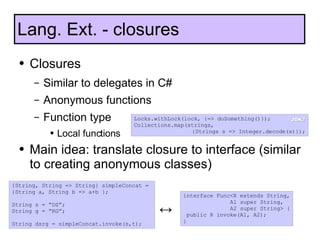
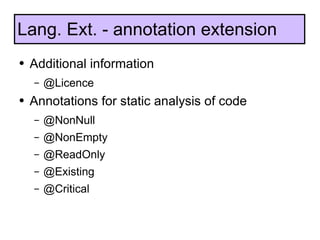
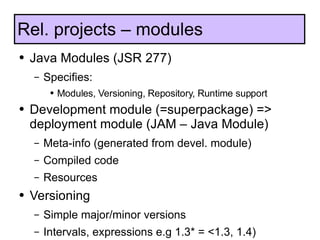
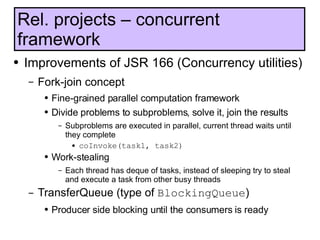
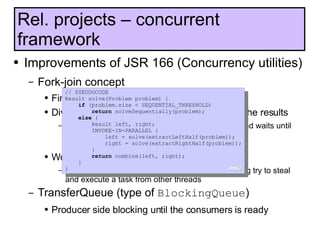
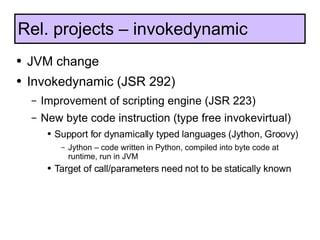
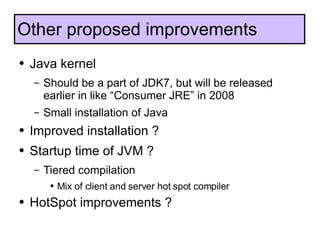
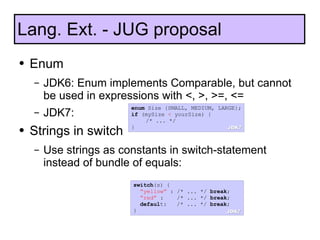
The document discusses the development and features of Java 7, including the Java development process and various proposals for language extensions such as closures, chained invocations, and enhanced exception handling. It outlines JSR proposals, the Java Module System, and related projects while emphasizing community input through OpenJDK. Additionally, it highlights improvements in concurrency utilities and scripting support, indicating ongoing development and changes within the Java ecosystem.




![Generics Constructors without duplicate declaration Map<String, List<String>> anagrams = new HashMap<>(); instead of Map<String, List<String>> anagrams = new HashMap<String, List<String>>(); Generics are not still covariant! List<Integer> li = new ArrayList<Integer>(); List<Number> ln = li; // illegal ln.add(new Float(3.1415)); // legal More type safe packages JDK 5: static Object newInstance(Class<?> componentType, int size) Because of backward compatibility JDK 5,7: static<T> T[] newInstance(Class<T> componentType, int size) More type-safe, can be called Array.<String>newInstance(String.class, 10) Inference of method arguments static<E> Set<E> emptySet(); void print(Set<Man> men) {...} Call: print(Collection.emptySet()) // in JDK5,6 is necessary to explicitly specify which method should be called: Collection.<Man>emptySet(); Template type information available at runtime Lang. Ext. - JUG proposal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-7-quo-vadis-1196867879950073-2/85/Java-7-Quo-vadis-5-320.jpg)


![Creation of XML fragments XML embedded in Java code <tag> or #tag Data coders in according to XSD date/time XPath language support Lang. Ext. - XML lang. support public void addMember(XML xml, String name, Integer age) { xml.addChild(<member> <name> { name } </name> <age> { 26 } </age> </member>); } public void makeYounger(XML fs, Integer newAge) { List<XML> l = fs.findAll(“member[age>25]”); for (XML a : l) { a.get(“age”).set(newAge); } } JDK7 JDK7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-7-quo-vadis-1196867879950073-2/85/Java-7-Quo-vadis-9-320.jpg)