The document summarizes new features introduced in Java 5 and Java 6. Java 5 introduced generics, autoboxing/unboxing, enhanced for loops, and annotations. Java 6 added support for XML processing and web services using annotations, the Rhino JavaScript engine, improved GUI APIs, and Java DB for database connectivity.






![Java
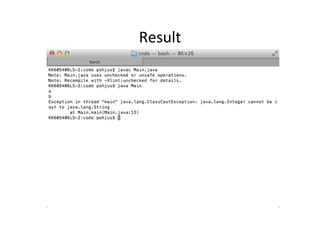
1.4
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String [] args) {
// Does not work, 5 is not a Object type!
someMethod(5);
}
public static void someMethod(Object a) {
System.out.println(a.toString());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-9-320.jpg)
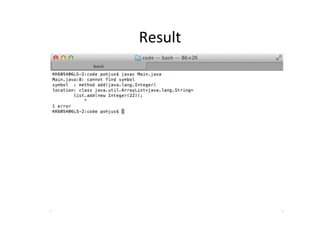
![Java
1.4:
SoluQon
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String [] args) {
Integer temp = new Integer(5);
someMethod(temp);
}
public static void someMethod(Object a) {
System.out.println(a.toString());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-10-320.jpg)

![Autoboxing
Comes
to
Rescue!
class Main {
public static void main(String [] args) {
// Boxing
Integer a = 2;
// UnBoxing
int s = 5 + a;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-12-320.jpg)
![Java
1.5
class Main {
public static void main(String [] args) {
// Works!
someMethod(5);
}
public static void someMethod(Object a) {
System.out.println(a.toString());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-13-320.jpg)
![Java
1.5
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String [] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(5);
list.add(new Integer(6));
list.add(7);
for(int number : list) {
System.out.println(number);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-14-320.jpg)

![Usage
enum Color {
WHITE, BLACK, RED, YELLOW, BLUE;
}
class Main {
public static void main(String [] args) {
System.out.println(Color.WHITE);
Color c1 = Color.RED;
System.out.println(c1);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-16-320.jpg)

![Enum
enum Color {
WHITE, BLACK, RED, YELLOW, BLUE;
}
class Main {
public static void main(String [] args) {
for (Color c : Color.values()) {
System.out.println(c);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-18-320.jpg)
![StaQc
Import
(1/2)
class Main {
public static void main(String [] args) {
int x = Integer.parseInt("55");
int y = Integer.parseInt("56");
int x = Integer.parseInt("57");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-19-320.jpg)
![StaQc
Import
(2/2)
import static java.lang.Integer.parseInt;
class Main {
public static void main(String [] args) {
int x = parseInt("55");
int y = parseInt("56");
int z = parseInt("57");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-20-320.jpg)

![Override:
Does
not
Compile!
class Human {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Eats food");
}
}
class Programmer extends Human {
@Override
public void eatSomeTypo() {
System.out.println("Eats pizza");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String [] args) {
Programmer jack = new Programmer();
jack.eat();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-22-320.jpg)

![System.out.format
import java.util.Date;
class Main {
public static void main(String [] args) {
Date d = new Date();
// Lot of format characters available!
System.out.format("Today is %TF", d);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-24-320.jpg)
![Variable
Argument
List
class Main {
public static void printGreeting(String... names) {
for (String n : names) {
System.out.println("Hello " + n + ". ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String [] names = {"Jack", "Paul"};
printGreeting("Jack", "Paul");
printGreeting(names);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-25-320.jpg)



![Server
import javax.xml.ws.Endpoint;
class Publish {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Endpoint.publish(
"http://localhost:8080/circlefunctions",
new CircleFunctions());
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-29-320.jpg)

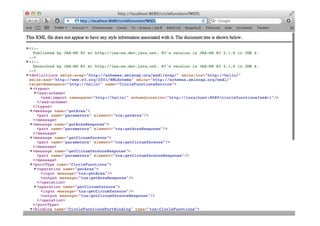

![Example
import javax.script.ScriptEngine;
import javax.script.ScriptEngineManager;
import javax.script.ScriptException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScriptEngineManager mgr = new ScriptEngineManager();
ScriptEngine engine = mgr.getEngineByName("JavaScript");
// Now we have a script engine instance that
// can execute some JavaScript
try {
engine.eval("print('Hello')");
} catch (ScriptException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java56-120414041005-phpapp02/85/Java-5-and-6-New-Features-33-320.jpg)


