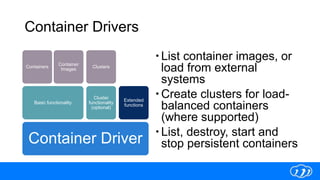
Libcloud is an open-source Python library designed to offer a unified interface for managing multiple cloud services across public and private providers, with over 200,000 monthly downloads. It supports various cloud functionalities including IaaS, DNS, storage, and load balancing, and is evolving to include container management APIs. The document highlights the need for a container API and provides examples of utilizing Libcloud to interact with container services such as Docker, Amazon ECS, and Google Kubernetes.