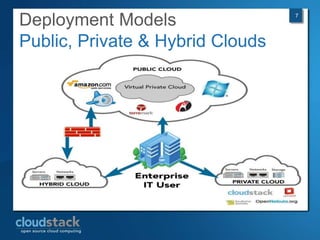
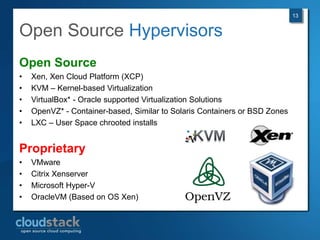
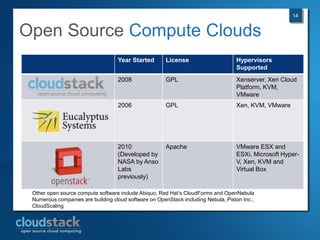
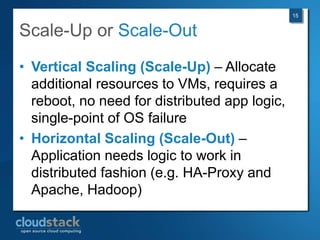
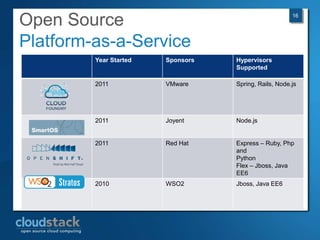
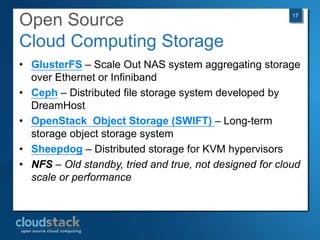
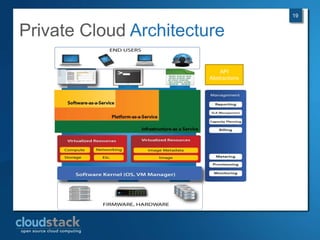
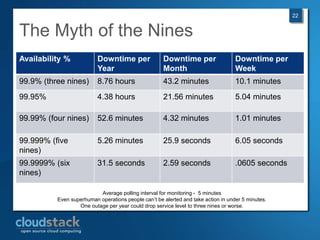
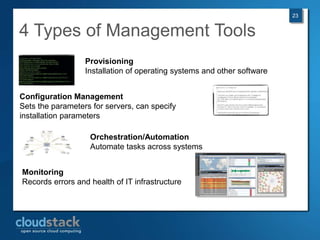
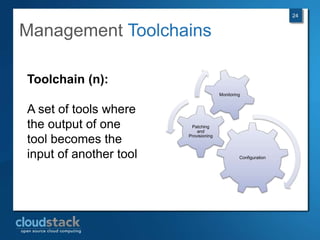
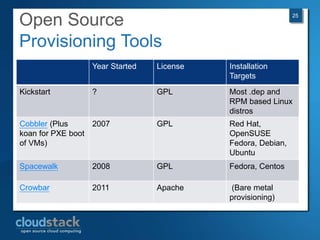
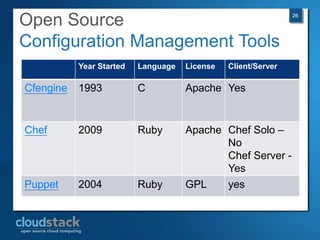
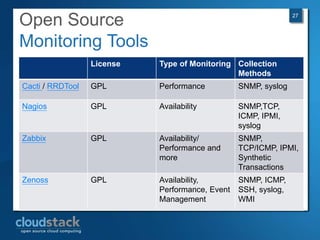
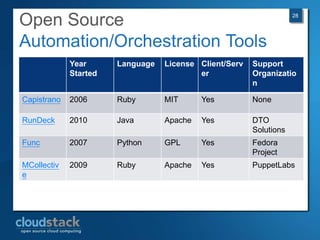
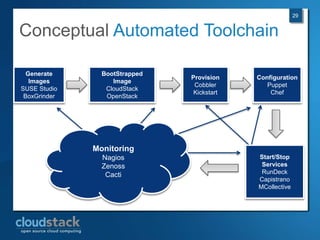
This document provides an overview of open source cloud computing presented by Mark R. Hinkle. It discusses key cloud concepts like virtualization formats, hypervisors, compute clouds, storage, platforms as a service, APIs, private cloud architecture, provisioning tools, configuration management, monitoring, and automation/orchestration tools. The presentation aims to educate about building clouds with open source software and managing them using open source management tools. Contact information is provided for Mark R. Hinkle for any additional questions.