psychosomatic Research, 23, 165-173.
Kawakami, N., & Fujigaki, Y. (1996). Reliability and Paoli, E (1997). Second European survey on working
validity of the Japanese version of Job Content Question- conditions, 1996. Dublin, Republic of Ireland: European
naire: Replication and extension in computer company Foundation for the Improvement of Living and Working
employees. Industrial Health, 34, 295-306. Conditions.
Kawakami, N., Kobayashi, E, Araki, S., Haratani, T., & Peters, M., Godaert, G. C. R., Ballieux, R. E., Brosschot,
Furui, H. (1995). Assessment of job stress dimensions I. E, Sweep, C. G. J., Swinkels, L. M. J. W., Vliet, M.,
based on the job demands-control model of employees of Heijman, C. J. (1998), Immune responses to experimental](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jcq-120618163639-phpapp01/85/JCQ-SCALE-31-320.jpg)
![SPECIAL SECTION: JOB CONTENT QUESTIONNAIRE 353
stress: Effects of mental effort and uncontrollability. Jacobs, G. (1983). Manual for the state-trait anxiety
Manuscript submitted for publication. inventory. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press.
Reuvers, M., de Jonge, J., Houtman, I., Bongers, P., & Spielberger, D., & Sydeman, S. (1994). State-trait anxiety
Kompier, M. (1998). Linear or nonlinear effects of job inventory and state--trait anger expression inventory. In
characteristics on subjective outcomes and sickness M. Maruish (Ed.), The use of psychological tests for
absence? Manuscript submitted for publication. treatment planning and outcome assessment (pp. 292-
Sante-Quebec. (1994). Et votre ca va? Rapport d'enquire 321). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
que coise sur la sante cardiovasculaire [What about your Stata statistical software: Release 5.0 [computer software].
heart? Report of the Quebec Cardiovascular Health (1997). College Station, TX: Stata
Survey]. Vieneuil, France: Govemement du Quebec. Theorell, T., & Karasek, R. A. (1996). Current issues relating
SAS Institute. (1990). SAS/Stat. user's guide (Version 6, 4th to psychosocial job strain and cardiovascular disease
ed). Cary, NC: Author. research. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 1,
Sauter, S. L., & Murphy, L. M. (1995). The changing face of 9-26.
work and stress. In S. L. Sauter & L. M. Murphy (Eds.), Theorell, T., Tsutsumi, A., Hallquist, J., Reuterwall, C.,
Organizational risk factors for job stress (pp. 1--6). Hogstedt, J., Fredlund, P., Emlund, N., & Johnson, J. V.
Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. (1998). Decision latitude, job strain, and myocardial
Schnall, P. L., & Landsbergis, P. A. (1994). Job strain and infarction: A study of working men in Stockholm.
cardiovascular disease. Annual Review of Public Health, American Journal of Public Health, 88, 382-388.
15, 381-411. Uehata, T. (1991). Long working hours and occupational
Schor, J. B. (1991). The overworked American: The stress-related cardiovascular attacks among middle-aged
unexpected decline of leisure. New York: Basic Books. workers in Japan. Journal of Human Ergology, 20,
Schwartz, J., Pieper, C., & Karasek, R. A. (1988). A 147-153.
procedure for linking job characteristics to health Vahtera, J., Pentti, J., & Uutela, A. (1996). The effect of
surveys. American Journal of Public Health, 78, objective job demands on registered sickness absence
904-909. spells: Do personal, social and job-related resources act
Seyle, H. (1976). The stress of life. New York: McGraw-Hill. as moderators? Work & Stress, 10, 286-308.
(Original work published 1936) Warren, (1998). Psychosocial, biomechanical, and organiza-
Shimomitzu, T., & Levi, L. (1992). Recent working life tional contributors to development of musculoskeletal
changes in Japan. European Journal of Public Health, 2, disorders in the Dutch Monitor Survey. Unpublished
76-86. doctoral dissertation, University of Massachusetts Low-
Siegrist, J. A. (1996). Adverse health effects of high-effort/ ell, Department of Work Environment.
low-reward conditions. Journal of Occupational Health Watson, D., & Pennebaker, J. (1989). Health complaints,
Psychology, 1, 27-41. stress, and disease: Exploring the central role of negative
Spielberger, C., Gorsuch, R., Lushene, R., Vagg, P., & affectivity. Psychological Review, 96, 234-254.
(Appendix follows on next page)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jcq-120618163639-phpapp01/85/JCQ-SCALE-32-320.jpg)