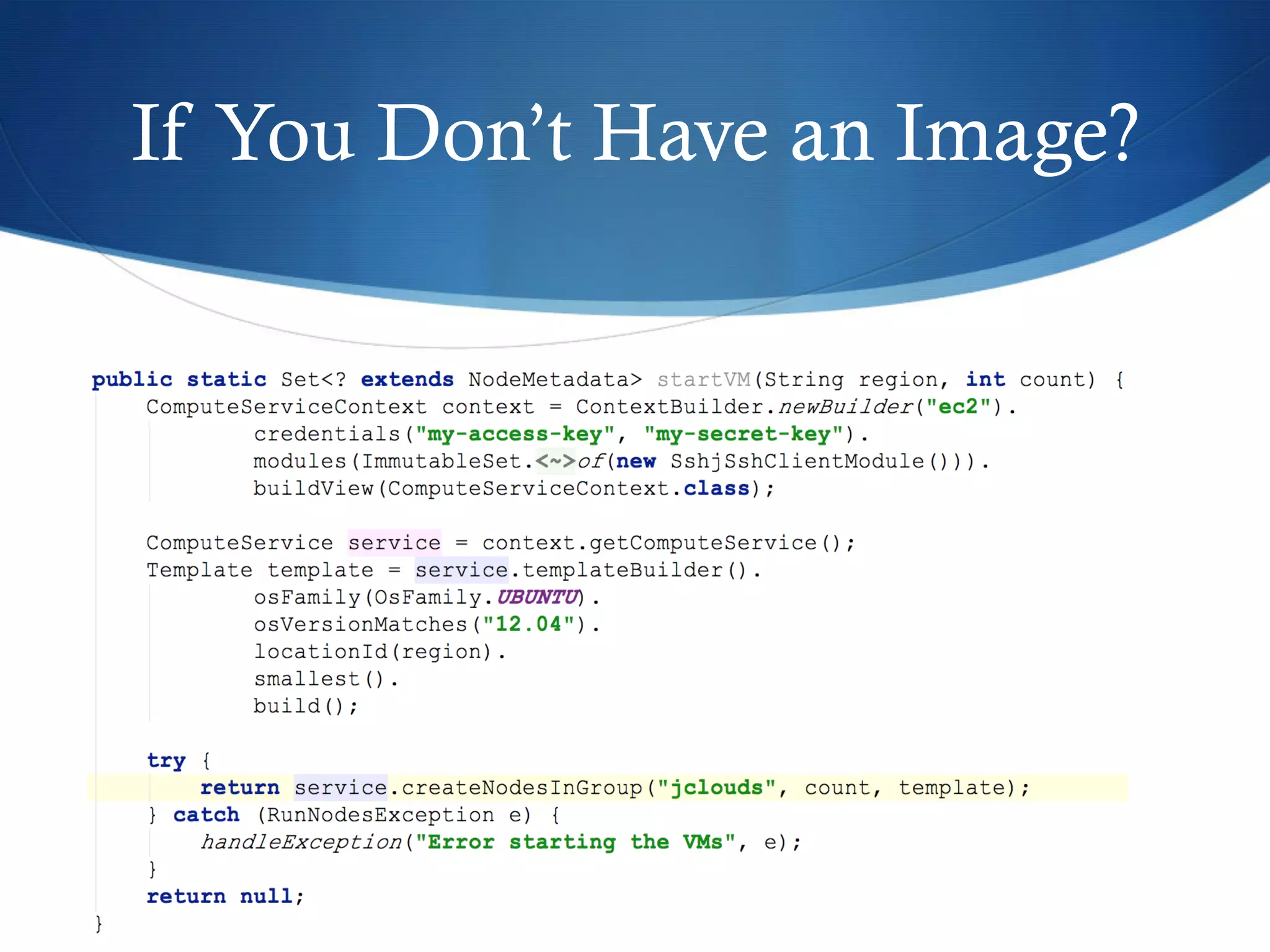
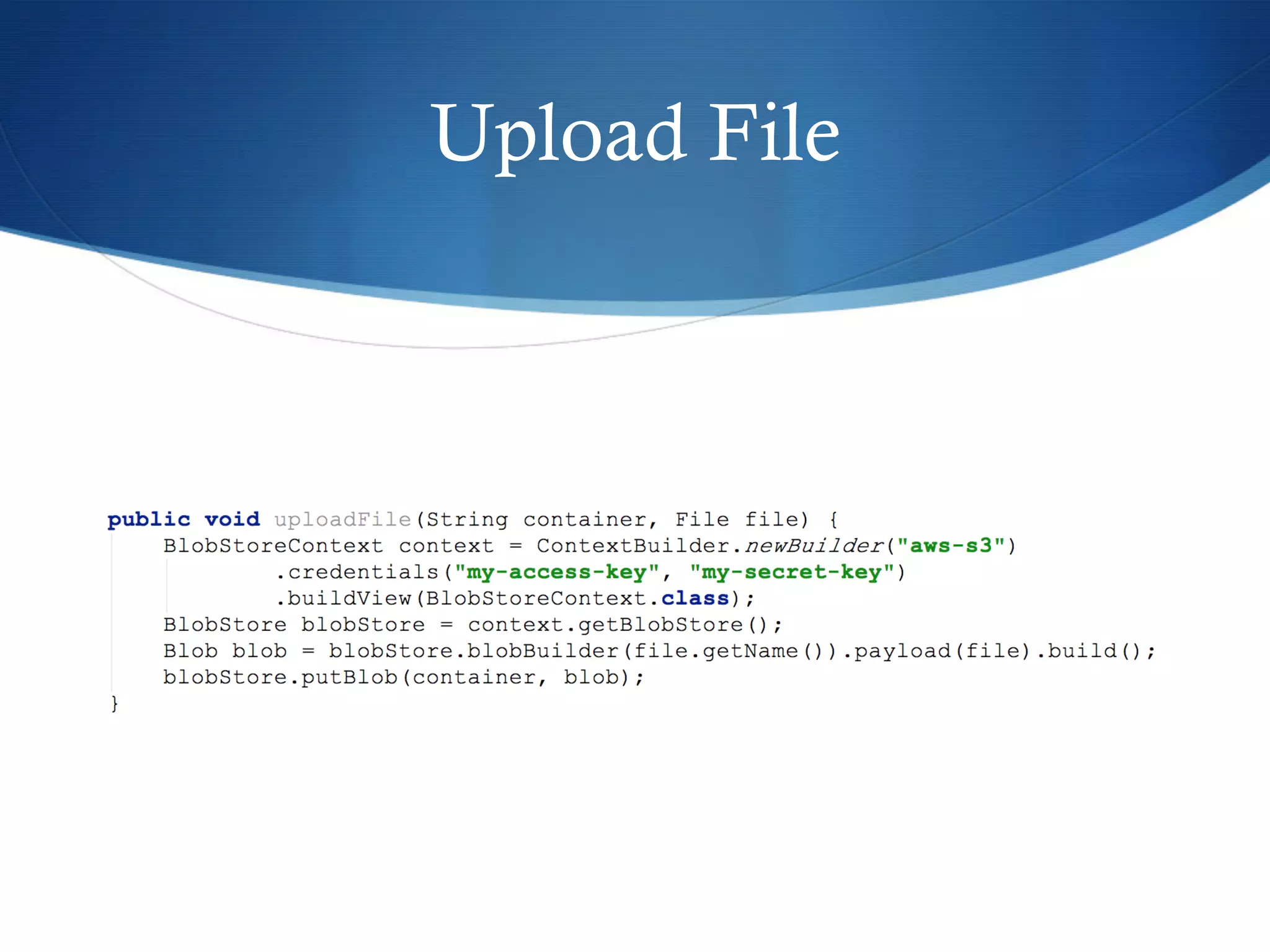
This document discusses Apache JClouds, an open source library that facilitates developing applications for a wide range of cloud providers. It allows developers to implement applications using JClouds APIs and run them on different cloud platforms without code changes, addressing challenges of cloud portability. The document outlines JClouds' compute and blob storage APIs, demonstrates its use, and notes its benefits like simplicity and portability while acknowledging limitations like documentation. It concludes that JClouds provides a simple approach for building portable cloud applications across multiple vendors.