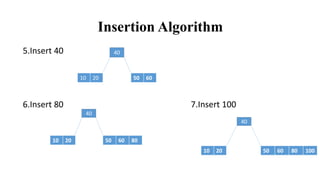
The document discusses B-Trees, which are self-balancing search trees used to store large blocks of data efficiently, such as in database and file systems. It describes the insertion and deletion algorithms for B-Trees, providing an example of inserting values into an initially empty B-Tree. B-Trees allow for efficient searching, insertion, deletion and modification of huge collections of records.