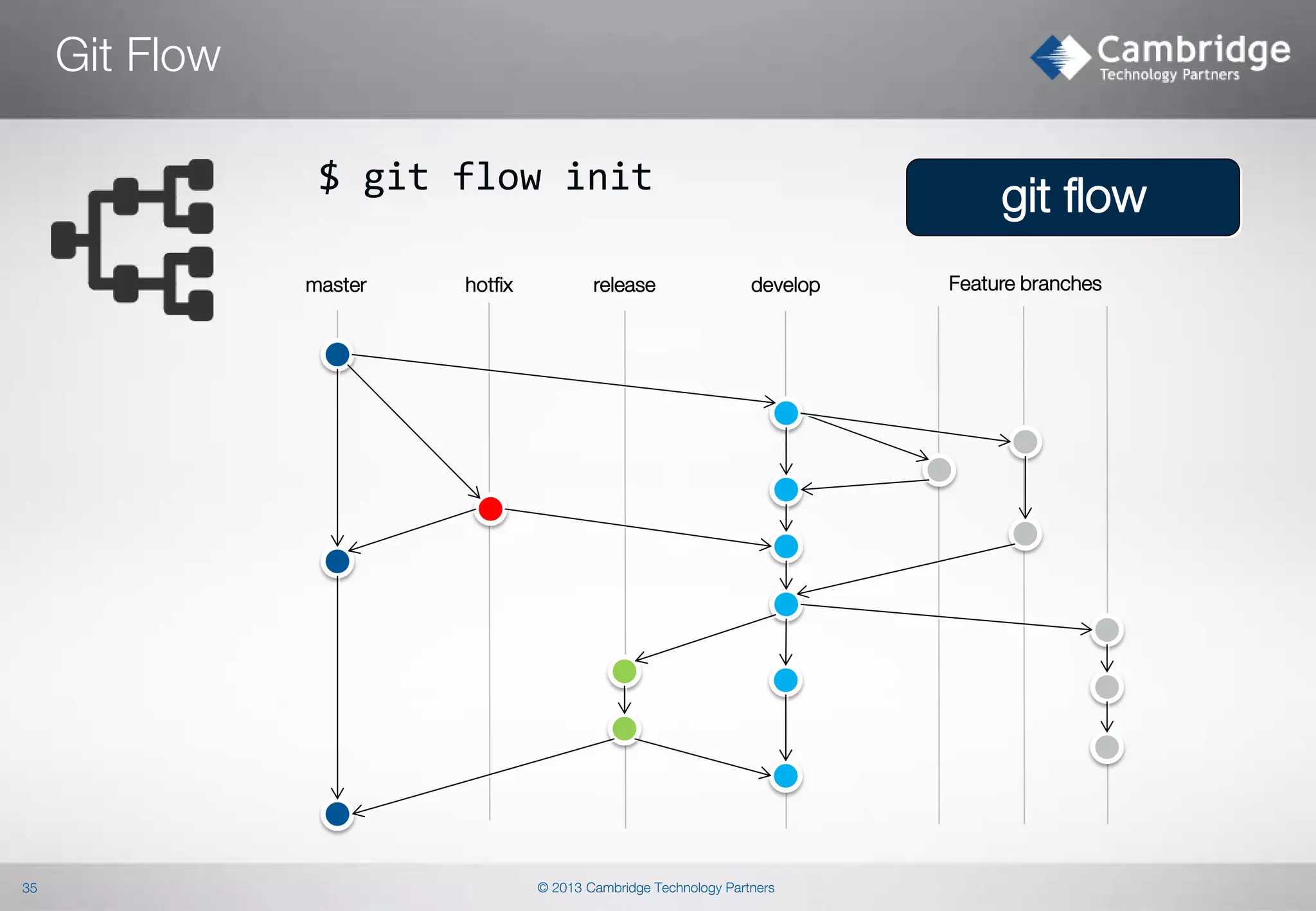
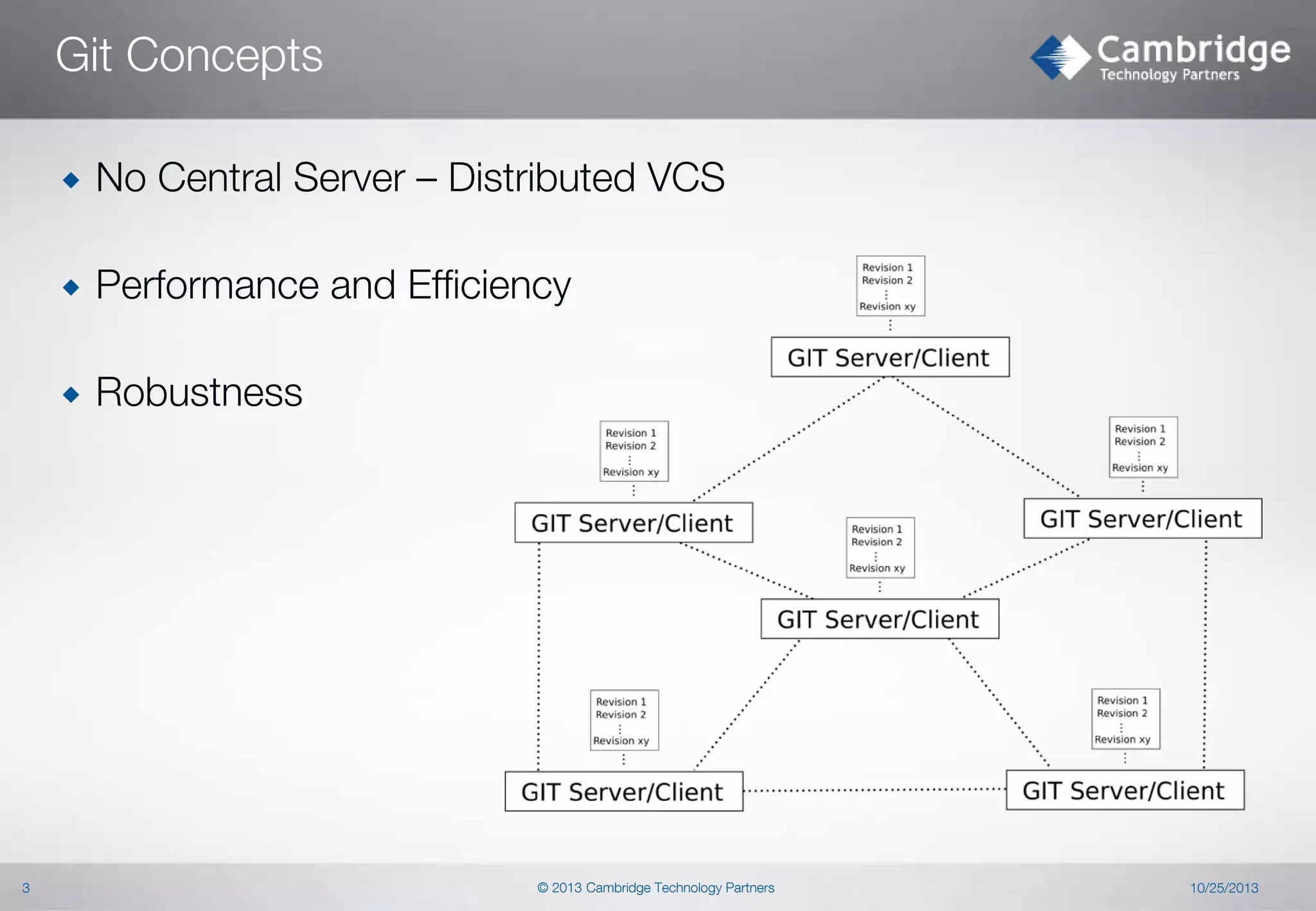
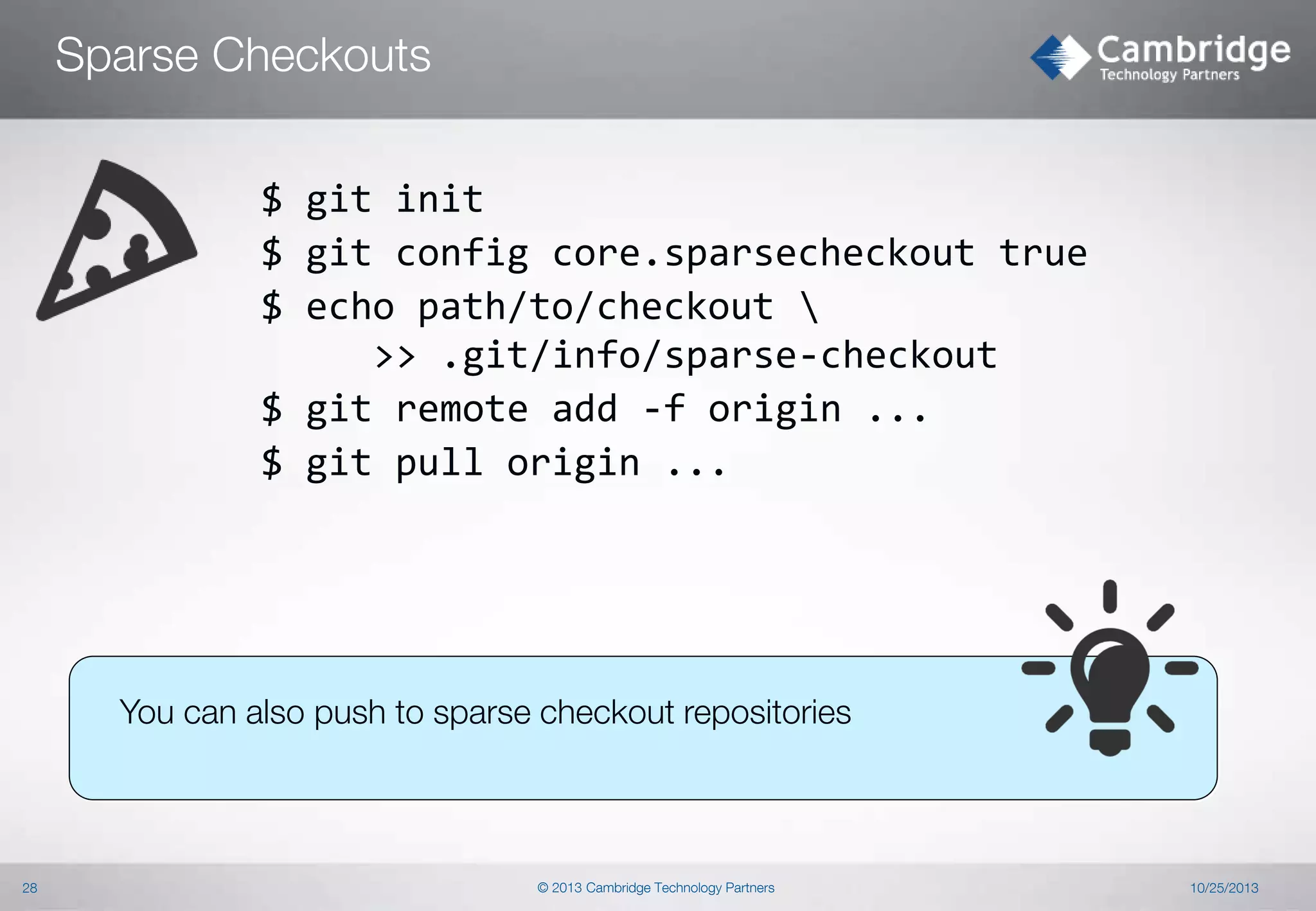
This document provides an overview of Git concepts and workflows. It discusses key Git concepts like its distributed nature, object model, and storage model. It also covers common Git commands and techniques like rebasing, cherry-picking, filtering, and recovering from mistakes. The document describes sharing code through archives, bundles, and notes. It discusses advanced topics such as sparse checkouts, orphan branches, and hooks. Finally, it briefly introduces Git workflows like Git Flow.





![All your base are belong to us
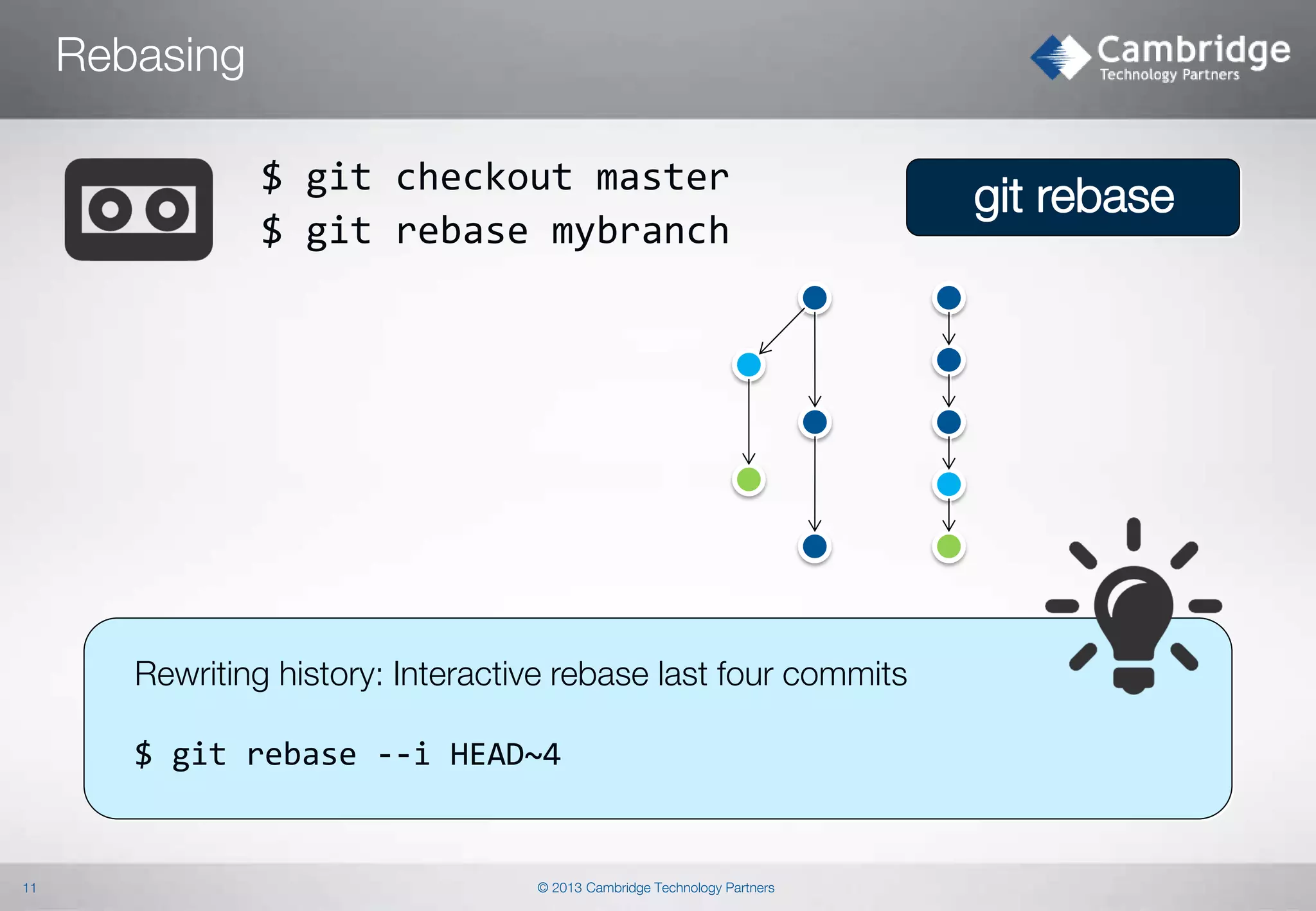
Objectives: Learn how interactive rebasing works.
Experiment with interactive rebase on selected branch
Reword
commit messages
Combine commits into one
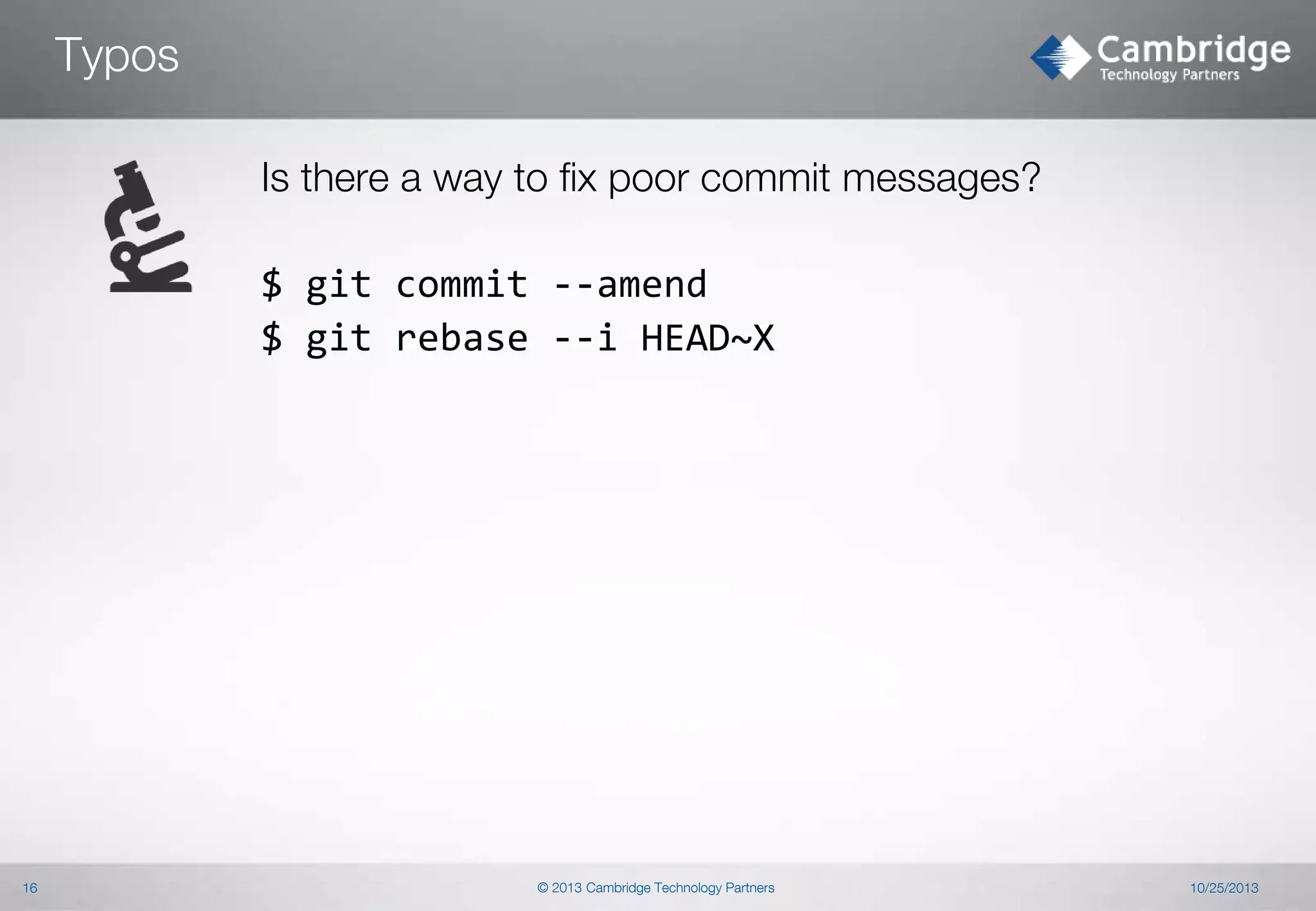
$ git rebase –i [commits range]
12
© 2013 Cambridge Technology Partners
10/25/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jazoon13-bartoszmajsak-gitworkshop-kungfu-131028074724-phpapp01/75/JAZOON-13-Bartosz-Majsak-Git-Workshop-Kung-Fu-12-2048.jpg)
![Cherry-pick
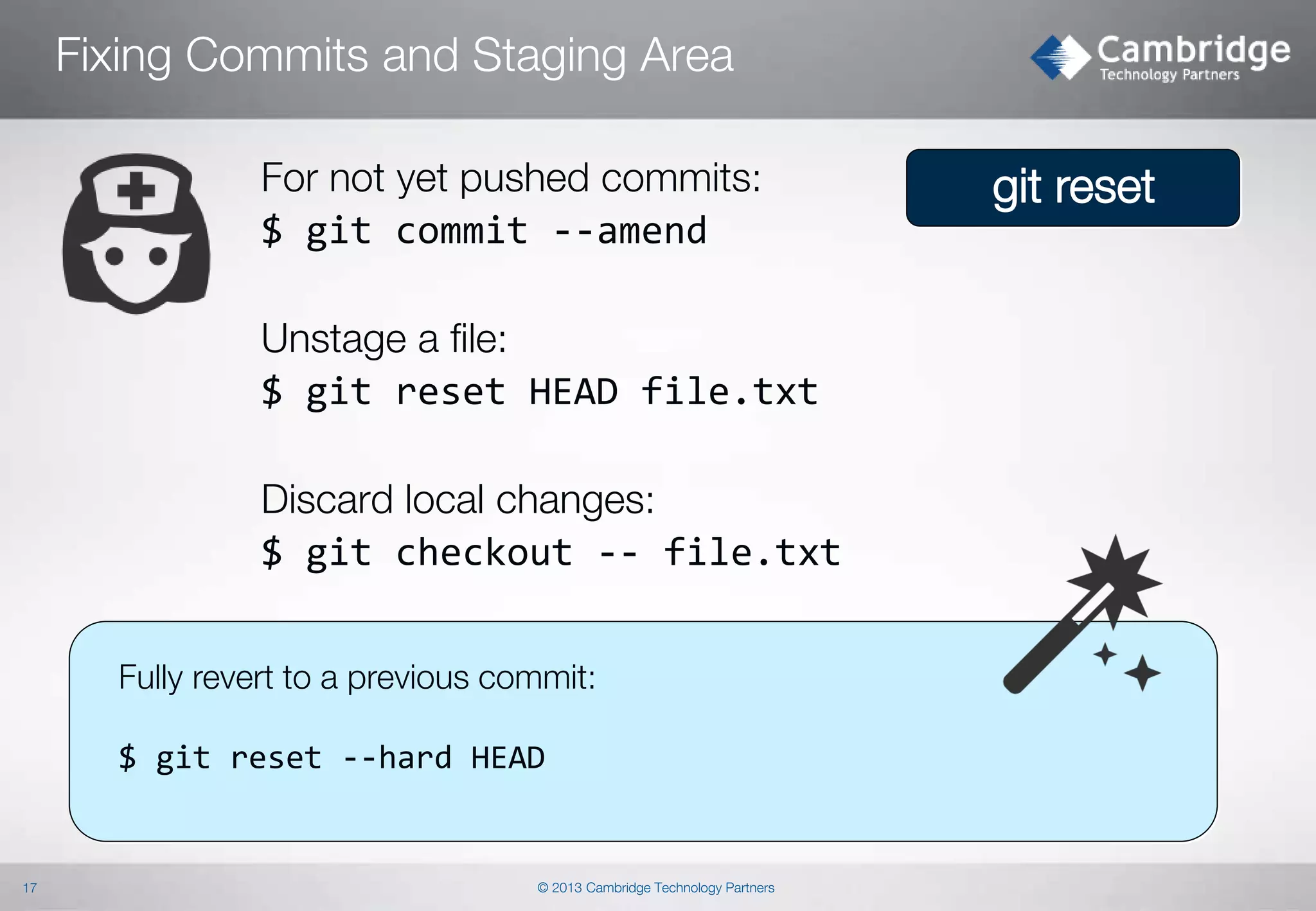
$ git cherry-pick [-x]
$ git cherry –v <other_branch>
Lets you check if given commit from other branch
has been already applied on the current branch
13
© 2013 Cambridge Technology Partners
Feature
Cherry-pick „replays” arbitrary commits onto
your current branch.
10/25/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jazoon13-bartoszmajsak-gitworkshop-kungfu-131028074724-phpapp01/75/JAZOON-13-Bartosz-Majsak-Git-Workshop-Kung-Fu-13-2048.jpg)



![Who broke the build?! - Pickaxe
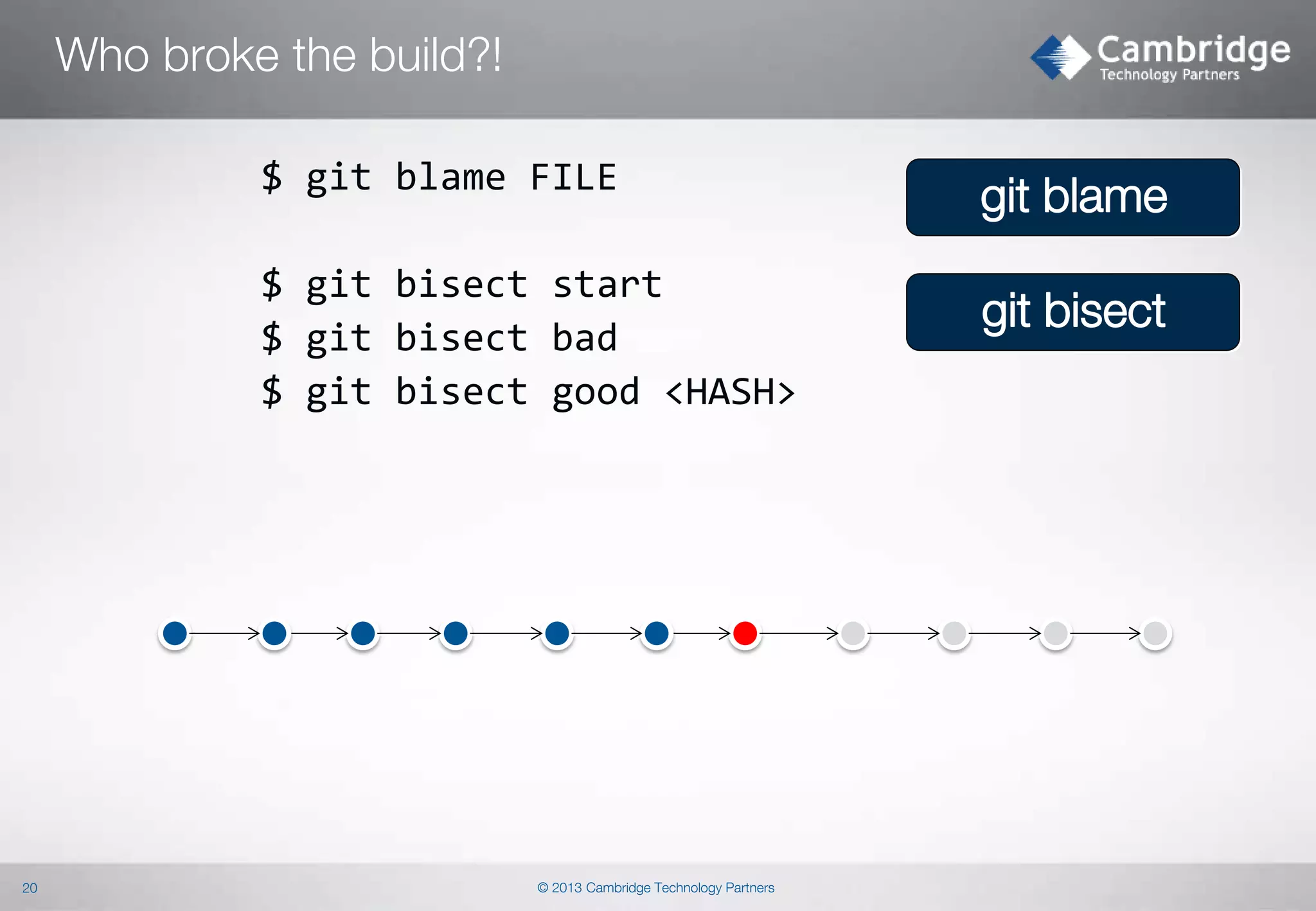
$ git log –S'search_term' [-p] <resource>
$ git log –G'regex'
git log –S|G
--name-status
--pickaxe-all
21
© 2013 Cambridge Technology Partners](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jazoon13-bartoszmajsak-gitworkshop-kungfu-131028074724-phpapp01/75/JAZOON-13-Bartosz-Majsak-Git-Workshop-Kung-Fu-21-2048.jpg)


![Orphan Branches
??
$ git checkout --orphan [branch]
$ git rm -rf *
Use for:
Documentation (combine with hooks or CI server!)
Resources
Have a look at the GitHub gh-pages for some ideas
what orphan branches can do.
29
© 2013 Cambridge Technology Partners
10/25/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jazoon13-bartoszmajsak-gitworkshop-kungfu-131028074724-phpapp01/75/JAZOON-13-Bartosz-Majsak-Git-Workshop-Kung-Fu-29-2048.jpg)