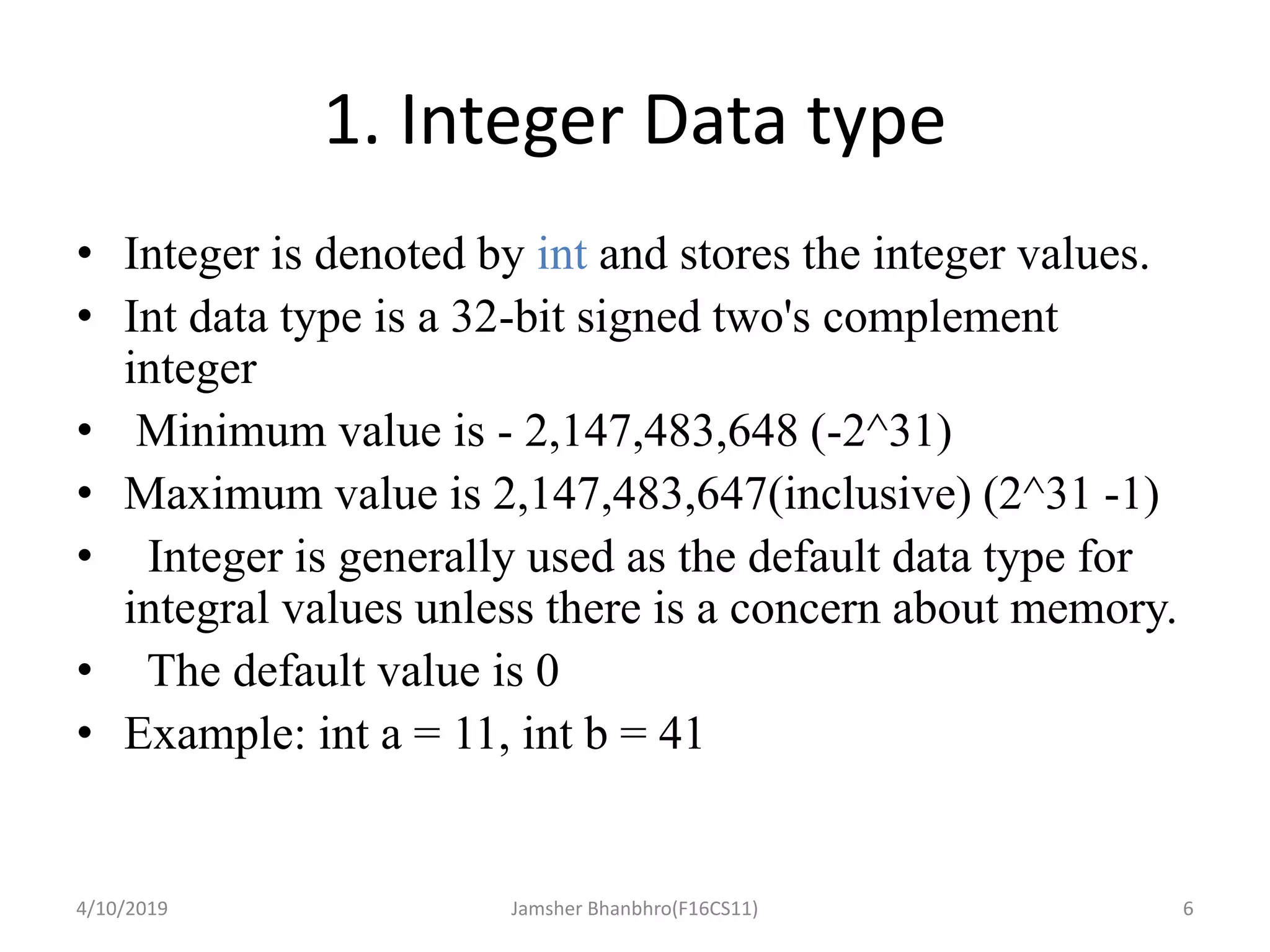
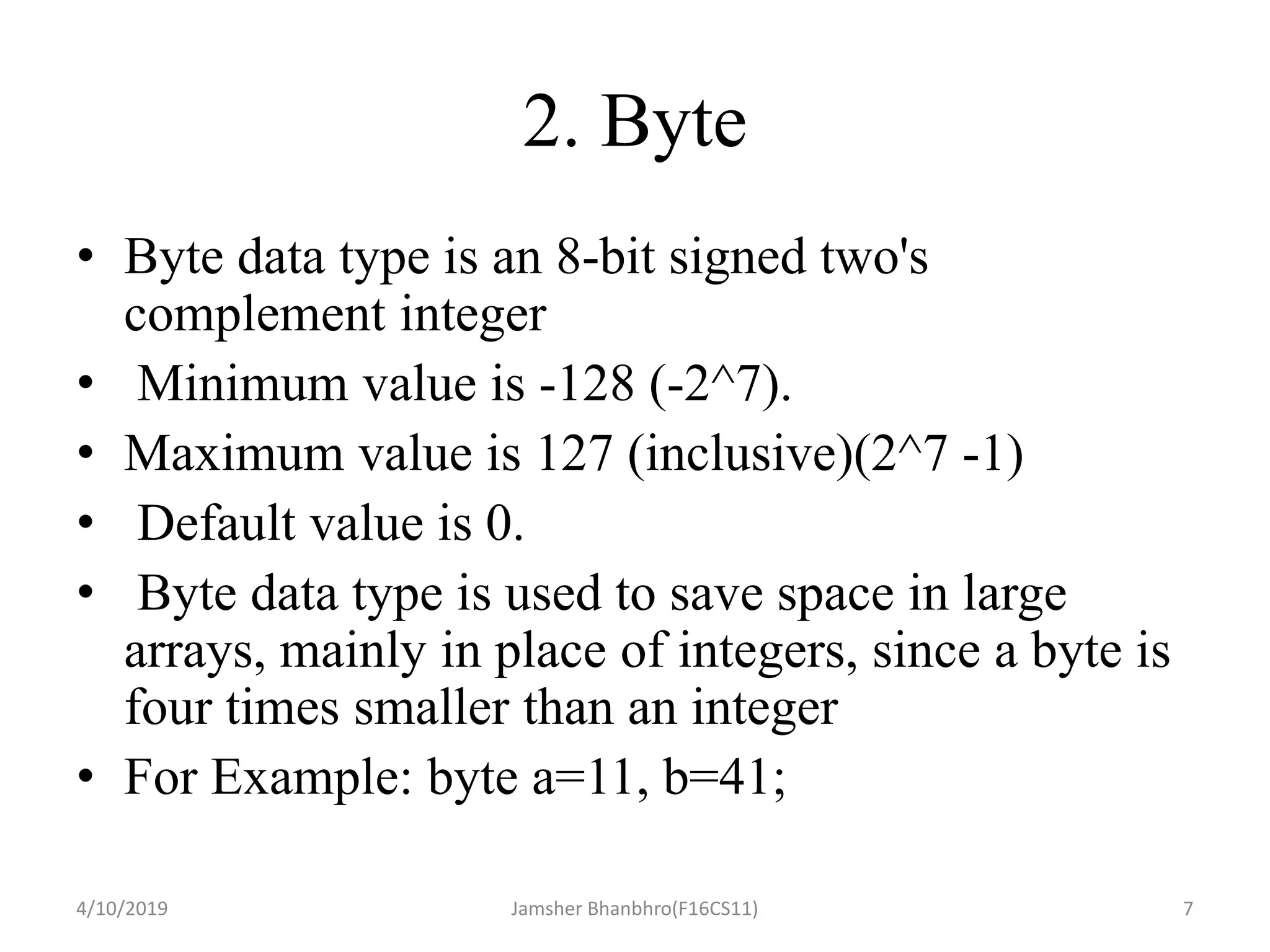
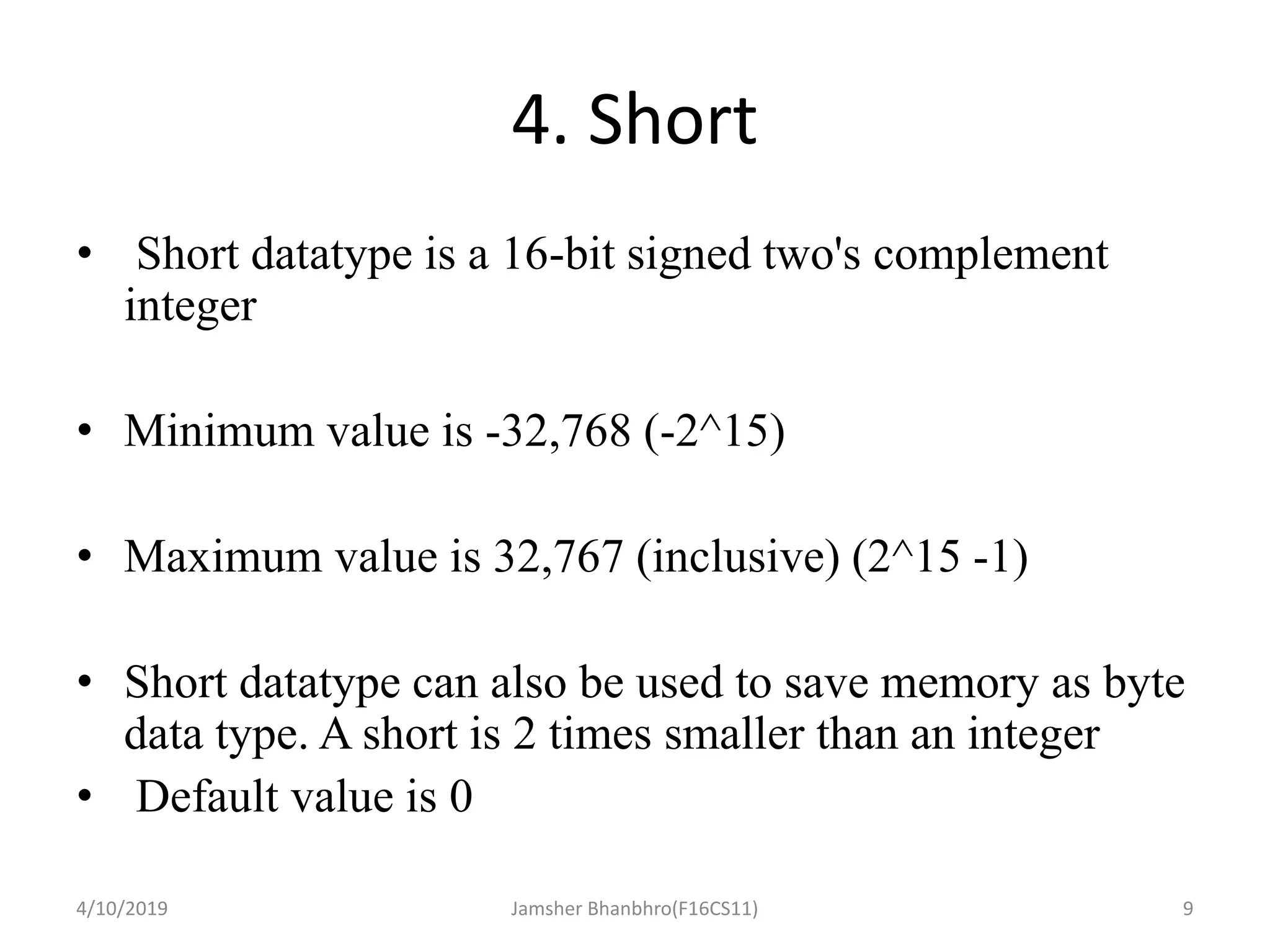
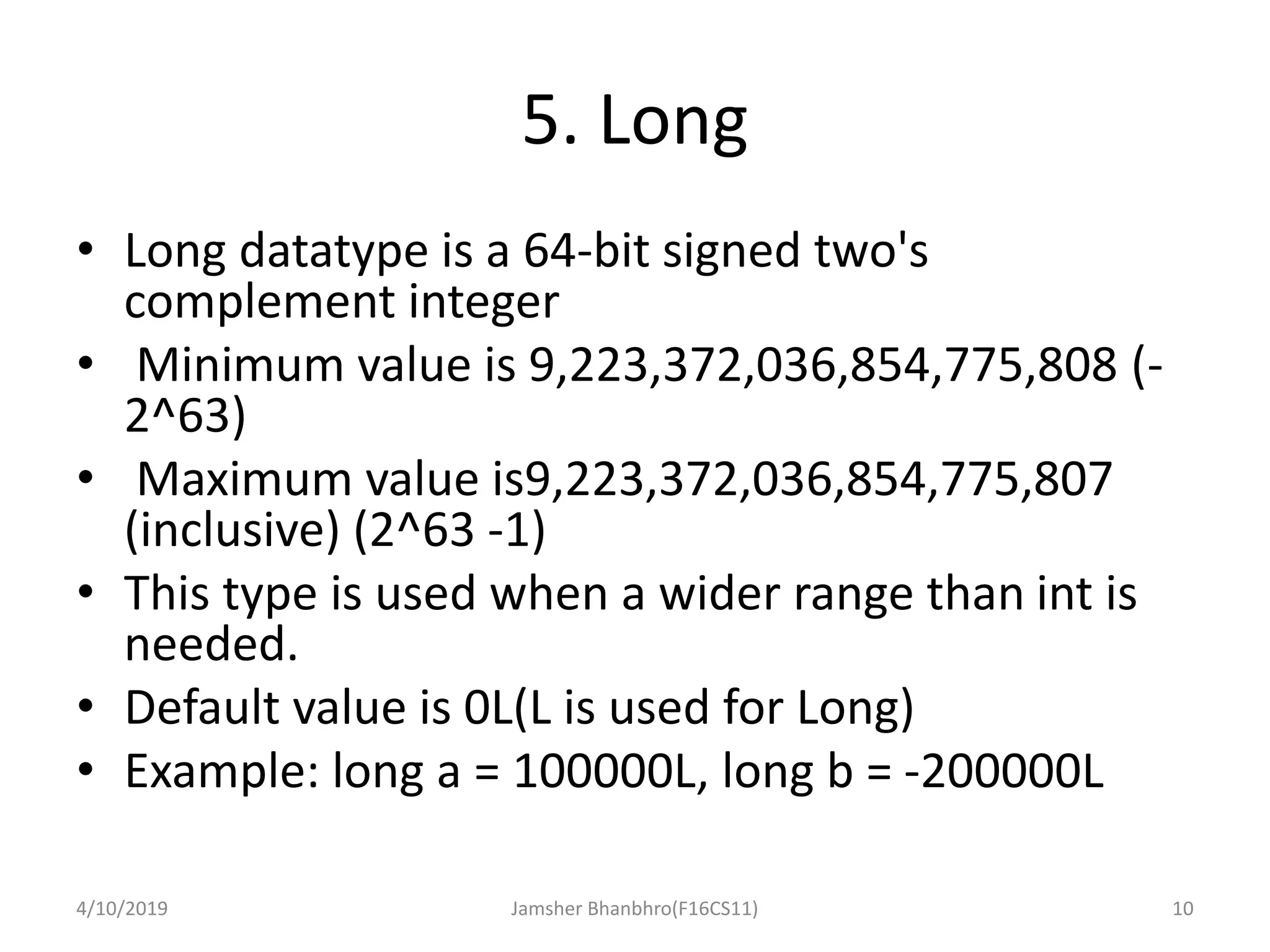
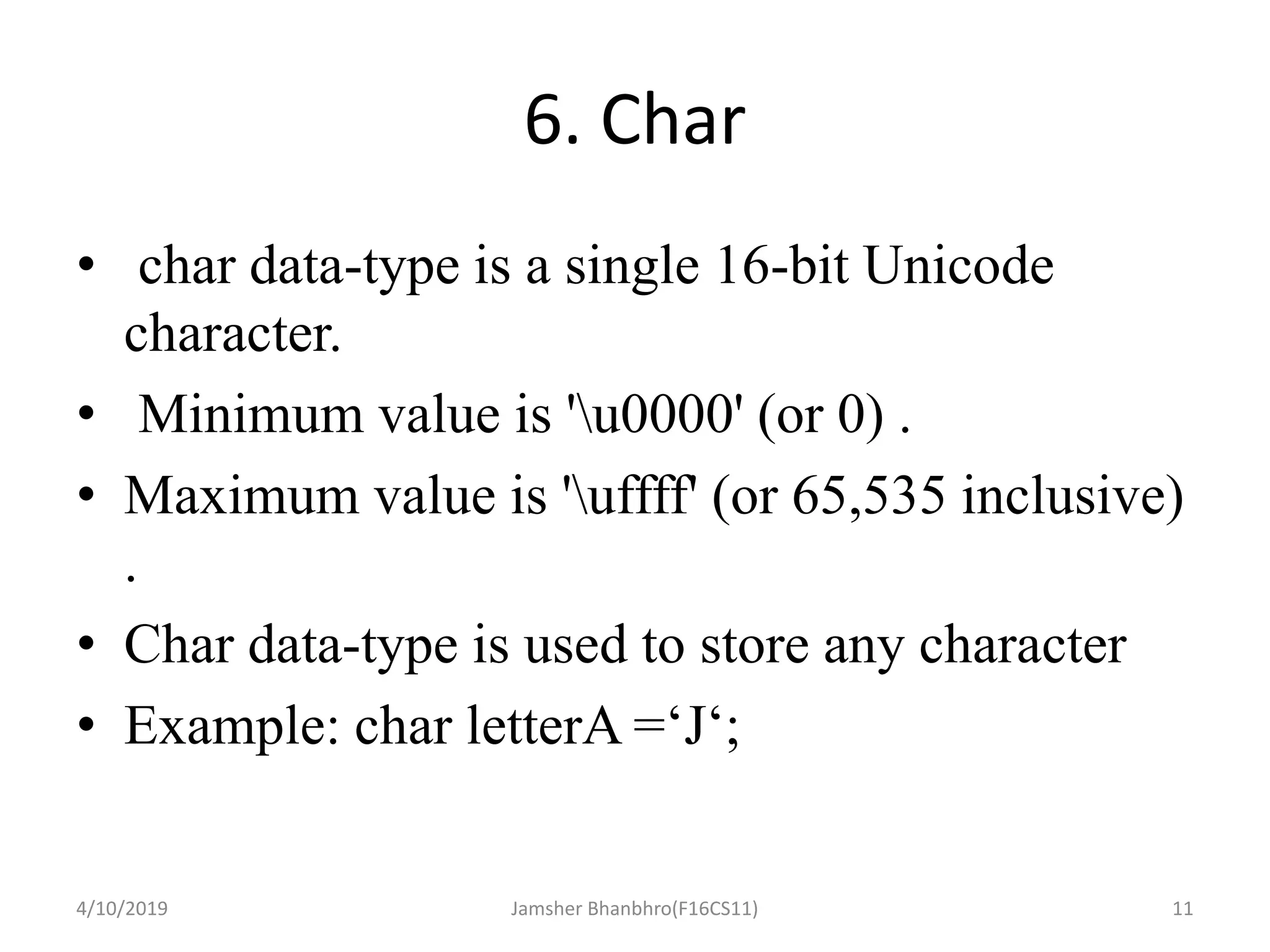
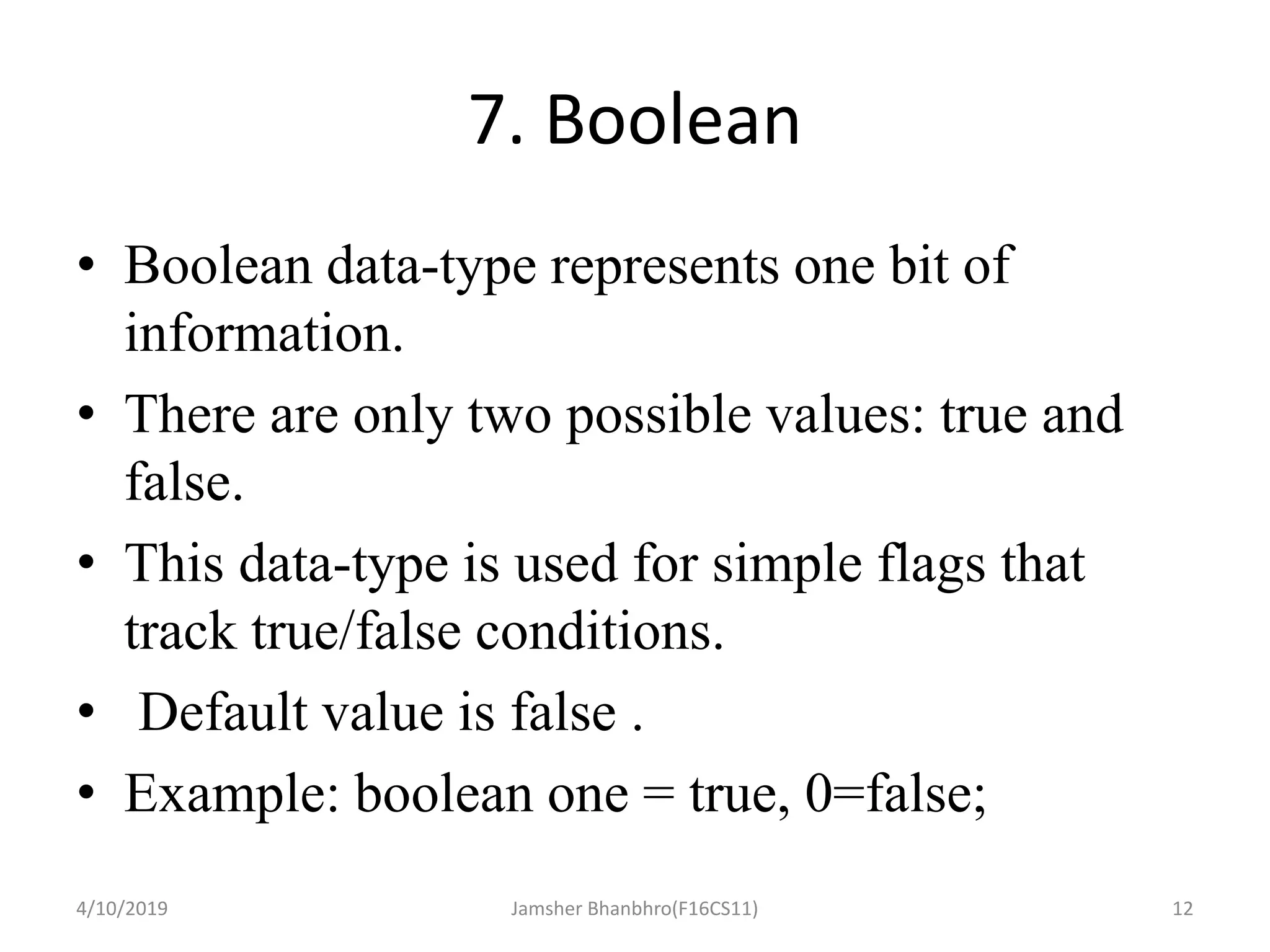
This document discusses identifiers, keywords, and data types in Java. It defines identifiers as names for classes, variables, and methods, and notes that keywords are reserved names that cannot be used as identifiers. It then describes the 8 primitive data types in Java - byte, short, int, long, float, double, boolean, and char - and provides details on their sizes, ranges, and typical uses.