Embed presentation
Download to read offline
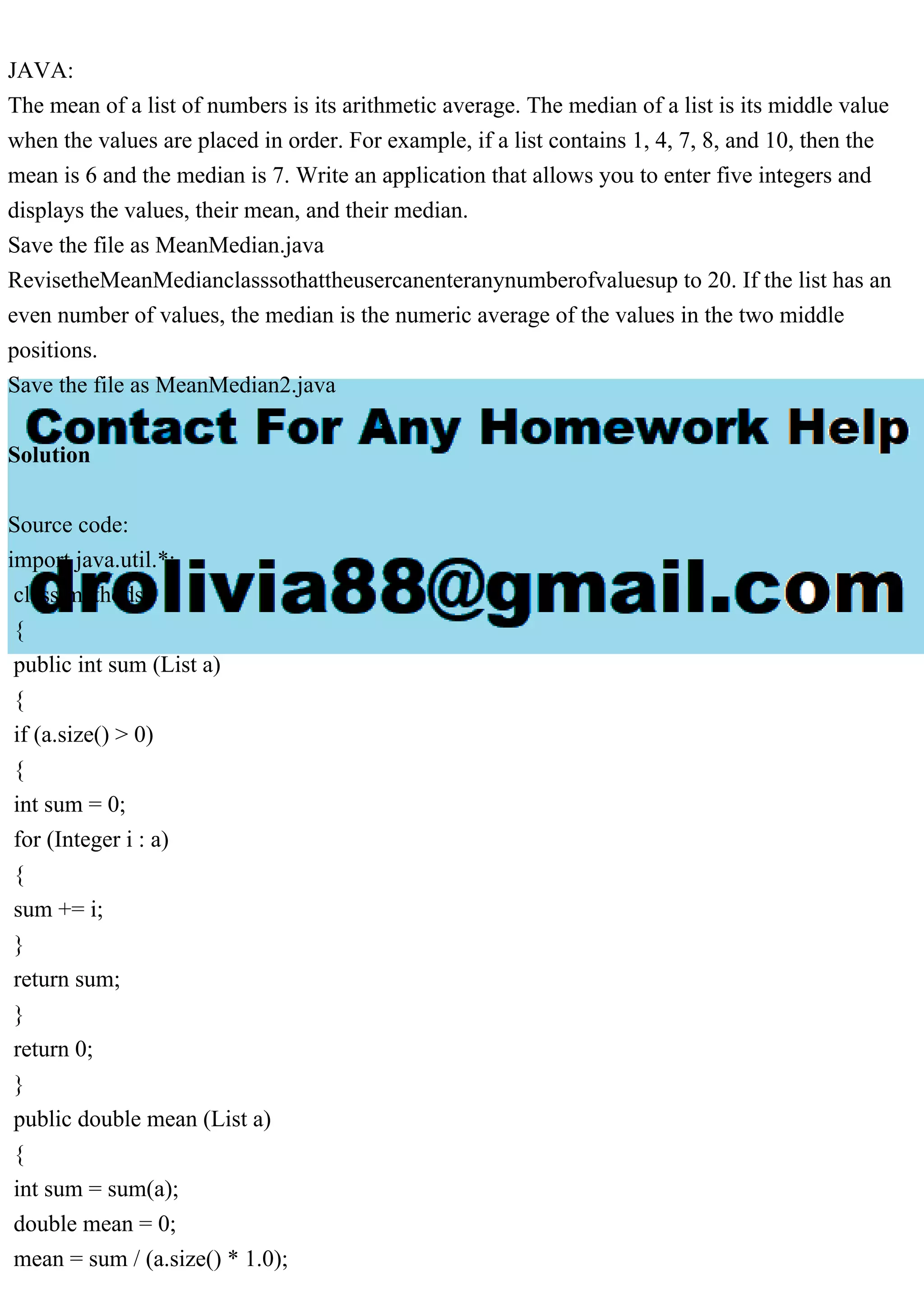
![return mean;
}
public double median (List a)
{
int middle = a.size()/2;
if (a.size() % 2 == 1) {
return a.get(middle);
}
else {
return (a.get(middle-1) + a.get(middle)) / 2.0;
}
}
class t {
public static void main (String[]args)
{
methods m = new methods();
List c = Arrays.asList(1,4,7,8,10);
Collections.sort(c); System.out.println(m.median(c)); System.out.println(m.mean(c));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javathemeanofalistofnumbersisitsarithmeticaverage-230704163833-5716d578/75/JAVAThe-mean-of-a-list-of-numbers-is-its-arithmetic-average-The-pdf-2-2048.jpg)
The document explains how to calculate the mean and median of a list of numbers in Java, providing an example list and its calculations. It instructs the reader to create an application that accepts five integers and displays their mean and median, followed by an updated version to allow up to 20 integers. A source code implementation is included for the calculations and main method.

![return mean;
}
public double median (List a)
{
int middle = a.size()/2;
if (a.size() % 2 == 1) {
return a.get(middle);
}
else {
return (a.get(middle-1) + a.get(middle)) / 2.0;
}
}
class t {
public static void main (String[]args)
{
methods m = new methods();
List c = Arrays.asList(1,4,7,8,10);
Collections.sort(c); System.out.println(m.median(c)); System.out.println(m.mean(c));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javathemeanofalistofnumbersisitsarithmeticaverage-230704163833-5716d578/75/JAVAThe-mean-of-a-list-of-numbers-is-its-arithmetic-average-The-pdf-2-2048.jpg)