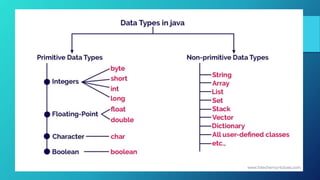
The document provides an overview of data types in Java, categorizing them into primitive and non-primitive types. It details eight primitive data types: boolean, byte, char, short, int, long, float, and double, along with their characteristics and example code snippets. Each data type is described in terms of its value range and default value, emphasizing their use in data manipulation.





![Example - 1
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int myAge = 25;
int votingAge = 18;
System.out.println(myAge >= votingAge);
// returns true (25 year olds are allowed to vote!)
}
}
Output:
true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypes-240718041615-34316400/85/DATA-TYPES-in-Python-done-by-Sanajai-of-MCA-7-320.jpg)

![Example - 1
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
byte myNum = 100;
System.out.println(myNum);
}
}
Output:
100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypes-240718041615-34316400/85/DATA-TYPES-in-Python-done-by-Sanajai-of-MCA-9-320.jpg)

![Example - 1
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
short myNum = 5000;
System.out.println(myNum);
}
}
Output:
5000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypes-240718041615-34316400/85/DATA-TYPES-in-Python-done-by-Sanajai-of-MCA-11-320.jpg)

![Example - 1
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int myNum = 100000;
System.out.println(myNum);
}
}
Output:
100000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypes-240718041615-34316400/85/DATA-TYPES-in-Python-done-by-Sanajai-of-MCA-13-320.jpg)

![Example - 1
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
long myNum = 15000000000L;
System.out.println(myNum);
}
}
Output:
15000000000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypes-240718041615-34316400/85/DATA-TYPES-in-Python-done-by-Sanajai-of-MCA-15-320.jpg)
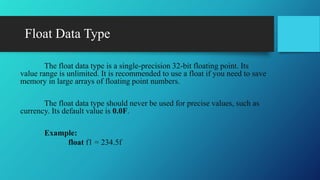
![Example - 1
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float myNum = 5.75f;
System.out.println(myNum);
}
}
Output:
5.75](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypes-240718041615-34316400/85/DATA-TYPES-in-Python-done-by-Sanajai-of-MCA-17-320.jpg)

![Example - 1
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
char myGrade = 'B';
System.out.println(my Grade);
}
}
Output:
B](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypes-240718041615-34316400/85/DATA-TYPES-in-Python-done-by-Sanajai-of-MCA-19-320.jpg)

![Example - 1
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double myNum = 19.99d;
System.out.println(myNum);
}
}
Output:
19.99](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypes-240718041615-34316400/85/DATA-TYPES-in-Python-done-by-Sanajai-of-MCA-21-320.jpg)
