Arrays in Java allow storing multiple values of the same type sequentially. There are several key points about arrays in Java:
1. Arrays are declared with square brackets and the type, such as int[] or String[].
2. Arrays are initialized with the new keyword, specifying the size. For example, int[] arr = new int[5];.
3. Elements can be accessed via indexes from 0 to length-1. The length property gives the number of elements in the array.
4. Arrays can have multiple dimensions, such as a 2D array to represent a grid. Jagged arrays allow rows of different lengths.
5. Default values are used if elements
![WHAT ARE ARRAYS?
It is a user defined homogeneous datatype. Unlike
a variable used to store a single value,
int debt =2;
an array declared is used to store series
of values of the same type(homogeneous),
sequentially.
int marks[]=new int[5];
2
debt
s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-2-320.jpg)
![DECLARING AN ARRAY VARIABLE
Array in java is created in two steps.
In first step we just create a reference name
int [ ] marks;
int marks[ ];
Both syntaxes are equivalent. No memory allocation
at this point.
To create actual array we use new operator as shown
below:
marks=new int[5];
OR
We can also create array in single step as:
int marks[]=new int[5];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-3-320.jpg)
![INITIALIZATION OF AN ARRAY
While initializing an array new operator is not required
int[ ] marks={72,61,81,79,72};
In JAVA, int is of 4 bytes, total space=4*5=20 bytes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-4-320.jpg)
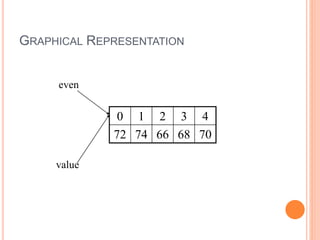
![GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION
marks[0] marks[1] marks[2] marks[3] marks[4]
72 61 81 79 72
marks
Index
value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-5-320.jpg)
![WHAT HAPPENS IF …
If we define
int[ ] marks=new long[5];
marks.java:5: incompatible types
found: long[ ]
required: int[ ]
int[ ] marks = new int[5];
^
The right hand side defines an array, and thus
the array variable should refer to the same
type of array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-6-320.jpg)
![WHAT HAPPENS IF …
Valid code:
int k=5;
int[ ] marks = new int[k];
Invalid Code:
int k;
int[ ] marks =new int[k];
Compilation Output:
More marks.java:6: variable k might not have been initialized
int[ ] marks = new int[k];
^](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-7-320.jpg)
![ARRAY SIZE THROUGH INPUT
….
BufferedReader in1 = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int num;
System.out.println("Enter a Size for Array:");
num = Integer.parseInt(in1.readLine( );
int [ ] marks = new int[num];
System.out.println(“Array Length=”+marks.length);
….
SAMPLE RUN:
Enter a Size for Array:
4
Array Length=4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-8-320.jpg)



![WHAT HAPPENS IF …
int[] marks = new int[5];
marks[6]=33;
….
Runtime Error:
Exception in thread “main”
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 6
at marks.main(marks.java:6)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-12-320.jpg)
![REUSING ARRAY VARIABLES
Array variable is separate from array itself
Like a variable can refer to different values at
different points in the program
Use array variables to access different arrays
int[] marks=new int[5];
……
marks=new int[50];
Previous array will be discarded
Cannot alter the type of array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-13-320.jpg)
![INITIALIZING ARRAYS
Initialize and specify size of array while
declaring an array variable
int[] marks={2,3,5,7,11,13,17}; //7 elements
You can initialize array with an existing array
int[] even={72,74,66,68,70};
int[] value=even;
One array but two array variables!
Both array variables refer to the same array
Array can be accessed through either variable
name](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![DEMONSTRATION
int[] marks = new int[20];
marks[0] = 2;
marks[1] = 3;
int[] marks2=marks;
System.out.println(marks2[0]);
marks2[0]=5;
System.out.println(marks[0]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-16-320.jpg)

![ARRAY LENGTH
Refer to array length using length
A data member of array object
array_variable_name.length
for(int k=0; k<marks.length;k++)
….
Sample Code:
int[] marks = new int[5];
System.out.println(marks.length);
Output: 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-18-320.jpg)


![import java.io.*;
class Array1{
public static void main(String args[])throws IOException
{
int n,i,noe;
BufferedReader in1=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Enter no of array elements");
noe=Integer.parseInt(in1.readLine());
int arr[]=new int[noe];
System.out.println("Array details"+arr);
System.out.println("Enter "+ noe+" array elements");
for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
{
arr[i]=Integer.parseInt(in1.readLine());
}
System.out.println("Entered array elements are as follows:");
for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
{
System.out.print(" "+arr[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-21-320.jpg)
![System.out.println("nLets increase number of elements by 2 ");
arr=new int[noe+2];
System.out.println("Array details after increased size"+arr);
System.out.println("Enter "+ (noe+2)+" array elements");
for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
{
arr[i]=Integer.parseInt(in1.readLine());
}
System.out.println("Entered array elements are as follows:");
for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
{
System.out.print(" "+arr[i]);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-22-320.jpg)
![SAMPLE PROGRAM
class MinAlgorithm
{
public static void main ( String[] args )
{
int[] array = { -20, 19, 1, 5, -1, 27, 19, 5 } ;
int min=array[0]; // initialize the current minimum
for ( int index=0; index < array.length; index++ )
if ( array[ index ] < min )
min = array[ index ] ;
System.out.println("The minimum of this array is: " + min );
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-24-320.jpg)
![ARRAYS OF ARRAYS
Two-Dimensional arrays
float[][] temperature=new float[10][365];
10 arrays each having 365 elements
First index: specifies array (row)
Second Index: specifies element in that array (column)
In JAVA float is 4 bytes, total Size=4*10*365=14,600
bytes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-25-320.jpg)
![INITIALIZING ARRAY OF ARRAYS
int[][] array2D = { {99, 42, 74, 83, 100}, {90, 91, 72,
88, 95}, {88, 61, 74, 89, 96}, {61, 89, 82, 98, 93},
{93, 73, 75, 78, 99}, {50, 65, 92, 87, 94}, {43, 98,
78, 56, 99} };
//7 arrays with 5 elements each](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-26-320.jpg)
![ARRAYS OF ARRAYS OF VARYING LENGTH
(JAGGED ARRAYS)
All arrays do not have to be of the same length
float[][] samples;
samples=new float[5][];//defines no of rows in an array
samples[0]=new float[6];
samples[1]=new float[101];
Not required to define all arrays](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-27-320.jpg)
![INITIALIZING VARYING SIZE ARRAYS
int[][] uneven = { { 1, 9, 4 }, { 0, 2}, { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 } };
//Three arrays
//First array has 3 elements
//Second array has 2 elements
//Third array has 5 elements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-28-320.jpg)
![To allocate memory for a 2D array, we need to specify the
memory for the first(Leftmost) dimension. Then remaining
dimensions can be allocated separately.
For eg:
int arr2d[][]=new int[3][];
arr2d[0]=new int[3];
arr2d[1]=new int[3];
arr2d[2]=new int[3];
Above declaration allocates memory for the first dimension of
arr2d when it is declared. Then we allocate memory for the
second dimension separately. There is no benefit of doing
memory allocation this way in above example but it is helpful
when we may want to allocate unequal number of elements
across each row. An array created in this fashion in java is called
Jagged Array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-29-320.jpg)
![JAGGED ARRAY
Class JaggedArray {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int twoD[][] = new int[4][];
twoD[0] = new int[1];
twoD[1] = new int[2];
twoD[2] = new int[3];
twoD[3] = new int[4];
int i, j, k = 0;
for(i=0; i<4; i++)
{ for(j=0; j<i+1; j++)
{
twoD[i][j] = k;
k++;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-30-320.jpg)
![for(i=0; i<4; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<i+1; j++)
{
System.out.print(twoD[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:
0
1 2
3 4 5
6 7 8 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-31-320.jpg)
![SAMPLE PROGRAM
class unevenExample3
{
public static void main( String[] arg )
{ // declare and construct a 2D array
int[][] uneven = { { 1, 9, 4 }, { 0, 2}, { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 } };
// print out the array
for ( int row=0; row < uneven.length; row++ ) //changes row
{
System.out.print("Row " + row + ": ");
for ( int col=0; col < uneven[row].length; col++ ) //changes
column
System.out.print( uneven[row][col] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-32-320.jpg)

![TRIANGULAR ARRAY OF ARRAYS
Triangular Array
for(int k=0; k<samples.length;k++)
samples[k]=new float[k+1];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-34-320.jpg)
![MULTIDIMENSIONAL ARRAYS
A farmer has 10 farms of beans each in 5 countries,
and each farm has 30 fields!
Three-dimensional array
int[][][] beans=new int[5][10][30];
//beans[country][farm][fields]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-35-320.jpg)
![VARYING LENGTH IN MULTIDIMENSIONAL
ARRAYS
Same features apply to multi-dimensional arrays as
those of 2 dimensional arrays
int beans=new int[3][][];//3 countries
beans[0]=new int[4][];//First country has 4 farms
beans[0][4]=new int[10];
//Each farm in first country has 10 fields](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-36-320.jpg)





![// Demonstrate various Vector operations.
import java.util.*;
class VectorDemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// initial size is 3, increment is 2
Vector v = new Vector(3, 2);
System.out.println("Initial size: " + v.size());
System.out.println("Initial capacity: " + v.capacity());
v.addElement(new Integer(1));
v.addElement(new Integer(2));
v.addElement(new Integer(3));
v.addElement(new Integer(4));
System.out.println("Capacity after 4 additions: " +
v.capacity());](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaarrays-230602032235-670932ce/85/javaArrays-pptx-42-320.jpg)


